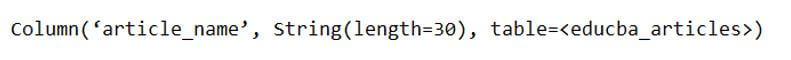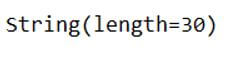Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQLAlchemy Metadata
SQLAlchemy Metadata acts as an interface that helps describe the objects of the tables inside the database. Usually, the metadata object comprises many table objects representing all the database tables, and the Column object describes columns of every database table in the python framework. However, a single application of python needs only a single metadata thing and is sufficient for it. Here, we will see at following integrities of SQLAlchemy consisting of what is sqlalchemy metadata, sqlalchemy Metadata Schema, sqlalchemy metadata databases, examples, and conclusion about the same.
What is SQLAlchemy Metadata?
SQLAlchemy metadata is used to describe the single or multiple databases that the python application is using. The complete detailed structure of the database is defined inside the metadata object using the data structures of python for every column of every table in the database. Metadata’s database information comprises two types of things named Tables and Columns.
The primary use and purpose of database Metadata are an ORM tool for object-relational mapping and generating the necessary SQL queries inside the application. Metadata in SQLAlchemy proves to be helpful in the generation of the database schema. Some virtual objects required in Metadata and used more often include tables, columns, and Metadata.
SQLAlchemy Metadata Schema
Schema is nothing but the structure of various tables inside the database described by using metadata in SQLAlchemy. Let us first understand how queries are generated and how to define schema with the help of an example. The queries are formed on the tables inside the database. In SQLAlchemy’s Metadata, the tables inside the database are referred to with the help of the Table object, while columns of the table in the database are referred to with the use of the Column object.
The object of Metadata is made up of Table objects paired up with their names in the database.
We can create an object of Metadata by following the below syntax:
Syntax:
From sqlalchemy import MetaData
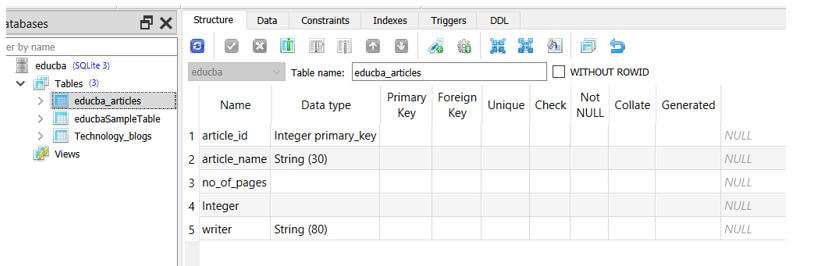
Sample_object_metadata = MetaData()Creating a single instance of MetaData suffices the needs of the entire application. We can now look at how the schema is defined by considering one table named educba_articles having columns article_name, no_of_pages, and writer with the article_id column acting as the primary key.
We can now go for defining the schema by using the below code:
Code:
from sqlalchemy import MetaData
from sqlalchemy import Integer, String, Column, Table
sample_object_metadata=MetaData()
articles_table = Table(
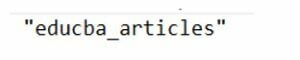
"educba_articles",
sample_object_metadata,
Column('article_id', Integer, primary_key=True),
Column('article_name', String(30)),
Column('no_of_pages',Integer),
Column('writer', String(80))
)The Table object in the above code refers to the database table, which is further assigned to the object of MetaData. The column refers to the column of the table existing in the database and is given to the table’s object. The Column object is generally made up of the column’s name in string format and the object type that is allowed to store in that column which can be String, Integer, Boolean, datatime, etc.
The above code refers to the following table of educba_articles as shown below:
SQLAlchemy metadata databases
The database can be described in detail in the python application using the object of MetaData of SQLAlchemy. We can create and define the database’s schema by describing the tables as shown in the above format for accessing the table’s data in the database inside the python application.
We can access the values inside the tables of the database by using SQLAlchemy’s Metadata with the help of the format shown below:
We can use the object created while describing the schema to fetch the table’s name.
For example, if we want to access the name of the table in the above-described schema, then we can make the use of the below statement:
Code:
articles_table.nameOutput:
All the columns of the table usually get stored in the associative array named table_name.c, which means using the .c notation, we can access the information about the table’s column.
For example, if you want to access the article_name column, we can make the use of the below command:
Code:
articles_table.c.article_nameOutput:
To access the name of the column, you can execute the below command:
Code:
articles_table.c.article_name.nameOutput:
To only access the column storage type that is the data type of column, we can execute the command shown below:
Code:
articles_table.c.article_name.typeThe execution of the above command only retrieves the type of the column, which is as shown below:
Output:
Similarly, suppose we want to retrieve the primary vital details. In that case, all you need to do is append the primary_key keyword after the hierarchical flow is shown above, which will get the information about the primary key associated with the current table.
We can create the tables and drop all the tables present inside the database using the methods of MetaData named createAll() and dropAll(), which will delete all the tables of that particular metadata object. Remember, while calling this method, you must use instances of Metadata you created in your code.
Example of SQLAlchemy Metadata
Given below is the example of SQLAlchemy Metadata:
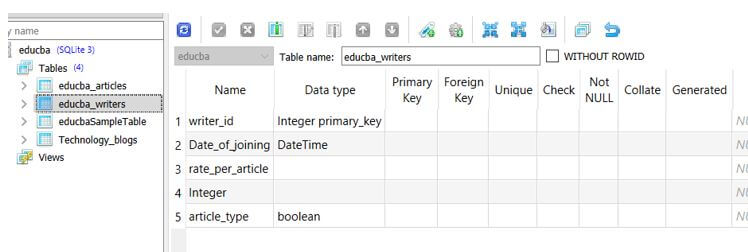
Let us consider one example which will contain multiple columns of various types of data types and formats. We will create a table named educba_writers which will have columns of types DateTime used for timestamp value.
Code:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy import Numeric, DateTime, Enum
writer_table = Table(
"educba_writers",
educba_metadata_obj,
Column("writer_id", String(50), primary_key=True),
Column("Date_of_joining", DateTime),
Column("rate_per_article", Numeric(100, 2)),
Column("article_type", boolean),
)
# creating an engine object
sample_engine = create_engine("sqlite+pysqlite:///:educba:",
echo=True, future=True)
# emitting DDL
educba_metadata_obj.create_all(sample_engine)Output:
The output of the above code refers to the following table of educba_writers as shown below:
Conclusion
We can use SQLAlchemy Metadata to describe all the tables, columns, and database-related details in terms of python data structures in the python application by using the instance object of MetaData SQLAlchemy.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQLAlchemy Metadata. Here we discuss the introduction, SQLAlchemy metadata schema, and example. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –