Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQL DROP DB
The following article provides an outline for SQL DROP DB. An existing SQL database can be deleted using the DROP DATABASE statement. Dropping a database requires one to be linked to the master (Tomcat, Apache) database. Only one database can be dropped at the moment, and the DROP DATABASE command must be the only statement in a SQL batch.
Key Takeaways
- Privileges assigned expressly for a database are not immediately removed when the database is removed. They have to be manually dropped.
- The database name should always be distinct inside the RDBMS.
What is SQL Drop Database?
The DROP DATABASE statement forever disregards the database and all associated tables. As a result, one must use this statement with extreme caution. One can double-check whether a database has already been correctly dropped by checking the database list after dropping a database.
Code:
Create database db name; // Creates a database
Use database; // Using a database to store a records
Show databases; // Displays available databases;
DROP database ; // Deletes a particular database.How to Use SQL Drop Database Statement?
Drop statements are used in a database system, where a separate room is created in MySQL to place records. If we do not require a database for further use or a garbage collector, we can use the DROP keyword in a SQL Statement to completely discard a record in the System.
The table structure and related statistics, permissions, triggers, and restrictions are completely removed. SQL Views and stored procedures may reference the SQL table. These stored procedures and views are left in place by SQL Server. We have to drop them expressly. Before deleting a SQL table, we need to look at object dependencies.
The DROP DATABASE statement’s syntax is demonstrated by the following:
DROP DATABASE db_name;
After the DROP DATABASE keywords in this statement, users enter the database name they wish to destroy.
A MySQL error will be generated if we attempt to delete a database that doesn’t exist. One can use the IF EXISTS option to stop an error from happening if we remove a database that doesn’t exist. MySQL will stop the statement in this situation without throwing an error.
The DROP DATABASE statement returns the number of tables that were destroyed.
By using a single DROP syntax, we could also quickly destroy many databases:
DROP DATABASE Db_Name1, [ Db_Name2, ……., Db_NameN ] ;
This statement eliminates the need for several commands to delete various databases. As the syntax above demonstrates, we may specify all the databases in a short statement by inserting a comma.
The DROP DATABASE statement deletes the documents and folders that MySQL might generate during regular operation from the specified database location. All documents with the below extensions are included in this: BAK, CFGS, DAT, DB, and IBD. The database directory cannot be deleted if additional files or directories are present in it after MySQL deletes the previously mentioned items. In this situation, one must carefully delete any lingering files or directories and issue another DROP DATABASE statement. Any TEMPORARY tables created in a database are not deleted when it is dropped. The session that created the temporary tables finishes with the automatic removal of the temporary tables.
SQL Drop DB Delete
- DB Delete uses where clause when used in Filtering Query Statement. And SQL drop doesn’t use the Where clause to drop a database.
- When seeing on Memory Management drop command frees the memory allocations. And in DB, delete memory space is not free even though the records are deleted as it doesn’t delete the entire database.
- Since the Drop command directly affects data, it cannot be rolled back. But the DB delete can be.
- A database table’s whole contents are removed with a SQL DELETE query. On the target table, delete rights are necessary to run a DELETE query. Select permissions are also necessary if a WHERE clause is used in a DELETE.
Examples of SQL DROP DB
We will see how to drop a database with two different examples.
Example #1
Code:
* Create a table called Aerolist */
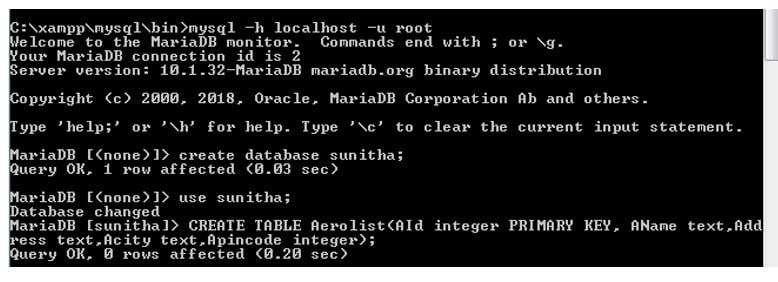
CREATE TABLE Aerolist(AId integer PRIMARY KEY, AName text, Address text, Acity text, Apincode integer);
/* Create a few records in this table */
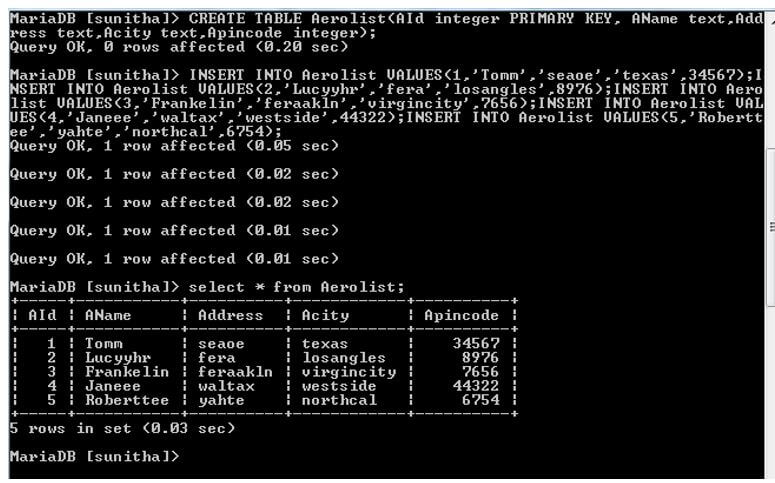
INSERT INTO Aerolist VALUES(1,'Tomm','seaoe','texas',34567);
INSERT INTO Aerolist VALUES(2,'Lucyyhr','fera','losangles',8976);
INSERT INTO Aerolist VALUES(3,'Frankelin','feraakln','virgincity',7656);
INSERT INTO Aerolist VALUES(4,'Janeee','waltax','westside',44322);
INSERT INTO Aerolist VALUES(5,'Roberttee','yahte','northcal',6754);
/* Display all the records from the table */
SELECT * FROM Aerolist;The below screenshot shows how to create a database.
Output:
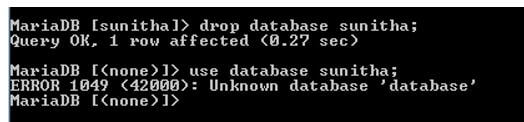
We can see in the below screenshot that once the database Sunitha is deleted using DROP, we cannot use that Database again. That’s why an error statement shows an Unknown database.
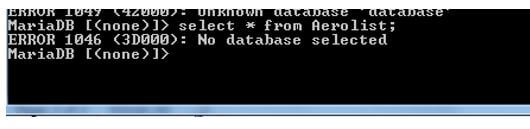
And we can see that if we try to use the existing table, it shows us the report like the Unknown database. Because we had dropped the database completely.
Example #2
Code:
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
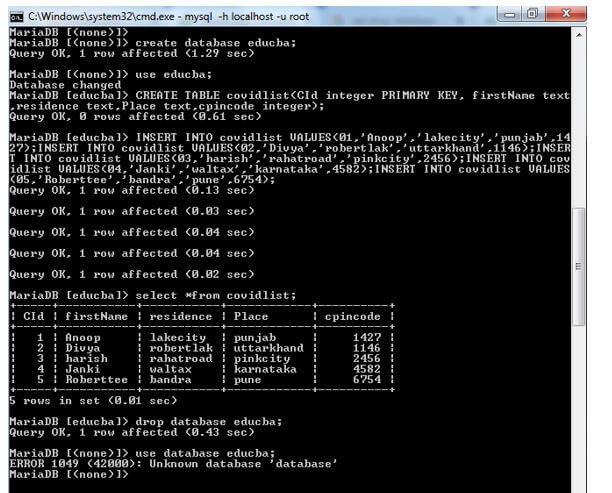
/* Create a table called covidlist */
CREATE TABLE covidlist(CId integer PRIMARY KEY, firstName text,residence text,Place text,cpincode integer);
/* Create a few records in this table */
INSERT INTO covidlist VALUES(01,'Anoop','lakecity','punjab',1427);
INSERT INTO covidlist VALUES(02,'Divya','robertlak','uttarkhand',1146);
INSERT INTO covidlist VALUES(03,'harish','rahatroad','pinkcity',2456);
INSERT INTO covidlist VALUES(04,'Janki','waltax','karnataka',4582);
INSERT INTO covidlist VALUES(05,'Roberttee','bandra','pune',6754);
COMMIT;
/* Display all the records from the table */
SELECT * FROM covidlist;Output:
FAQ
Given below are the FAQs mentioned:
Q1. What for a DROP database is used?
Answer:
A database and all of its tables can be fully deleted with the DROP DATABASE statement.
Q2. You have a table with some of the fields to enter and already the database is dropped. Create a function to convert ‘meter ‘into ‘centimeters. Would you be able to create a function further?
Answer:
No, I cannot create a function or alter a table field as the database is dropped by the user. So, we cannot access a table to do the task.
Conclusion
We have seen DROP command usages and their Privileges in Detail along with examples.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQL DROP DB. Here we discuss the introduction, how to use SQL drop database statement? examples and FAQ. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –