Updated March 8, 2023
Introduction to SQL Delete View
We can delete the created view in SQL by using the command named DROP VIEW. This completely deletes the existence of views and structure and contents of the view. Note that the tables using which we have defined the view that we are trying to delete remains intact and all the contents of the original table and tables are not affected on the deletion of the view from the database. This happens because the view is not the physical entity that stores the data that is present in the database. It is simply a query that is defined and stored as per our requirement and behaves like a virtual table. When we delete the view SQL internally simply deleted the query that was stored to create the view and its contents.
We may need to delete the view permanently due to some reason. Another reason for deleting the view also involves that we have to make some changes in the existing view. In that case, there is no other way out but to delete the view and recreate it again as per the necessary changes that are required to be incorporated. In this article, we will see about the sage of the DROP VIEW command to delete the view, its syntax, and implementation along with the examples that implement the command.
Syntax of SQL Delete View
The syntax of deletion of view using the drop view command is as shown below:
DROP VIEW view_nameIn the above syntax, the view_name is the name of the view that we wish to delete.
The alternative syntax of deleting the view is as shown below:
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS view_name;The use of IF EXISTS keyword is optional but the advantage of using it that it handles the error that might occur if the view which is trying to delete doesn’t exist in our database. If we use the above syntax of drop view command then the execution of the query statement will simply raise a warning instead of error if the view with the specified name does not exist.
We can even delete multiple views using the single drop view command by using the following syntax:
DROP VIEW
view_name1,
view_name2,
view_name3,
...;Or
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS
view_name1,
view_name2,
view_name3,
...;The difference between both the above-mentioned syntaxes is the same as shown about the syntax of deleting a single view syntaxes. We can delete multiple views by specifying the list of the names of the view that need to be deleted in a comma-separated format. We can specify as many view names as we want in the above-mentioned syntaxes.
Examples of SQL Delete View
Given below are the examples of SQL Delete View:
Example #1
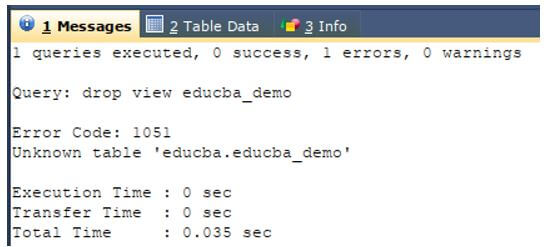
Let us first try deleting the view named educba_demo that doesn’t even exist in our database by using the first syntax of the DROP VIEW command.
Code:
DROP VIEW educba_demo;The execution of the above query statement gives the output as shown below along with the error saying that none of the tables with educba_demo exists in our database named educba.
Output:
Example #2
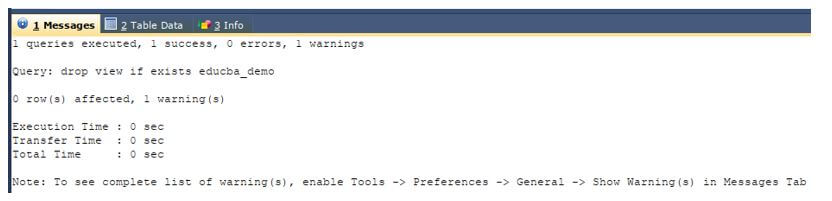
Now, let us use the second syntax of DROP VIEW command that includes IF EXISTS statement in the syntax for deleting the same view with name educba_demo that does not exist in educba database using the following query statement.
Code:
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS educba_demo;The execution of the above query statement gives the output as shown below along with the warning instead of error.
Output:
Example #3
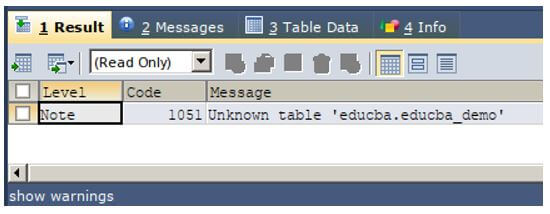
Let us check the warning by executing the following query statement.
Code:
SHOW WARNINGS;The execution of the above query statement gives the output saying that the name educba_demo is unknown because there is no table with the same name present in our database.
Output:
Example #4
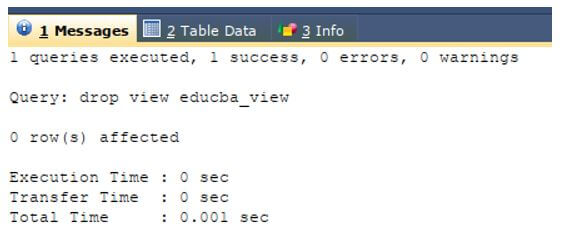
Now, we will try deleting the view named educba_view that actually exists in our database named educba using the first syntax of DROP VIEW command.
Code:
DROP VIEW educba_view;The execution of the above query statement gives the output with success message.
Output:
Example #5
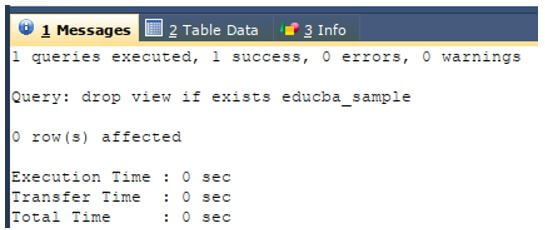
Let us try deleting an existing view named educba_sample that exists in our database using the second syntax of DROP VIEW command and following query statement.
Code:
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS educba_sample;The execution of the above query statement gives the output with success message.
Output:
We can observe that both the syntaxes give the same output when the view that we are trying to delete already exists in our database.
Example #6
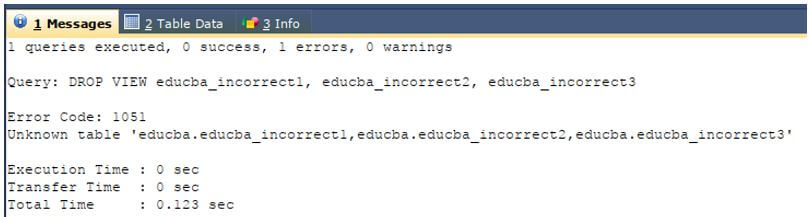
Now, we will try deleting multiple views that don’t exist in our database using the third syntax of drop view command. We will try deleting views named educba_incorrect1,educba_incorrect2, and educba_incorrect3 that are not present using the following query statement.
Code:
DROP VIEW educba_incorrect1,
educba_incorrect2,
educba_incorrect3 ;Output:
Example #7
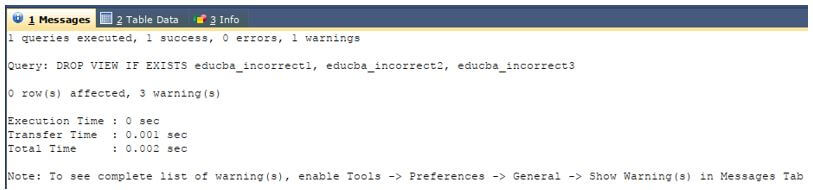
Let us use the same query statement along with the fourth format of DROP VIEW command that means using IF EXISTS statement in the above query statement.
Code:
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS educba_incorrect1,
educba_incorrect2,
educba_incorrect3 ;The execution of the above query statement gives the output as shown below along with the warning instead of error.
Output:
Example #8
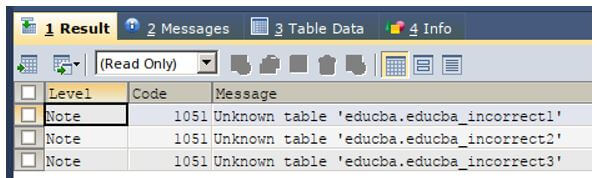
Let us check the warning by executing the following query statement.
Code:
SHOW WARNINGS;The execution of the above query statement gives the output saying that the name educba_incorrect1, educba_incorrect2, and educba_incorrect3 is unknown because there are no tables with the same names present in our database.
Output:
Example #9
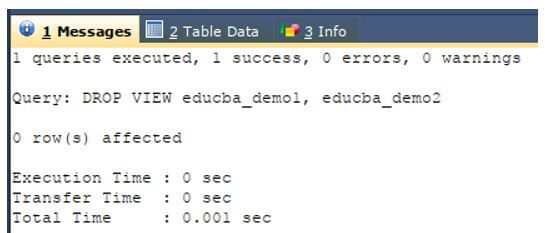
We will delete the views named educba_demo1 and educba_demo2 that exists in our database using the following query statement using the third syntax and following query statement.
Code:
DROP VIEW educba_demo1,
educba_demo2 ;Output:
Example #10
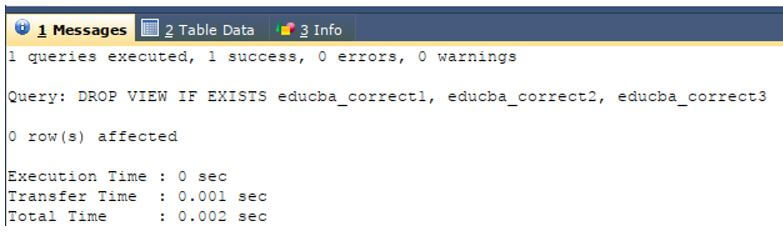
Now, we will delete all the existing views named educba_correct1, educba_correct2, and educba_correct3 that exists in our database using the fourth syntax.
Code:
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS educba_correct1,
educba_correct2,
educba_correct3 ;Output:
Conclusion
We can delete the views that exist in our database using the DROP VIEW command in SQL and deleting so will not affect any table on which the view was defined.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Delete View” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.