Updated May 9, 2023
Introduction to SQL LIKE Operator
SQL LIKE Operator is used with where condition to filter the table data by using a pattern that we have defined in the query. We can use SQL-like operators with date, string, and number values, but SQL-recommended operators must be used with string values. The like operator is not case-sensitive in MySQL, MSSQL, and SQLite databases but case-sensitive in PostgreSQL and Oracle databases.
What is SQL LIKE Operator?
- An ISO and ANSI standard operator compares one column value with another. We can also compare the quoted string by using the like operator.
- It supports the different kinds of quoted-string wildcard characters. In addition, it will allow us to search a text-based string of a specified pattern.
- It is used with the where clause in select, update, and delete SQL statements. We can use any wildcard character to find the specified pattern data from the column we defined in the query.
SQL LIKE Operator Pattern
It uses the following characters of wildcards to specify the pattern of the like operator as follows.
1. Percentage (%)
This pattern will match one, zero, or multiple characters or numbers.
Below is the syntax of the Percentage like operator pattern as follows.
Syntax:
Select name_of_column from name_of_table where name_of_column like 'xxx%';Select name_of_column from name_of_table where name_of_column like '%xxx%';Select name_of_column from name_of_table where name_of_column like '%xxx';Below is an example of a percentage pattern as follows.
Code:
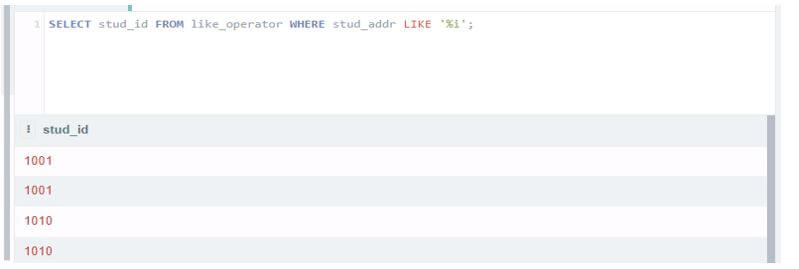
Select stud_id from like_operator where stud_addr like '%i';
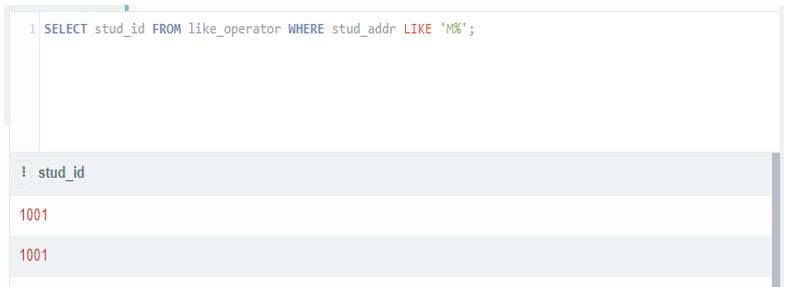
Select stud_id from like_operator where stud_addr like 'M%';
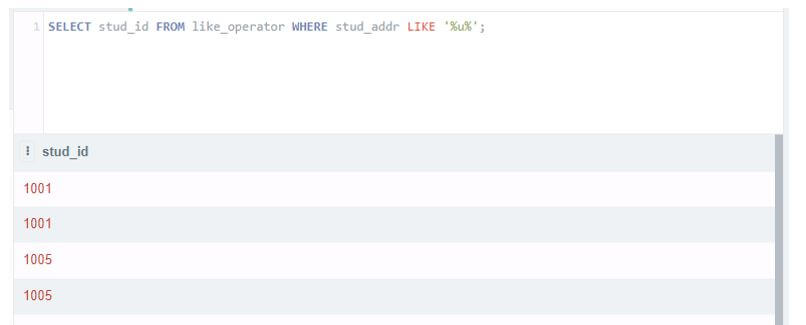
Select stud_id from like_operator where stud_addr like '%U%';Output:
2. Underscore (_)
This pattern will match one character or number.
Below is the syntax of the underscore-like operator pattern as follows.
Syntax:
Select name_of_column from name_of_table where name_of_column like 'xxx_';Select name_of_column from name_of_table where name_of_column like '_xxx_';Select name_of_column from name_of_table where name_of_column like '_xxx';Below is an example of the underscore pattern as follows.
Code:
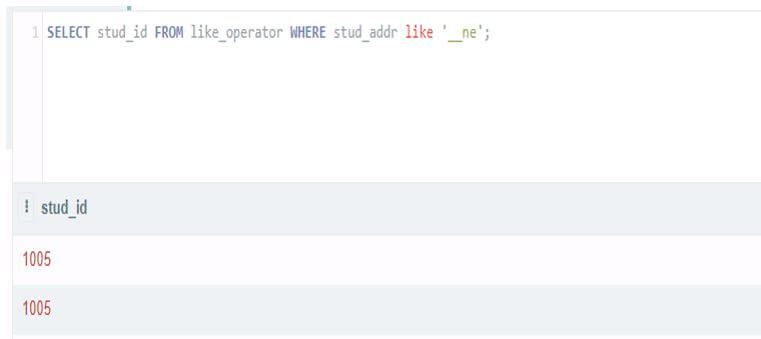
Select stud_id from like_operator where stud_addr like '__ne';
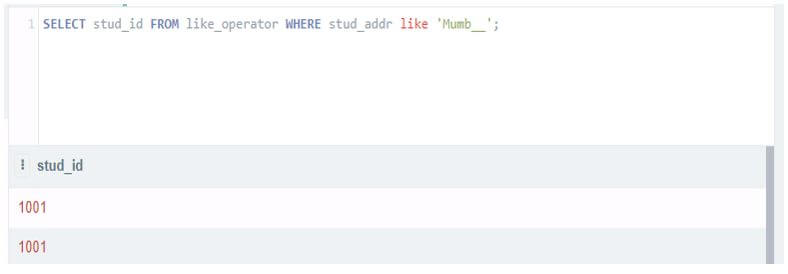
Select stud_id from like_operator where stud_addr like 'Mumb__';
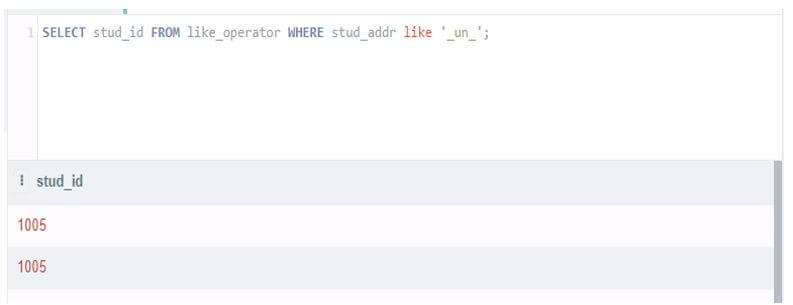
Select stud_id from like_operator where stud_addr like '_un_';Output:
3. []
This pattern will match one character. So, suppose we have a defined pattern like ‘P[e, n, u],’ this string will match the Pune string.
Below is the syntax of the [] pattern as follows.
Syntax:
Select name_of_column from name_of_table where name_of_column like 'P[e, n, u]';Below is the example of [] pattern as follows.
Code:
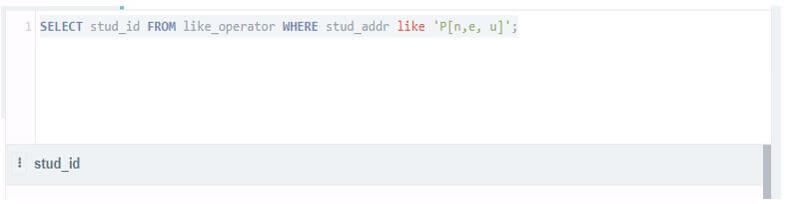
Select stud_id from like_operator where stud_addr like 'P[n, e, u]';Output:
4. [^]
This pattern will match every single character except the specified range. For example, the ‘P[^u, e, n]’ this string matches everything which starts from p, but it will not match the string which contains u, e, and n letters.
Below is the syntax of the [] pattern as follows.
Syntax:
Select name_of_column from name_of_table where name_of_column like 'P[^e, n, u]';Below is the example of [] pattern as follows.
Code:
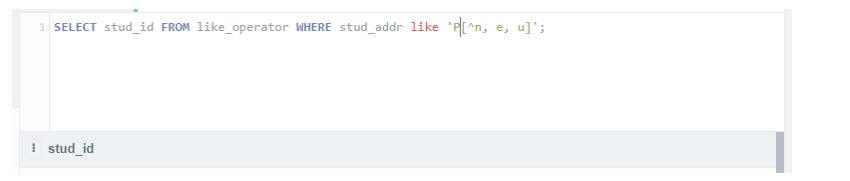
Select stud_id from like_operator where stud_addr like 'P[^n, e, u]';Output:
SQL-LIKE Operator Tables
It is also used with two tables. We can join the two tables and use the like operator on this after joining. The table slightly differs from the normal-like operator we used on a single column. Tables define query the like operator on two different tables.
Below is the syntax as follows.
Syntax:
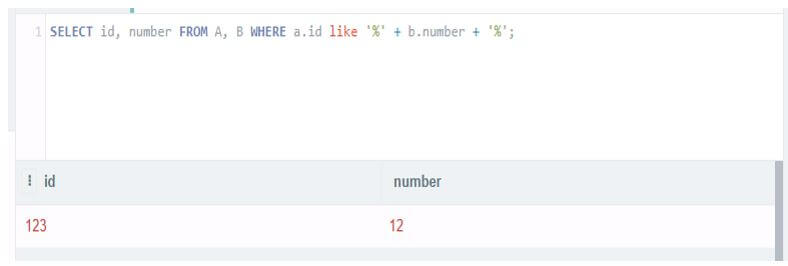
Select name_of_column1, name_of_column2, …, name_of_columnN from name_of_table1, name_of_table2 where table_name.column_name like '%' + table_name.column_name like '%'In the above syntax, we have used two tables. Therefore, we match standard columns from both tables to retrieve records from both tables.
We can also use all the tables from the column to retrieve matching records from the specified column, which we apply to both tables.
Below is an example as follows.
Example:
Code:
select id, number from A, B where a.id like '%' + b.number + '%';Output:
SQL Script LIKE Operator
SQL script-like operator is used in SQL DB systems. The SQL script-like operator will extract and match the specified pattern data. The SQL script-like operator performs large queries on our data tables. We can simplify complex queries by using SQL script-like operators. We are using an SQL script-like operator to speed up our query performance. When wildcards are used, the results are significantly faster. SQL Wildcards have already been used with a script-like operator in SQL. SQL script-like operator is used in our database to operate wildcards. When searching for complex data, we use SQL wildcards.
Below is an example of an SQL script-like operator as follows.
Example:
Code:
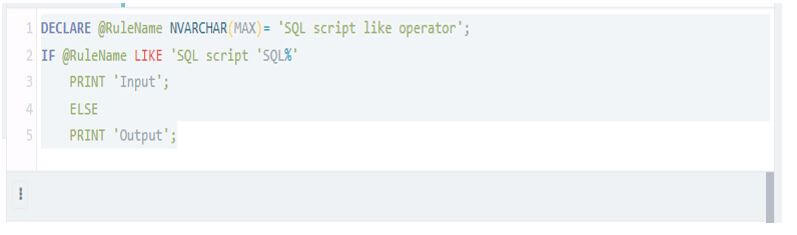
DECLARE @RuleName NVARCHAR (MAX)= 'SQL script like operator';
IF @RuleName LIKE 'SQL script 'SQL%'
PRINT 'Input';
ELSE
PRINT 'Output';Output:
List
We are using different types of SQL-like operators. The wildcard operator is mainly used with SQL-like operators.
Wildcard operator plays a vital role in SQL-like operators.
Below is the list of wildcard SQL-like operators as follows:
- Percentage (%)
- Underscore (_)
- []
- [^]
All the above operators we are using with SQL-like operators at the time of using the same in our query. Suppose we have a defined pattern like ‘AB%’; this string will match the AB string and all the strings coming after the AB string. Suppose we have a defined pattern like ‘AB_,’ this string will match the AB string and one character after the AB string.
Conclusion
It supports different kinds of quoted-string wildcard characters. It will allow us to search text-based strings of a specified pattern. It is used with the where condition to filter the table data by using a pattern that we have defined in the query.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL LIKE Operator” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.