Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQLAlchemy Alias
The SQLAlchemy Alias is one of the types import, and it mainly corresponds to the sqlalchemy sql; it is selected to the object and turned into an alias from the Clause. The alias() method configured and produced the construction for each type of the function in the alias() using the sqlalchemy.sql module that represented the alias for applicable to any tables and sub-select tables with AS as the sql keyword.
What is SQLAlchemy Alias?
The SQLAlchemy import package is more necessary to trigger the function call for the established postgresql database. The alias looks like the temporary name for each table which is a more convenient time for readable formats. This facilitates a simple name instead of the complex table name or column names from multiple tables in the single query. This alias() function generally forms the sqlalchemy module with each set of metadata objects while connecting to the database. With the help of alias name to execute the query with all stages of results across the method like the fetchall() method for iterating the loop conditions through the results.
Using SQLAlchemy Alias
We can show n number of column names from the table with the specified alias like if suppose we can use the text box column name that will alias as the label with the help of the .label() method. Sometimes we may use the same requirement with the exact function definition for using a different name with the same label() method. And some column values for the specified attribute column will calculate the values based on the other attributes, which call it the same set of values to be calculated upon the user requirements. The sqlalchemy query will take more time to execute the user operations from the backend to retrieve the results. Generally, the query is the source of all the Select statements that the ORM generates, and the sql alias will facilitate the simple name to be used in every area of the complex tables. It is used multiple times in the query.
So that it will be a more convenient time and readable format for the simple name to be placed in the complex table name, which has to be used multiple times in a query. The alias() function is one of the sqlalchemy.sql modules, representing the sql alias from the metadata object initialized for connecting the database. So by using the alias table name, which executes the query to retrieve the results with the help of the fetchall() function to iterate the loop condition, It will be mapped to the other objects that are supposed to be added to the RDBMS(Relational Database Management System). It allows the database administrators and other database users to reduce the codes required to understand the obfuscation and techniques to give the database fields.
1. The table rows and columns are mapped to the table correlated with the name, like the correlation name, and the coder will temporarily assign it to the table name.
2. First, we need to import the sqlalchemy alias using the sqlalchemy.sql packages.
3. Then, we will create the database engine to connect the database from the front end to the backend.
4. The created_engine() will have separate arguments or parameters like sqlite drivers, which helps connect the database already created on the sqlite database.
5. The query performance will be calculated for every user and stored in a separate session to handle the user cookies datas.
6. We can use the alias() function with other in-built functions like filter and other dbsession queries to handle the user datas based on their needs.
7. Session will handle every classname separately, and if suppose the name itself to be mapped with the other names or short form of names by using the alias() function.
8. Not only for the class names, method name, variables, and other default keywords will act and alias() as the database relationship mapper and parse the sql queries in the different areas.
9. The variable executes the conditional statements, i.e.) alias name to perform the operations.
Examples of SQLAlchemy Alias
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1
Code:
import sqlalchemy
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, MetaData,Table, Column, Numeric, insert, Integer,VARCHAR, update, text, delete
from sqlalchemy.engine import result
engs = create_engine(
'sqlite:///Mar9.db', echo = True)
md = MetaData(bind=engs)
MetaData.reflect(md)
apr = Table(
'April26', md,
Column('id', Integer, primary_key=True),
Column('name', VARCHAR),
Column('sex', VARCHAR),
Column('city', VARCHAR)
)
md.create_all(engs)
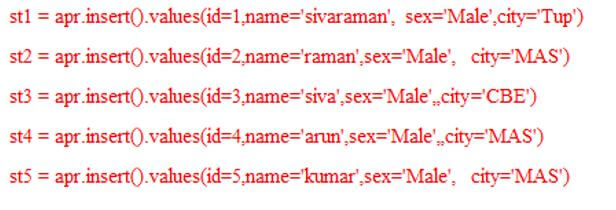
st1 = apr.insert().values(id=1,name='sivaraman', sex='Male',city='Tup')
st2 = apr.insert().values(id=2,name='raman',sex='Male', city='MAS')
st3 = apr.insert().values(id=3,name='siva',sex='Male',,city='CBE')
st4 = apr.insert().values(id=4,name='arun',sex='Male',,city='MAS')
st5 = apr.insert().values(id=5,name='kumar',sex='Male', city='MAS')
engs.execute(st1)
engs.execute(st2)
engs.execute(st3)
engs.execute(st4)
engs.execute(st5)
from sqlalchemy.sql import alias, select
apr = md.tables['April26']
a = apr.alias("a")
s = select([a]).where(a.c.id > 2)
res = engs.execute(s).fetchall()
for out in res:
print("Welcome To my domain", out)Output:
1. In the above example, first, we can import the sqlalchemy drivers, classes, and functions to execute the operations.
2. We imported an additional alias package to use the user operations like an alias.
3. First, we created tables using the Table() method with separate parameters with an additional call for the other way like create_all() by using metadata.
4. By using the insert() method, we can insert the values with the help of specific techniques like values() additional parameters.
5. Finally, we can use the alias() method to execute the operations and print them on the same console.
Example #2
Code:
from sqlalchemy.sql import alias, select
import sqlalchemy
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, MetaData,Table, Column, Numeric, insert, Integer,VARCHAR, update, text, delete
from sqlalchemy.engine import result
engss = create_engine(
'sqlite:///Mar9.db', echo = True)
meta = MetaData(bind=engine)
MetaData.reflect(meta)
fr = meta.tables['First']
a = fr.alias("p")
res = select([a]).where(a.c.id > 3)
outss = engine.execute(res).fetchall()
for r in outss:
print("\n", r)Output:
1. In the second example, we used the same as the previous example; we can use the alias method in the different tables.
2. The database engine is executed using the create_engine() method instance.
3. Using the loop, we can iterate the values along with the alias output.
Conclusion
The sqlalchemy has n number of functions, classes, and keywords to perform the user operations in various ways. For example, we can use the alias() keyword and the function that acts as the alternate name of the methods, variables, and other functional operations. By using the default methods, the datas are stored and retrieved successfully.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQLAlchemy Alias. Here we discuss the introduction, using SQLAlchemy alias and examples for better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –