Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQL Syntax
SQL syntax is nothing but how SQL statements work correctly while executing on the database server. We are assigning the table name of each table. Tables are made up of data records. SQL is adhered to by a distinct rule known as All SQL statements begin with one of these keywords, like the show, create, delete, alter, insert, update use, and they all end with a semicolon (;).
Overview
We know that one database contains more than one table in single database. The most important thing to remember about SQL is SQL is not case sensitive; SELECT and select have the same meaning in SQL statements. Table names in MySQL, on the other hand, differ. Many people are unaware that SQL was initially intended to be typed into a console, and the results are displayed on a screen. As a result, the syntax is similar to that found in English. However, this never occurred because the operator risked causing significant issues typing on the query. For example, consider typing ‘DELETE Customer WHERE Id = 101, but we have pressing enter after customer, which causes an SQL syntax error.
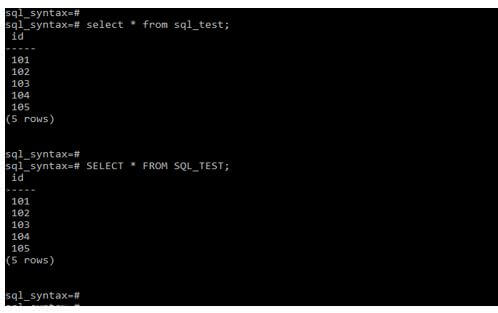
The below example shows it is not case sensitive. In the first example below, we have used all the query words in lower case letters; executing this query will return the result without error. Also, In the below second example, we have used all the query words in upper case letters; after executing this query, it will return the result without error because SQL syntax is not case sensitive.
Code:
# select * from sql_test;
# SELECT * FROM SQL_TEST;Output:
Various SQL Syntax
Below is the various syntax which is used in the database at the time of executing the specified query as follows:
1. Syntax of SQL select statement
Select statement of SQL syntax will vary per the SQL query we used on the DB server.
Syntax:
Select name_of_column1, name_of_column2, ….., name_of_columnN from name_of_table;2. SQL distinct clause
Below is the SQL distinct clause as follows.
Syntax:
Select distinct name_of_column1, name_of_column2, ….., name_of_columnN from name_of_table where condition;3. SQL where clause
Below is the SQL where clause as follows.
Syntax:
Select name_of_column1, name_of_column2, ….., name_of_columnN from name_of_table where condition;4. SQL AND/OR clause
Below is the SQL AND / OR clause as follows.
Syntax:
Select name_of_column1, name_of_column2, ….., name_of_columnN from name_of_table where condition1 {AND / OR} condition1;5. SQL IN clause
Below is the SQL IN clause as follows.
Syntax:
Select name_of_column1, name_of_column2, ….., name_of_columnN from name_of_table where name_of_column IN (Val1, Val2, …., ValN);6. SQL between clause
Below is the SQL between clauses as follows.
Syntax:
Select name_of_column1, name_of_column2, ….., name_of_columnN from name_of_table where name_of_column between Val1 AND val2;7. SQL-like clause
Below is the SQL-like clause as follows.
Syntax:
Select name_of_column1, name_of_column2, ….., name_of_columnN from name_of_table where name_of_column like {pattern};8. SQL count clause
Below is the SQL count clause as follows.
Syntax:
Select count(name_of_column) from name_of_table where condition;9. SQL drop database statement
Below is the SQL syntax of the drop database statement as follows.
Syntax:
Drop database name_of_database;10. SQL commit, rollback, and use database statement
Below is the syntax of commit, rollback, and use database statement.
Syntax:
Commit;
Rollback
\c name_of_database (in postgresql); use name_of_database; (in MySQL)11. SQL delete statement
Below is the syntax of the SQL delete statement as follows.
Syntax:
Delete from name_of_table where condition;12. SQL insert statement
Below is the syntax of the SQL insert statement as follows.
Syntax:
Insert into name_of_table (col1, col2, …, colN) values (val1, val2, …, valN);SQL Syntax Table
If suppose we need to perform any operation on any database, we must write predefined syntax of a query defined by the specified database. This syntax is distinct in each database, a distinct set of rules and guidelines that are not case-sensitive. Of course, we can write our query in uppercase and lowercase letters, but writing our SQL syntax in the uppercase letter will improve the query readability. It will tell the database which type of operations we perform on structured data and what information we want to retrieve.
Below is the SQL create table statement as follows.
Syntax:
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column1 name_of_datatype,
name_of_column2 name_of_datatype, ….
name_of_columnN name_of_datatype,
primary key (name of one or more column));Below is the syntax of the drop table and drop database statement.
Syntax:
Drop table name_of_table;Below is the syntax for updating table records.
Syntax:
Update name_of_table set name_of_column1 = val1, name_of_column2 = val2, …, name_of_columnN = valN [condition of where];Below syntax shows an altered table to change the table’s name as follows.
Syntax:
Alter table name_of_table to new_table_name;Below syntax shows altered table statement as follows.
Syntax:
Alter table name_of_table {DROP | MODIFY | ADD} name_of_column {data_type};Examples of SQL Syntax
Different examples are mentioned below:
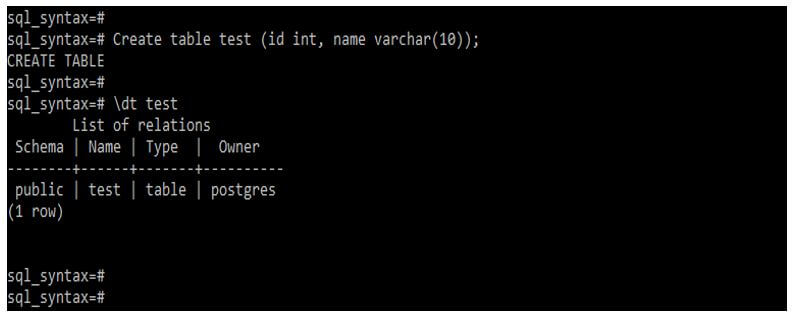
Example #1 – Create table
Code:
Create table test (id int, name varchar(10));Output:
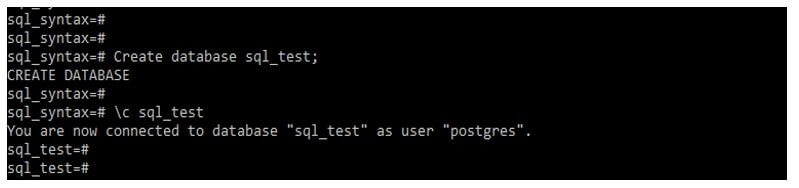
Example #2 – Create database
Code:
Create database sql_test;Output:
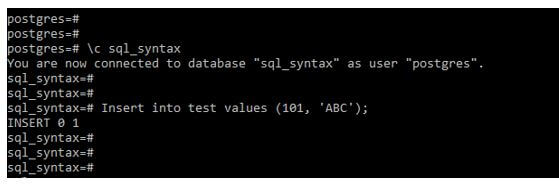
Example #3 – Insert statement
Code:
Insert into test values (101, ‘ABC’);Output:
Example #4 – Update statement
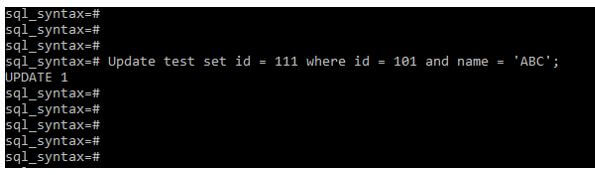
Code:
Update test set id = 111 where id = 101 and name = ‘ABC’;Output:
Example #5 – Delete statement
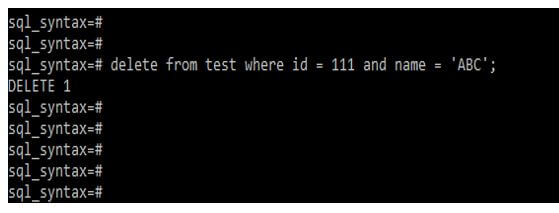
Code:
Delete from test where id = 111 and name = ‘ABC’;Output:
Example #6 – Alter statement
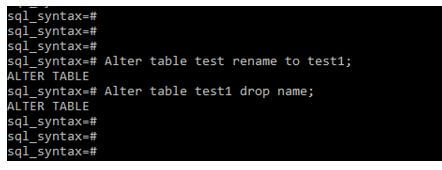
Code:
Alter table test rename to test1;
Alter table test1 drop name;Output:
Example #7 – Select statement
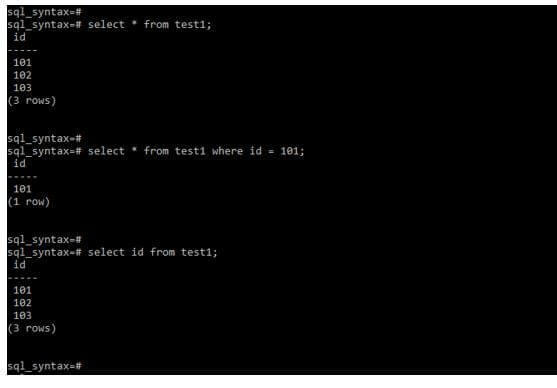
Code:
Select * from test1;
select * from test1 where id = 101;
select id from test1;Output:
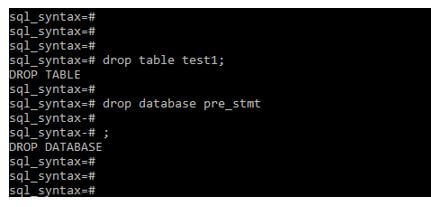
Example #8 – Drop table and database
Code:
Drop table test1;
drop database pre_stmt;Output:
Conclusion
Text lines are required for SQL statements and syntax. SQL statements are straightforward, easy to use, and understand. They are similar to plain English but have a different syntax. It is nothing but how the SQL statement works correctly while executing on the database server.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQL Syntax. Here we discuss the introduction, overview, various SQL syntax, and examples for better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –