Updated March 10, 2023
Introduction to SQL Clone Table
SQL Clone Table is to create a table that is an exact duplicate or a copy of the original table in SQL using query statements. Sometimes, there may be a situation when you want to perform certain actions and test the changes on the table such that the contents of the original table should not get affected. In such situations, what we can do is simply create a new table with the same structure, indexes, and contents as that of the original one that is also called a clone of the original table and perform all your operations and trials and tests on the newly created clone table instead of the original one, so that the original one does not get hampered.
Using simple SHOW CREATE TABLE Query
The first step in creating a new clone table of the existing table will be to create the table consisting of the same columns, attributes, and indexes. For this, we can use the SQL statement SHOW CREATE TABLE name of the original table to get the query statement of CREATE TABLE for the original table. Then you can simply copy-paste the retrieved query statement and replace the name of the original table in the query statement with the clone table name that you wish to create.
The next step is to copy the contents and records of the original table to the cloned table. For this, you can make use of the INSERT INTO AND SELECT statement collectively. Let us learn about how we can create a clone by using the first method by considering one example.
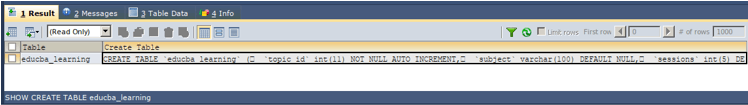
Suppose that there exists a table named educba_learning and we have o clone that table and create a new copy or clone of that table named educba_learn_clone. Let us follow the above-discussed steps one by one. Firstly, we will execute the following query statement to get the query statement of creating a table of the original table educba_learning –
SHOW CREATE TABLE educba_learning;The execution of the above query statement gives the following output along with the query statement of CREATE TABLE for educba_learning table consisting of all its columns, attributes, and indexes –
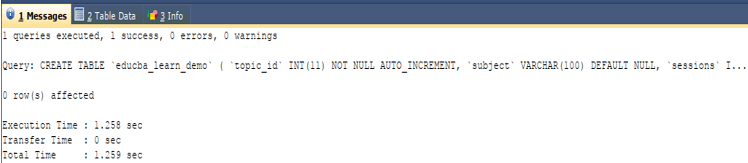
Now, we will simply copy the output query statement retrieved from the above output and replace the name of the table educba_learning with educba_learn_clone and execute the following query statement to create the clone of the table –
CREATE TABLE `educba_learning` (
`topic_id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`subject` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`sessions` INT(5) DEFAULT '0',
`expert_name` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`charges` DECIMAL(7,2) DEFAULT '0.00',
KEY `topic_id` (`topic_id`)
) ;The execution of the above query gives the following output –
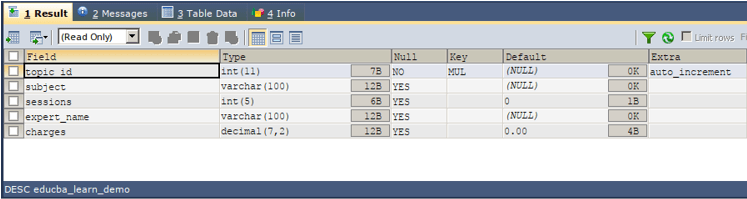
The execution of the above table will create a new table with the same structure as that of the educba_learning table with the name educba_learn_clone with no records in it. We can check the structure of the table by simply describing the table using the following query –
DESC educba_learn_demo;That results in the following output after execution –
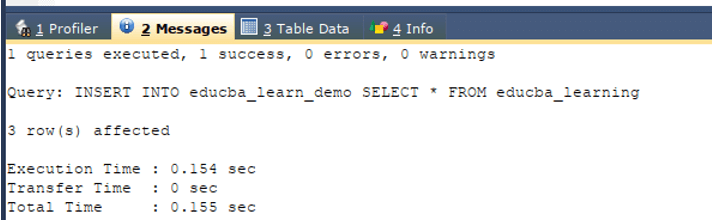
Now, the next step is to copy all the records of the educba_learning table to the clone of the table that we created with name educba_learn_clone using INSERT INTO clone table SELECT * FROM original table. Our query statement will be as shown below –
INSERT INTO educba_learn_demo SELECT * FROM educba_learning;The execution of the above query gives the following output –
Let us check the contents of the cloned table and verify the contents of the original table too to see whether all the records are copied successfully. The statements will be somewhat as follows–
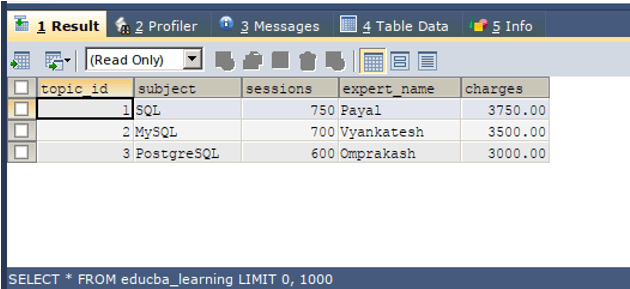
SELECT * FROM educba_learning;The execution of the above query gives the following output –
We can observe that the clone of the table educba_learning has been successfully been created with the name educba_learn_demo table and all the operations and testing that you want to perform without affecting the original table edcba_learning can be done on its clone table edcba_learn_demo table.
An alternative way to create a clone of the table
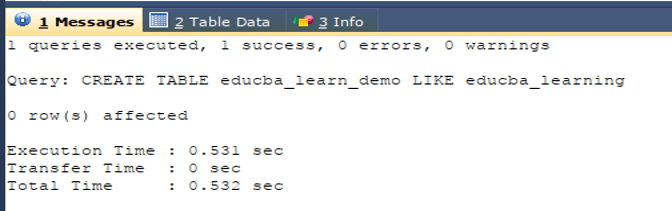
We can use the CREATE TABLE LIKE statement instead of SHOW CREATE TABLE query statement and then copy the query and replace the table name. The syntax of using the CREATE TABLE LIKE statement is as shown below –
CREATE TABLE clone_table LIKE existing_table;In the above example, we could have used
CREATE TABLE educba_learn_demo LIKE educba_learning;The execution of the above query gives the following output –
And then further copy the records by using the same INSERT INTO and SELECT statement togetherly.
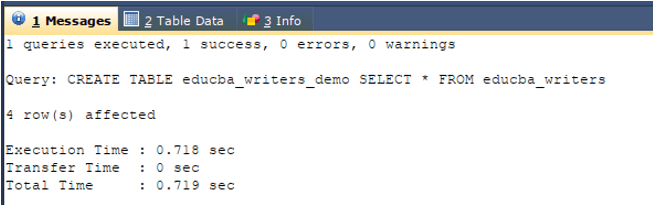
One more alternative way of creating the cloned table and inserting the records to it too is to use the following query statement that combines CREATE TABLE and SELECT query statements.
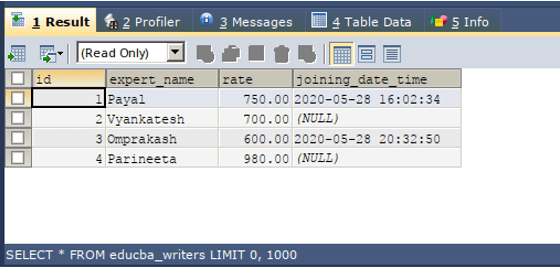
CREATE TABLE clone _table SELECT * FROM existing _table;Let us consider one example, I have one table named educba_writers that contains the following columns and records as shown by the output of the select query statement mentioned below –
SELECT * FROM educba_writers;Now, we have to use the CREATE TABLE and SELECT statement togetherly to create a clone of the table educba_writers with name educba_writers_demo table. For this, our query statement will be as follows –
CREATE TABLE educba_writers_demo SELECT * FROM educba_writers ;The execution of the above query gives the following output –
Let us retrieve the contents of the newly created clone table educba_writer_demo suing the following query statement –
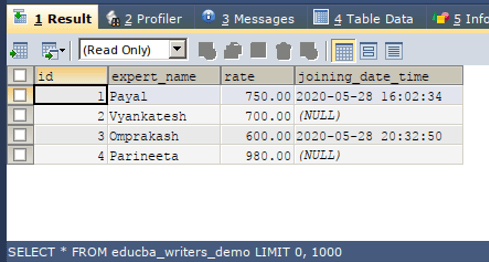
SELECT * FROM educba_writers_demo ;The execution of the above query gives the following output –
From the above output, we can observe that a clone table has been successfully created by using a single query statement and a single step. The use of CREATE TABLE and SELECT togetherly is considered as one of the simplest and easiest ways of creating the clone of the table. This cloned table can be used further for any of the purposes for which we have created the clone table.
Conclusion
We can create the clone of the existing table in SQL by using the CREATE TABLE, SELECT and INSERT query statements togetherly as shown in the above two methodologies of creating a copy of the original table in SQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Clone Table” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.