Updated March 27, 2023

Introduction to SQL Inner Join
The rows from two or more tables are combined to form a set of rows in the temporary table by the SQL JOIN clause. At least if one field is present in common in two or more tables and a relationship exists between them and if there are matching values between the two tables, the records with the matching rows are pulled into a temporary table and this is called SQL Inner join. Rows that do not contain the matching values are rejected and the temporary table contains only the matching values. The most common SQL join is SQL Inner join. The primary key of one table is joined to the foreign key of another table is the most common scenario in SQL inner join.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM tab1 INNER JOIN tab2
ON tab1.col_name = tab2.col_name;Where,
- tab1 is the first table
- tab2 is the second table
- tab1.col_name is the column name in the first table
- tab2.col_name is the column name in the second table.
Working of SQL Inner Join
If there are matching values in the two tables, the records with the matching values are returned to form a set of rows in a temporary table by SQL inner join. The pictorial representation of SQL inner join is represented below:
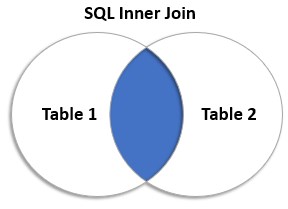
- The shaded portion in blue represents the matching values from both the tables.
- Consider two tables, orders table and customers table:
Orders Table
| IDord | IDCust | Ordval |
| 1 | 123 | 12 |
| 2 | 456 | 34 |
| 3 | 789 | 56 |
| 4 | 012 | 78 |
Customers Table
| IDCust | Custname | Origin |
| 456 | ABC | INDIA |
| 012 | DEF | US |
| 809 | GHI | CHINA |
| 134 | JKL | GERMANY |
- The IDCust column is common in both the orders table and Customer table. IDCust is the relationship between the orders table and the Customer table.
- We now create an SQL statement containing inner join to extract only those records from orders and customers table having matching values.
Code:
SELECT orders.IDord, orders.IDCust, customers.Custname, customers.origin
FROM orders
INNER JOIN customers ON orders.IDCust = customers.IDCust;Output:

Explanation to the above table: Orders table consists of three columns: order ID (IDord), Customer ID (IDCust) and order value (ordval). Customers table consists of three columns: Customer ID (IDCust), Customer name (Custname) and origin. The relationship between the two tables is Customer ID (IDCust).
Code:
SELECT orders.IDord, orders.IDCust, customers.Custname, customers.origin
FROM orders
INNER JOIN customers ON orders.IDCust = customers.IDCust;</code.Explanation to the above code: Above SQL statements Selects the columns order ID (IDord), Customer ID (IDCust), Customer name and Customer origin columns from orders and customers tables having matching values in Customer ID (IDCust) resulting in the table consisting of two records and four columns order ID (IDord), Customer ID (IDCust), Customer name and Customer origin. The SQL inner join is applied on order ID (IDord) column.
Examples to Implement SQL Inner Join
Below are the examples to implement in SQL Inner join:
Example #1
Consider the two tables Students Table and Marks Table
Students Table
| Rollno | Subject | Marks |
| 1 | A | 90 |
| 2 | B | 80 |
| 3 | C | 70 |
| 4 | D | 50 |
Marks Table
| Rollno | Student name |
| 3 | ABC |
| 4 | DEF |
| 5 | GHI |
| 6 | JKL |
- The Rollno column is common in both the Students table and Marks table. Rollno is the relationship between the orders table and the Customer table.
- We now create an SQL statement containing inner join to extract only those records from Students and Marks table having matching values.
Code:
SELECT students.Rollno, students.Subject, students.Marks, Marks.Studentname
FROM students
INNER JOIN Marks ON students.Rollno = marks.Rollno;Output:
Explanation to the above code: In the above example, there are two tables: the student’s table and the marks the table. The student’s table consists of three columns: Roll number (Rollno), Subject and Marks. Marks table consists of two columns: Roll number (Rollno), Student name (studentname). The relationship between the two tables is the Roll number (Rollno).
Code:
SELECT students.Rollno, students.Subject, students.Marks, Marks.Studentname
FROM students
INNER JOIN Marks ON students.Rollno = marks.Rollno;Explanation to the above code: Above SQL statements Selects the columns Roll number (Rollno), Subject and Marks and Student name (studentname) columns from students and marks tables having matching values in Roll number (Rollno), resulting in the table consisting of two records and four columns Roll number (Rollno), Subject, Marks and Studentname. The SQL inner join is applied on the Roll number (Rollno) column.
Example #2
Consider the two tables Company Table and Item Table
Company Table
| Company ID | Company name | Company city |
| 1 | A | Blore |
| 2 | B | Mysore |
| 3 | C | Mlore |
| 4 | D | Tumkur |
Item Table
| Item ID | Item name | Company ID |
| 3 | ABC | 3 |
| 4 | DEF | 4 |
| 5 | GHI | 5 |
| 6 | JKL | 6 |
- The Company ID column is common in both the Company table and Item table. Company ID is the relationship between the Company table and Item table.
- We now create an SQL statement containing inner join to extract only those records from the Company and Item table having matching values.
Code:
SELECT Company.Company ID, Company.Company name, Company.Company city, Item.item ID, Item.item name
FROM Company
INNER JOIN Item ON Company.Company ID = Item.Company ID;Output:

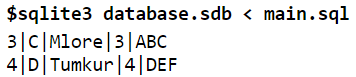
Explanation to the above code: In the above example, there are two tables: company table and item table. company table consists of three columns: Company ID, Company name and Company city. Item table consists of three columns: Item ID, Item name and Company ID. The relationship between the two tables is Company ID.
Code:
SELECT Company.Company ID, Company.Company name, Company.Company city, Item.item ID, Item.item name
FROM Company
INNER JOIN Item ON Company.Company ID = Item.Company ID;Explanation to the above code: Above SQL statements Selects the columns Company ID, Company name and Company city, Item ID and Item name columns from company and item tables having matching values in Company ID, resulting in the table consisting of two records and five columns Company ID, Company name and Company city, Item ID and Item name. The SQL inner join is applied to the Company ID column.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about different types of joins, their definitions, and differences, syntax join, explanation of the syntax, working, examples to implement and explanation of their results after executing the queries.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Inner Join” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

