Updated May 17, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL ORDER BY DESC
We use the SELECT statement to get the set of results, which returns the rows from the table in random order. To sort this result set, we use the PostgreSQL ORDER BY clause. When we use the ORDER BY clause with the SELECT statement for querying the data, the rows returned from the table can be sorted in ascending or descending order. We can use the columns and expressions to sort the results in descending order. PostgreSQL allows us to sort the rows in descending order when we specify the keyword DESC with the SELECT statement for sorting the table rows in descending order.
Syntax:
Consider the following syntax statement to understand the PostgreSQL ORDER BY DESC syntax:
SELECT
column_name_1,
column_name_2
FROM
table_name
ORDER BY
column_name_1 [ DESC],
column_name_2 [ DESC];Explanation:
- We need to define the name of the columns in the PostgreSQL clause to sort the results.
- It is possible in PostgreSQL to sort the table result with multiple columns, for which we need to specify the column names separated by commas.
- We can use the columns and expressions to sort the results in descending order.
Use the following statement to create the Tenants table, which consists of three columns:
id,
firstName,
lastName
contact.
CREATE TABLE Tenants (
id serial NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
firstName VARCHAR,
lastName VARCHAR,
email VARCHAR,
contact VARCHAR
);Now, we will insert some rows into the Tenants table with the help of the INSERT statement as follows:
INSERT INTO Tenants (firstName, lastName, email, contact)
VALUES
('Armstrong', 'Neil', '[email protected]', '111-222-333'),
('Bean', 'Roy', '[email protected]', '111-222-333'),
('Herbert', 'george', '[email protected]', '111-222-333'),
('Gray', 'Thomas', '[email protected]', '111-222-333'),
('Frost', 'Robert', '[email protected]', '111-222-333'),
('Eluard', 'Paul', '[email protected]', '111-222-333'),
('Drake', 'Nick', '[email protected]', '111-222-333'),
('Laurel', 'Stan', '[email protected]', '111-222-333'),
('Zola', 'Emile', '[email protected]', '111-222-333'),
('King', 'William', '[email protected]', '111-222-333'),
('Baba', 'Meher', '[email protected]', '111-222-333'),
('Arselan', 'Aip', '[email protected]', '111-222-333');
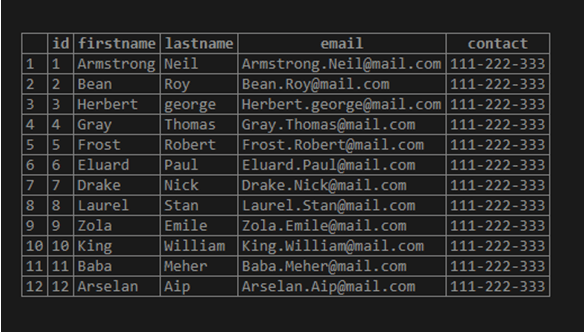
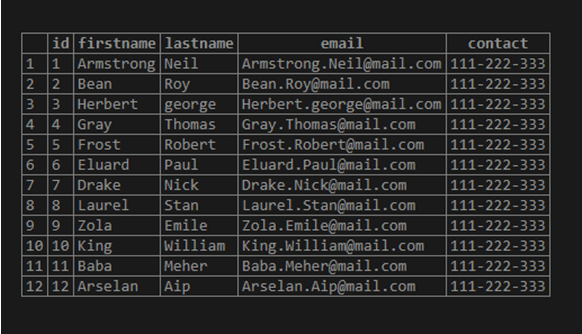
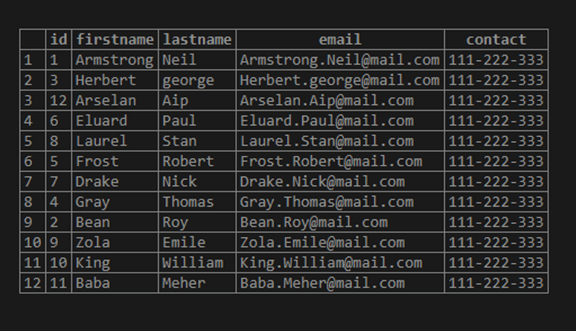
select * from Tenants;Now retrieve the data from the Tenants table with the help of the SELECT statement as follows:
SELECT
id,
firstName,
lastName,
email,
contact
FROM
Tenants;Illustrate the content of the Tenants table by using the following snapshot:
Consider the following example where you will use only one column in the ORDER BY clause.
SELECT
id,
firstName,
lastName,
email,
contact
FROM
Tenants
ORDER BY
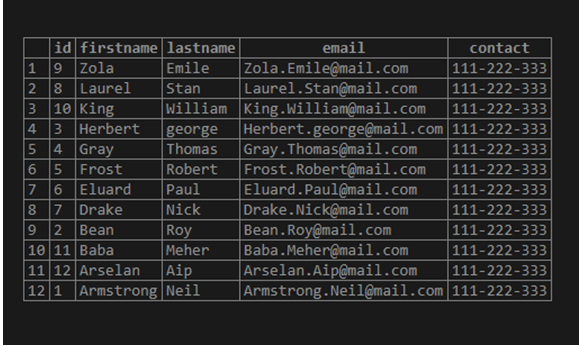
firstName DESC;In the above SQL statement, we have specified the ORDER BY clause with the column firstName and specified the DESC keyword, specifying the descending order. Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot:
Consider the following example where you will use multiple columns in the ORDER BY clause.
SELECT
id,
firstName,
lastName,
email,
contact
FROM
Tenants
ORDER BY
lastName DESC,
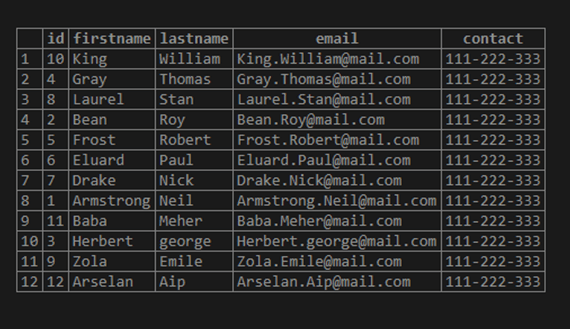
firstName DESC;In the above SQL statement, we have specified the ORDER BY clause with the columns lastName and firstName and specified the DESC keyword, specifying the descending order.
Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot:
Consider the example where we will use the expression in the ORDER Y clause.
We will use the LENGTH() function in the ORDER BY clause for sorting the result set as per the length of the firstName column. Consider the following SQL statement to understand the same, SELECT id, firstName, lastName, email, contact FROM Tenants ORDER BY LENGTH(firstName) DESC;
In the above SQL statement, we have specified the ORDER BY clause with LENGTH(firstName), which returns us the length of the firstName characters for each row, and the DESC keyword, which specifies the descending order.
Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot:
The LENGTH() function provided by PostgreSQL takes a string as an input and returns the input string’s length.
Conclusion
We hope from the above article, you have understood how to use the PostgreSQL SELECT statement with the ORDER BY clause to return the result set in descending order. Also, we have added several examples to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL ORDER BY DESC” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.