Updated February 28, 2023

Introduction to SQL RANK()
RANK() in standard query language (SQL) is a window function that returns a temporary unique rank for each row starting with 1 within the partition of a resultant set based on the values of a specified column when the query runs. The rank of a row is its sequential number within the partition set. The RANK() function provides the same rank to more than one row in case of ties. For example, it provides ranks like 1,2,2,4,5 etc. SQL RANK() function is similar to other window functions such as ROW_NUMBER(), DENSE_RANK(), NTILE() etc, in relational SQL databases.
Syntax and parameters:
The basic syntax for using RANK() function is as follows:
RANK()OVER([partition_by_clause]order_by_clause)Parameters:
1. partition_by_clause: partition by clause is used to partition the resultant set into multiple groups. Mention the column name based on which the groups will be created. If you do not mention anything then the entire row in the result set will be considered as one partition.
2. order_by_clause: order by clause is used to order the values in the partition set. Mention the column name based on the values of which you want to order the partition set.
3. RANK() function is used as part of the SELECT statement.
Examples of SQL RANK()
In order to illustrate the functions and applications of the RANK() function in SQL, let’s create an imaginary ‘students’ table. The table will contain student details such as their student id, first name, last name, marks, subject, etc.
The ‘students’ table can be created in the following manner.
Code:
CREATE TABLE students(
student_id int,
first_name varchar(255),
last_name varchar(255),
subject varchar(255),
marks numeric
);Let’s insert some values in the table to populate the dataset using the INSERT statements.
Code:
INSERT INTO Students VALUES
(1,'Rohit','Sharma','Maths', 472),
(2,'Michael','Douglas','Science', 430),
(3,'Aliya','K','Science', 320),
(4,'April', 'Howard','Maths',400),
(5,'Karthik','Narayan', 'Science', 240),
(1,'Rohit','Sharma','Science', 328),
(2,'Michael','Douglas','Maths', 470),
(3,'Aliya','K','Maths', 220),
(4,'April', 'Howard','Science',500),
(5,'Karthik','Narayan', 'Maths', 340);The data in the ‘students’ table after insertion looks something like this:
Code:
select * from Students;Output:
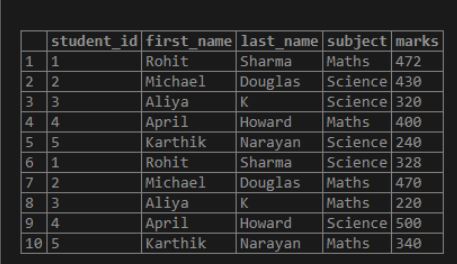
Example #1
SQL query to illustrate ranking of students based on marks obtained by them.
Case 1:
Rank without partition by clause.
Code:.
SELECT
student_id,
first_name,
last_name,
marks,
RANK() OVER (ORDER BY marks DESC) merit_list
FROM
students;Output:
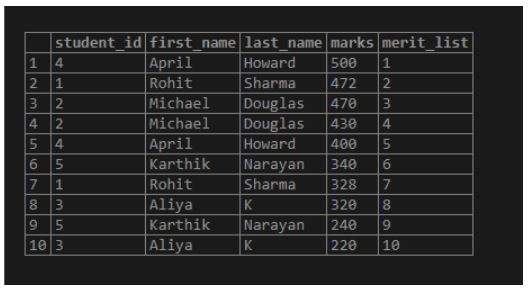
In this case, we can see that when we are ranking without partition function, the entire rows in the result set is considered as a single group and hence it does not yield a meaningful result.
Case 2:
Rank with partition by clause.
Code:
SELECT
student_id,
first_name,
last_name,
subject,
marks,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY marks DESC) merit_list
FROM students;Output:
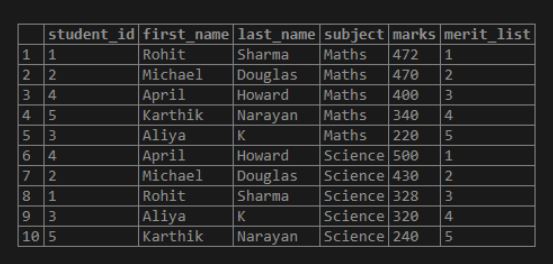
In this case, partition by clause divides the rows in the result set into two parts, one for maths and other for science and makes a more sensible ranking based on the subjects.
Example #2
Prepare a merit list of students based on the total marks obtained by them.
Code:
SELECT
student_id,
SUM(marks) as total_marks,
RANK() OVER (ORDER BY SUM(marks) DESC)
FROM students
GROUP BY student_id;Output:
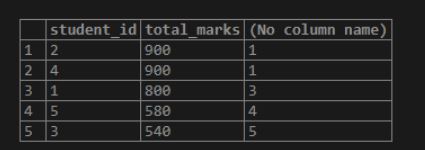
Above example provides a merit list based on the total marks obtained by the students. But it can be very confusing to some students as it does not have the first and last names of the students. Let’s prepare a merit list of students consisting of their student id, names and total marks obtained by them.
Code:
SELECT
student_id,
first_name,
last_name,
SUM(marks) as total_marks,
RANK() OVER (ORDER BY SUM(marks) DESC)
FROM students
GROUP BY student_id,first_name,last_name;Output:
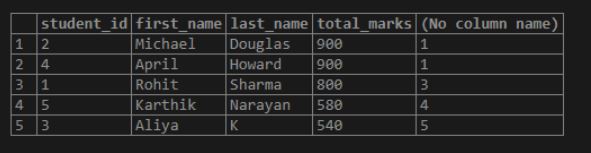
In this case, we can see that the student has been clearly identified along with his or her rank in the list.
Example #3
Find the details of the last three students who have scored lowest marks overall.
Code:
SELECT
student_id,
first_name,
last_name,
SUM(marks) as total_marks,
RANK() OVER (ORDER BY SUM(marks) ASC)
FROM students
GROUP BY student_id,first_name,last_name
LIMIT 3;Output:
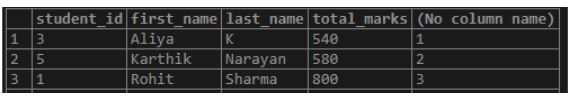
Example #4
Find the first name and last name of the student who scored third highest marks.
Code:
WITH student_details
AS (SELECT student_id,first_name,last_name,
SUM(marks) as total_marks,
RANK() OVER (ORDER BY SUM(marks) DESC) as rank
FROM students
GROUP BY student_id,first_name,last_name)
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM student_details
WHERE rank = 3;Output:
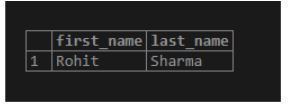
The above example teaches us how to use rank or any window function in the WHERE clause. We cannot directly use the rank column in the WHERE clause because rank is part of the SELECT statement and WHERE filtering happens before selection. So, in order to use the results of any window function we can make use of CTE or WITH expressions that let us create temporary tables.
Example #5
Find the first name and last name of the student who scored third lowest marks in mathematics.
Code:
WITH student_details
AS (SELECT student_id,first_name,last_name,
SUM(marks) as total_marks,
RANK() OVER (ORDER BY SUM(marks) ASC) as rank
FROM students
WHERE subject = 'Maths'
GROUP BY student_id,first_name,last_name)
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM student_details
WHERE rank = 3;Output:
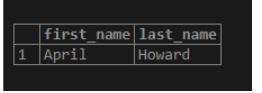
Conclusion
RANK() is a window function that sequentially ranks the rows based on the values of a specified column. It gives the same rank to more than one row in case of ties. It is very useful when we want to find the ranks such as third highest, second last etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQL RANK(). Here we discuss the introduction and examples of SQL RANK(). You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

