Updated March 10, 2023

Introduction to SQL Stuff
SQL stuff is the function available in SQL to manipulate the strings and concatenate one string to another at the position where we want and even modifying the previous string by deleting some of the characters from the original string and then placing the other string in the main string. When dealing with string manipulations in SQL we often face the situation when we have to remove some of the parts from the original string and replace it with some other string value by specifying the place where we want to add the second string and mentioning part of the original string that is too be removed. All these operations in SQL can be done by using a single method named Stuff().
In this article, we will learn about syntax, general usage of stuff function, and also learn how we can implement it while manipulating string values in SQL with the help of some of the examples.
Syntax:
The syntax of stuff() function in SQL is as shown below –
STUFF(original string, starting point, length, attached string)In the above syntax, the original string is any string literal value of the name of the column whose database is character-based such as VARCHAR or string-related which stores string value and the starting point is the position in the original string that is to be considered as the beginning point for removal of characters from the original string while the length helps us specify the number of the characters that are to be removed from the original string. The attached string is the new string that is to be appended at the position from where the characters in the original string were modified.
The new string is placed at the position where the characters from the original strings are removed. One of the key things that are to be noted here is that the number of the characters that are to be deleted and the number of the characters that are to be added that are present in the new string to be attached are not compulsorily to be same.
Examples of SQL Stuff
Let us consider a few examples where we will remove some of the characters from the original string and place the new string at the position from where the characters were removed. Firstly, we will consider a string literal value say “EDUCBA_CONSULTANCY.com is the best place to learn new things.” in which we want to remove the part that includes _consultancy.com and place a new word named platform at that place. For this, we will have to mention the start position as 7 and the number of characters to be removed as 16 because the string “_CONSULTANCY.com” contains 16 characters in it. We will use stuff() function and our query statement will be somewhat as shown below –
SELECT STUFF('EDUCBA_CONSULTANCY.com is the best place to learn new things.', 7, 16, ' Platform ');The execution of the above query statement gives an output which is as shown below –
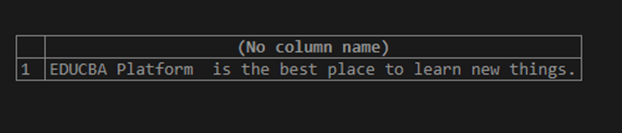
We can observe the new string that is prepared contains platform word after EDUCBA and the final string formed is “EDUCBA Platform is the best place to learn new things.
Now, we will consider one more example in which we will replace the deleted characters with string that will contain more than one words. Consider a string “To travel is to discover yourself and retreat the gift of life provided by god to you”. In this string we want to remove the characters “provided by god to you” and place a new string containing more than one word say “at fullest”.
The number of characters to be removed i.e “provided by god to you” are located at 65 position and the number of the characters to be removed are 23 because this string contains 23 characters in it. The final query string for doing so will be as follows –
SELECT STUFF('To travel is to discover yourself and retreat the gift of life provided by god to you', 65, 23, ' at fullest.');The execution of the above query statement gives an output which is as shown below –
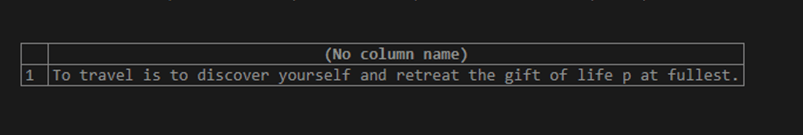
Now, we will learn how we can use stuff() function with column values stored in the tables by using it in the SQL query statements. Consider and existing table named dictionary whose contents and structure are as shown in the output of the following query statement –
SELECT * FROM dictionary;The execution of the above query statement gives an output which is as shown below –
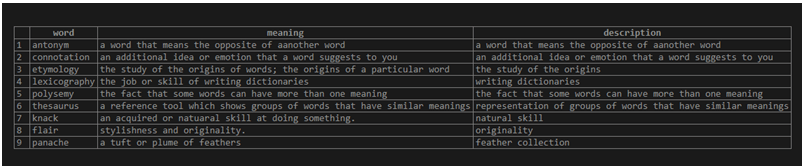
Now, we have to retrieve the value of the meaning of word named lexicography whose meaning string needs to replaced while retrieving such that instead of “the job or skill of writing dictionaries.” it will retrieve “the job or skill of writing articles.”. We can simply use the stuff function to do so by placing the start position of the characters to be removed as 29 because the dictionaries word is located at that position and the number of characters as 12 because it contains 12 characters in it. Our query statement will be as shown below –
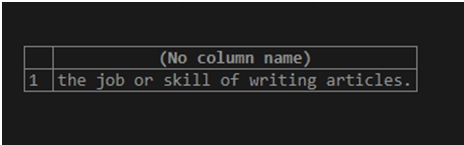
SELECT STUFF(meaning, 29, 12, ' articles.') FROM dictionary WHERE word = 'lexicography';The execution of the above query statement gives an output which is as shown below –
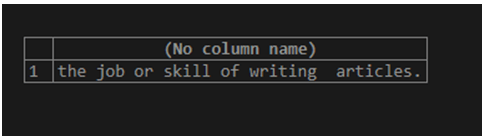
We can make the use of the function named CHRINDEX() to locate the position of particular string inside the main string by specifying the string whose position is to be found out at first position and the string value in which the search is to be made as its second position. Consider the same example in which we want to find out the position of dictionaries in the string “the job or skill of writing dictionaries” as and place this in the second parameter of the stuff method. All this things can be combined in a single query statement using following query –
SELECT STUFF('the job or skill of writing dictionaries', CHARINDEX('dictionaries','the job or skill of writing dictionaries'), 12, 'articles.');The execution of the above query statement gives an output which is as shown below –
Note that instead of string literal column name can also be mentioned by mentioning the name of the table from which data is to be retrieved as shown in the example before the current one.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Stuff” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

