Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to SQL Operators
SQL Operators are defined as a symbol or particular reserved keywords used to specify some action performed on the given expression, including several clauses to tell the system how the operators behave. Operators do calculations between the data items or operand and execute the Query result. It provides a condition in SQL statements or combines multiple conditions and conducts them between the operands (filters the results). The operators used between the data can come with single or binary operands. All the operators are specified with the conditional statements and the WHERE clause of SQL.
Types of SQL Operators
SQL is the foundation of database management systems that deals with a variety of manipulation of data. Therefore, SQL provides some SQL Operators to perform Operations, and Evaluating the Expression order of precedence is very important. Following are the various Operators used in SQls.
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Logical Operators
Let’s see them One by one in detail:
1. Arithmetic Operators
In the SQL query, these operators manipulate mathematical calibrations like addition, multiplication, division, subtraction, and other modulus numeric values.
Syntax:
Select <expression 1> operator <expression 2>1. Addition
This Operator Helps in adding values on both sides of the operators. Below are the unary Operators. Example: M + N
Code:
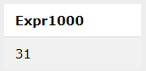
SQL> select 11+ 20;Output:
2. Subtraction
This Operator implies subtracting values on both sides of the Operator (good deal from the left). Example: M – N
Code:
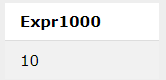
SQL> select 30- 20;Output:
3. Multiplication
This SQL operator does a multiplication operation between two operands. Example: M*N
Code:
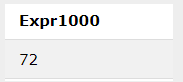
SQL> select 12 * 6;Output:
4. Division
This Operator performs actions by dividing one expression by the other expressions. Example: M/N
Code:
SQL> select 120 / 5;Output:
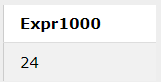
5. Modulus
This SQL operator returns the remainder of the division process between two operands. The following statement for this is:
Code:
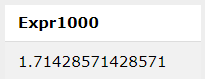
SQL> select 12 / 7;Output:
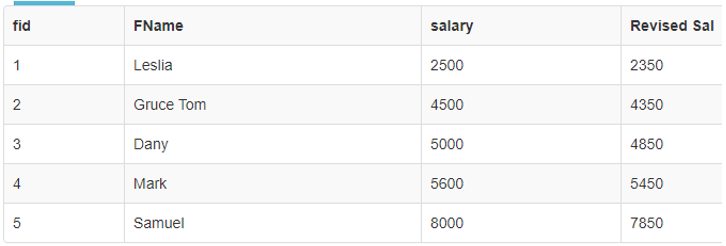
- Below Query using Arithmetic Operation on a specific Database Table. Consider a table ‘Finance’ with four Columns.
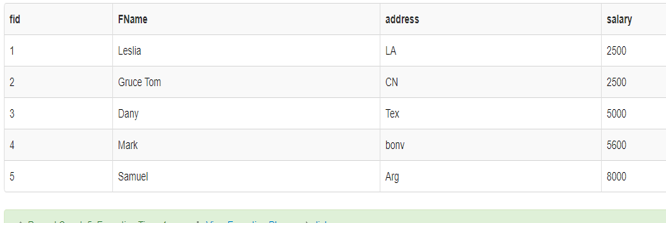
- I am using Arithmetic Operators on the Specific fields On the Table. Here I have taken the Salary column to perform the Arithmetic operation.
Example #1
Code:
SELECT fid, FName, salary, salary + 50
AS "Revised Sal" FROM finance;Output:
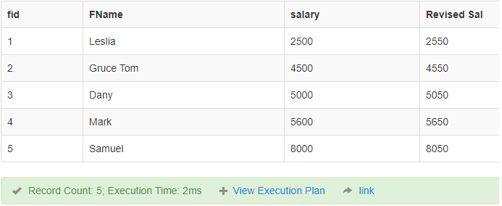
Example #2
Code:
SELECT fid, FName, salary, salary - 150
AS "Revised Sal" FROM finance;Output:
- That is all about the Arithmetic operations of SQL. In the next section, we shall see Comparison operators
2. Comparison Operators or Relational Operators
Being conditional takes two expressions, makes a useful comparison, and returns either True or False. It does the operations such as equal to, lesser than, greater than, or greater than similar to and other advanced concepts. This Operator joins their hands with the ‘where’ clause to select the particular columns in the records. Here in Below Section, we describe different types of relational operators and a few examples of them along with the syntax.
Syntax:
SELECT column FROM table WHERE condition1 Relational Operator condition2;1. Equal to (=)
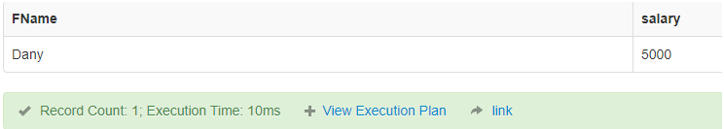
This Operator checks whether the value of the two operands is the same. If it is equal, it returns true; if not, it returns false.
Code:
SELECT FName, salary FROM finance where salary =5000;Output:
2. Not equal to or Inequality (! =), (<>)
It verifies whether the two operands’ values are equal or not. If they are not identical, then the statement returns True.
Code:
SELECT FName, salary FROM finance where salary <>2500;Output:
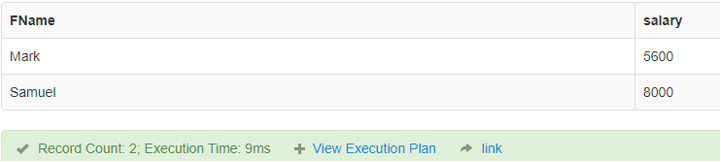
3. Greater than (>)
It is used in SQL to check for the more significant value between two operands.
Code:
SELECT FName, salary FROM finance where salary>5000;Output:
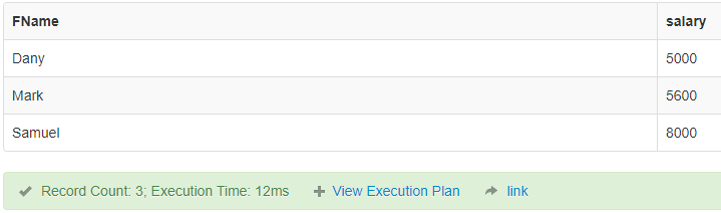
4. Greater than equal to (> =)
It is used in SQL to check for the greater than or equal to a value between two operands.
Code:
SELECT FName, salary FROM finance where salary>=5000;Output:
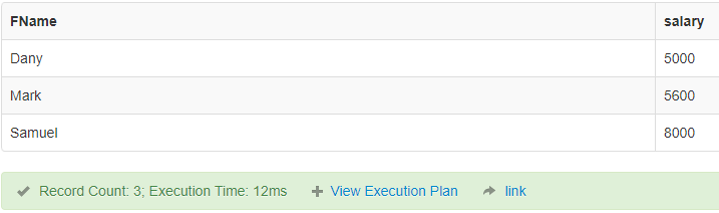
5. Lesser than (<)
This Operator in SQL checks whether a left operand is lesser than the right operand. If it is true, it results in the result.
Code:
SELECT FName, salary FROM finance where salary < 5000;Output:
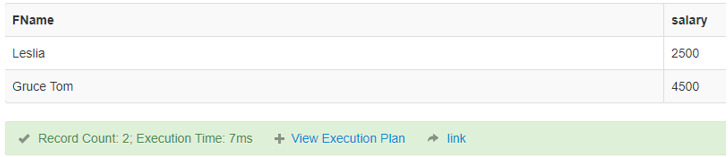
6. Lesser than or Equal to (<=)
This Operator in SQL checks whether a left operand is lesser than or equal to the right operand. If it is true, it results in the result.
Code:
SELECT FName, salary FROM finance where salary <=4500;Output:
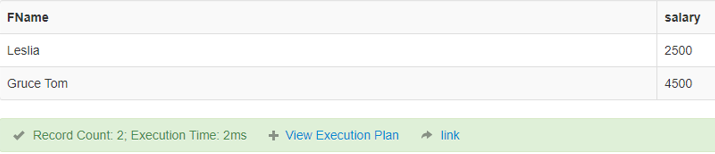
Some advanced operator is Like, IS Not Null, which we shall see later.
3. Logical Operators
The Logical Operators perform logical operations in the SQL, which are true or False. Different operators used here are listed below:
- AND
- OR
- NOT
- BETWEEN
- ANY
Syntax:
SELECT col name * | expr [logical operator]
[col name | * | expr..]
FROM tablename
WHERE <expr> [ logical operator |
arithmetic operator | ...] <expressions>;Considering the same database Finance to perform the Logical operators:
1. AND Operator
It gives preference to making use of multiple conditions with the WHERE clause.
Code:
SELECT fid,FName,address,salary
FROM finance
WHERE FName = 'Leslia' AND salary = 2500;Output:
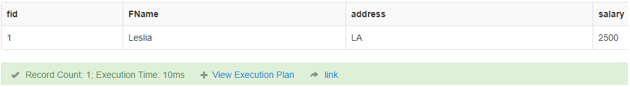
2. OR
This compares the expressions in the statement and returns true if either of the conditions is True.
Code:
SELECT fid,FName,address,salary
FROM finance
WHERE FName = 'Gruce TOM' OR salary = 2500;Output:

3. NOT
This Operator takes an argument as a single Boolean and returns true if it is false and vice-versa.
Code:
SELECT Fid , address FROM finance WHERE NOT FName = "Dany";Output:
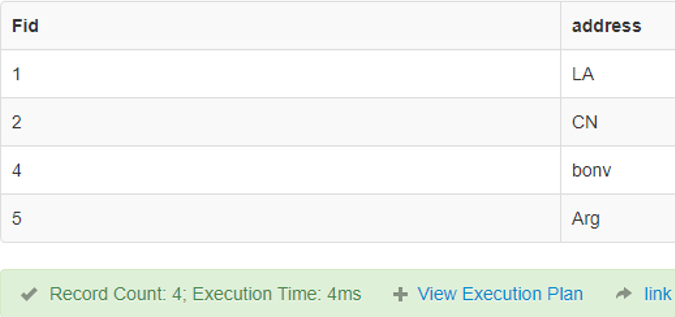
4. ANY
A specific value is taken and compared with any of the values in the fields.
Code:
SELECT * FROM finance
WHERE salary > ANY (SELECT salary FROM finance WHERE salary > 5000);Output:
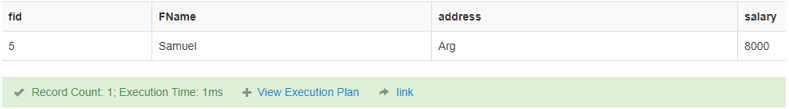
5. BETWEEN
This Operator is used when there is a limit range between the values.
Code:
SELECT * FROM finance
WHERE salary BETWEEN 2500 AND 5000;Output:

Conclusion
Therefore, in this article, we have learned how to use different operators in SQL Statements with an implementation. Also, we came across data filtering from the database using respective conditions as the operators allow checking two expressions to be the same.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Operators” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

