Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to SQL LEFT INNER JOIN
SQL LEFT INNER JOIN is the type of join that can be used to retrieve all the records of the left table, that is, the table name that is placed just after the from clause and all the matching records of the left and right join in it. The joins are used in cases when we have to find out the data by combining the records of two or more tables. The left inner join is specifically used when there is a condition in which, irrespective of whether a matching record is present in the right table or not, all the records of the left table should always be retrieved.
The left table is the table whose name is specified just after the from clause, and the table whose name is placed after the join keyword is considered as our right table while applying any join. If there is a matching record in the right table, then its contents are also retrieved, and if such matching records are not found, then a NULL value is retrieved for those columns retrieved from the right table.
Syntax of SQL LEFT INNER JOIN
Given below is the syntax of the LEFT INNER JOIN:
SELECT table name1.column name1,table name1.column name2,table name2.column name1,....
FROM table name1
LEFT JOIN table name2
ON table name1.matching_column name = table name2.matching_column name;The specification of the INNER keyword in the left inner join is optional as, by default, the left join is considered as the left inner join in SQL. Thus, the table name1 is our left table name, and the table name2 is the name of our right table of the left inner join. As we have to retrieve the resultsets combining both the tables, then the column names of both the tables are retrieved as shown in the above syntax; the column records are retrieved in the manner by specifying the name of the table and then the name of the column whose value is to be retrieved by simply separating them with the help of a dot.
All the column values that are to be retrieved are separated with the help of a comma between them. Further, the columns based on which the matching records are to be found from both the tables are mentioned in the ON clause of the syntax.
Example of SQL LEFT INNER JOIN
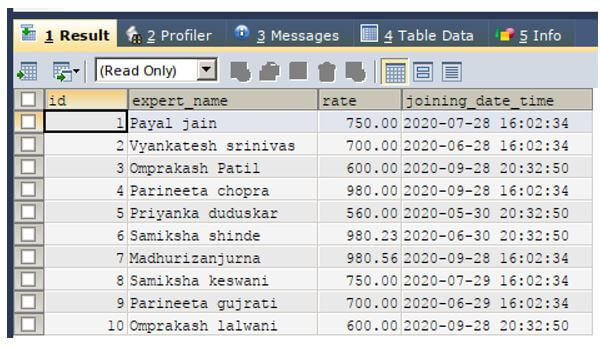
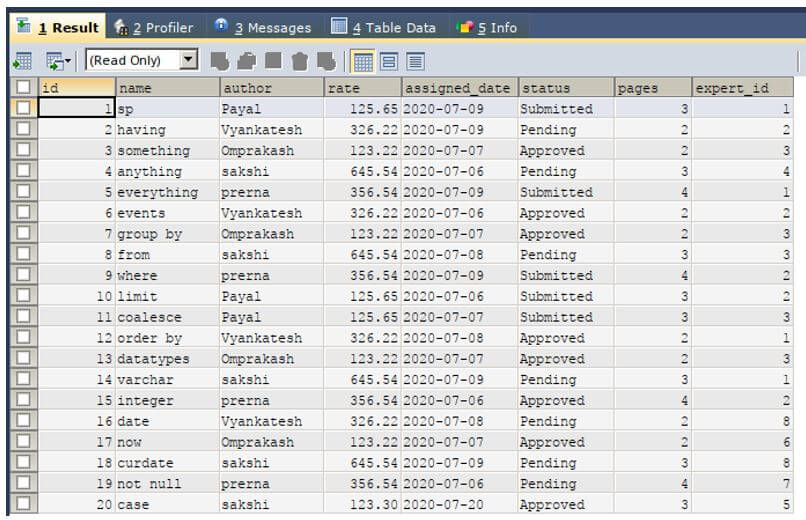
Let us consider two existing tables in my educba database named educba_experts which stores the records of all the experts and their details. Another table with the name educba_articles stores the details about the articles that have been assigned to the experts and their status. To see the structure and the contents of both the tables, we will make the use of following query statements:
Code:
SELECT * FROM `educba_experts`;Output:
Code:
SELECT * FROM `educba_articles`;Output:
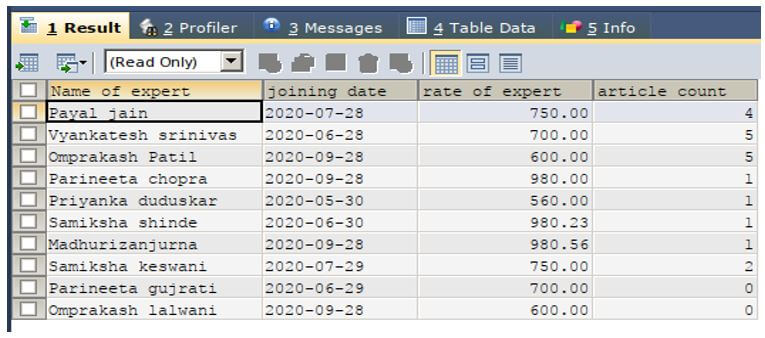
Now, we have to retrieve all the records from the expert table and then retrieve the count of the articles assigned to those experts. The details related to experts can be retrieved from the educba_experts table, while the count of the articles, if present for the experts, can be retrieved by performing a join on the table educba_articles. In this case, as we have to retrieve the records of the experts irrespective of whether there are any articles assigned to him/her, we have to make the use of left inner join.
Code:
SELECT
a.expert_name AS "Name of expert",
DATE(a.joining_date_time) AS "joining date",
a.rate AS "rate of expert",
COUNT(b.id) AS "article count"
FROM
`educba_experts` a
LEFT JOIN `educba_articles` b
ON a.id = b.expert_id
GROUP BY a.id;Output:
As we can observe, all the experts’ details are retrieved, such as the name of an expert, his/ her joining date, rate of expert, and the total article count from the table educba_articles. As none of the extry is found for parineeta gujrati and Omprakash Lalwani named experts in the table educba_articles, the NULL value is retrieved for them, and count of NULL is zero, 0 value is retrieved for the experts for whom the records are not present in educba_articles. As we have to group the article count on the basis of the id of the expert, we have grouped the results set on the id column of the alias “a,” which is the alias of educba_experts.
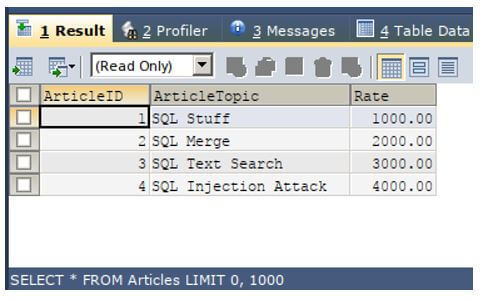
Let us understand the implementation of the left inner join with the help of one more example by considering two tables. First, consider the two existing tables named Articles and UpdatedArticles, whose contents and structure are as shown in the output of the following query statement.
Code:
SELECT * FROM Articles;Output:
Code:
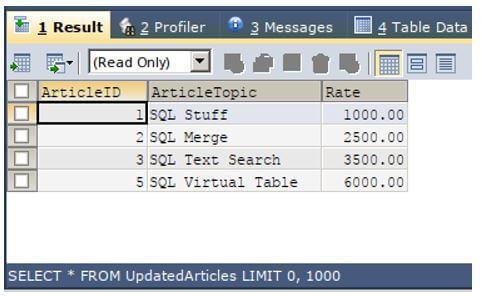
SELECT * FROM UpdatedArticles;Output:
Now, we have to retrieve all the records of the table updated articles irrespective of whether matching is found in the table articles.
Code:
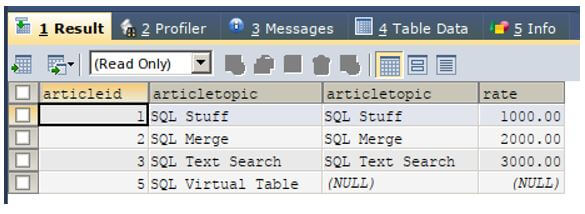
SELECT
a.articleid,a.articletopic , b.articletopic,b.rate
FROM
`UpdatedArticles` a
LEFT JOIN `Articles` b
ON a.articleid = b.articleid ;The execution of the above query statement gives an output which is as shown below, containing null values for which a matching entry is not found in the articles table.
Output:
Conclusion
We can make use of LEFT INNER JOIN by simply specifying the left join in the syntax. It helps in retrieving all the records of the left table irrespective of whether a matching record is found in the right table for it. A NULL value is retrieved for the right table’s column values if no matching record is found.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL LEFT INNER JOIN” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.