Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQLAlchemy Example
The following article provides an outline for SQLAlchemy Example. The SQLAlchemy is the kind of libraries that can be facilitated through the communication between the python programming languages and the databases with the kind of most wanted libraries that mapped to the Object Relational Mapper[ORM] tool it translated with the python classes on the table rows and columns to the relational databases it automatically converts to the function calls to the every SQL statements in the SQLAlchemy.
ORM Examples
The SQLAlchemy is mainly distributed for various examples, including the select set of patterns with some typical and some not. Is it all runnable and primarily found with the distribution directory, including source codes? The SQLAlchemy will configure the delete-orphan node feature, including the deleted object in the collection when they are parent removed or the parent is deleted. Next, it’s one of the simple functions that require the ORM with a method associated with the python classes with the database tables and the specified instances on the object rows to the corresponding tables. It includes the transparently synchronized system with all the changes in the object state columns and rows.
Then it is mainly referred to as the unit of work with the system expressing database queries in terms of the user-defined classes and their relationship with each other. SQLAlchemy can be used with or without the ORM features with the specified projects that can be chosen like SQLAlchmey core or the ORM with the configurations on the various types of applications software’s stacks and the backend databases. This can be achieved using any designs with valid options depending on the kind of applications for which we are coded. The benefit with many developers that can be accepted with the SQLAlchmey allows them to access the Python codes in the specified project from the application databases.
SQLAlchemy Code and Plain SQL with examples
The SQLAlchemy mainly takes care of the table creation, which would require creating a table statement in the python code for all the records instead of the plain SQL. The queries in python language which more often faster and more accessible for the python developers in the multiple tables and specified filtering fields for the questions to be written more quickly and more accessible for the python developers once the table is created. The best way and most comfortable zone for the SQLAlchemy is mainly digging with the read and write database-driven application resources for the helpful trouble getting information started into some edge cases. It’s the python-based object-relational mapper with several open-source projects. The articles listed on the data make it easier to understand the several implementations using the Django ORM framework, which handles the transactions, models, and queries. Many open-source projects rely on the SQLAlchemy to correctly work with the tools to read the codes defined by the class and functions.
It has n number of methods that must be used and called with the different areas. Like that add_columns(), add_entity(), count() and we can add the database drivers in the create_engine() method.
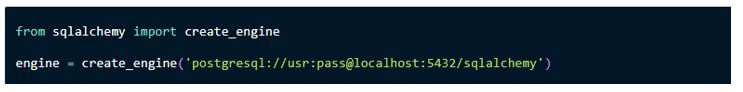
In the above screenshot, we can pass the PostgreSQL database drivers with the specified ports like 5432 as the valid credentials to interact with the SQLAlchemy database. Mainly while creating an engine, it does not connect the databases instantly; when we want to submit the query, it will update the design and update the table rows in the table. The DBAPI is the specification for interacting with the databases in the most common database management systems available for support. PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, and SQLite are the most common examples of the SQLAlchemy engines based on documentation. The transaction is the central role of the SQLAlchmey after the dB engine connection; it will perform the operations at some intervals.
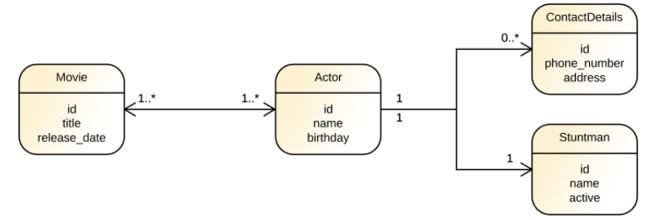
The above class diagram is the basic workflow of the SQLAlchemy classes to interact with the databases for the user data.
Example #1
Code:
from SQLAlchemy import Column, Integer, String
from SQLAlchemy import create_engine
engine = create_engine('sqlite:///D:/Mar9.db', echo = True)
from SQLAlchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
Base = declarative_base()
class Mar22(Base):
__tablename__ = 'test3'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key = True)
name = Column(String)
from SQLAlchemy.orm import sessionmaker
Session = sessionmaker(bind = engine)
session = Session()
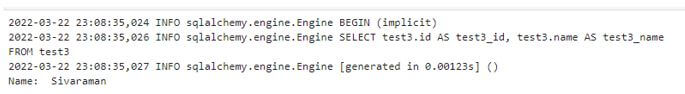
result = session.query(Mar22).all()
for row in result:
print ("Name: ",row.name)Output:
Example #2
Code:
from SQLAlchemy import create_engine, ForeignKey, Column, Integer, String
engine = create_engine('sqlite:///sales.db', echo = True)
from SQLAlchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
Base = declarative_base()
from SQLAlchemy.orm import relationship
class Fits(Base):
__tablename__ = 'test3'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key = True)
name = Column(String)
class secs(Base):
__tablename__ = 'secndtble'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key = True)
invid = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('test3.id'))
fts = relationship("Fits", back_populates = "secndtble")
Fits.secndtble = relationship("secs", order_by = secs.id, back_populates = "fts")
Base.metadata.create_all(engine)Output:
Example #3
Code:
from SQLAlchemy import text
res = engine.execute(
text(
"SELECT id, name \
FROM test3;"
)
)
print(res)Output:
Example #4
Code:
from SQLAlchemy import text
res = engine.execute(
text(
"SELECT id, name \
FROM test3 LIMIT 3;"
)
)
print(f"We selected {res.rowcount} rows.")
for a in res.fetchall():
print(a)Output:
We used SQLAlchemy in different areas in the above examples and passed the SQLAlchemy package with varying default methods. Initially, we must create the database engine for the specified database to connect the tables for performing the user data operations in the various areas. Additionally, we completed the one-to-one and other relational mappings combined with the SQLAlchemy in the SQLite databases. We should be added the corresponding dependencies and classes for each python script code.
Conclusion – SQLAlchemy Example
The SQLAlchemy is the query execution, and it’s one of the workflow engines for performing particular operations with the boilerplate codes. It must be the standard database connector to estimate the SQL procedures and the query data to fetchAll() the results with the claim data offers.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQLAlchemy Example” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.