Updated April 8, 2023
Introduction to SQL Create Table
In a database table, records are kept as data. The SQL CREATE TABLE statement is used to generate a database table. For instance, keyword tells the database system that we need to CREATE TABLE. We wish to make a new table in this instance. The CREATE TABLE statement is followed by the table’s distinctive name or identifier. The list describing each table column’s data type is then included between parentheses.
Key Takeaways
- CREATE is a DDL command used to define a database Structure.
- Practically all relational databases, including MySQL, Postgres, SQL Server, and others, the CREATE TABLE command is available.
- Data types play a vital role in creating a table.
Overview of SQL Create Table
The CREATE TABLE statement and the SELECT statement can be used to duplicate an existing table. When constructing a table, each column needs a data type.
| Data Type | Description | Example |
| Int | Stores number types | 10, 30 |
| Varchar(s) | Stores a variable character with a max value of ‘s’ | John(20) takes up to 10 characters |
| Text | Stores 6555 characters | It doesn’t specify the maximum length of the characters. We can store paragraph content |
| Boolean | Stores a binary type | Ex: T or F |
| Date | Gives the date format | Eg: 2022-08-23 |
The above table is very important when we specify the data type for each column and when creating a new SQL table. Once it has been established, we must adhere to it. For example, users won’t be able to include text, dates, or anything else if users specify a new column to have an integer data type.
How to Create SQL Table?
The syntax for creating a table is given below:
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
column3 datatype,
....
);CREATE TABLE is not user-defined; it is a SQL keyword and should be placed at the beginning of the statement Query. Let’s see an example to see the working of creation. The basic syntax of the CREATE TABLE statement is demonstrated by the following:
Now let’s work with SQL lite, we can also work with any other Managers, and the process Output will be the same in all the tools. Get the server connection or start the Database and execute this Query.
Example:
Code:
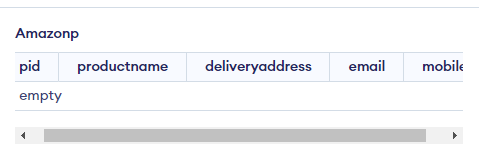
CREATE TABLE amazonp (
pid int,
product name varchar(50),
delivery address text,
email id varchar(50),
mobile varchar(10)
);A database called amazonp is created in this case via the SQL statement. pid, delivery address, mobile, and column (field) pid are all in the table. The data types int, varchar(25), and text indicate what information might be put in that field. Here are a few examples of frequently used data types.
Rules
- The column’s data is enclosed in parentheses. Commas must be used to separate the various columns.
- Remember to include the semicolon after the SQL statement.
- The three important Extra arguments that can be included in a Table are: Unique, NOT NULL, and Primary Key and all these parameters are optional.
Using IF NOT EXIST in Create Table
An error occurs when creating a table that already exists. We could add the optional IF NOT EXISTS command when establishing a table to resolve this problem. For instance:
Code:
CREATE TABLE chinaCustomers
AS (
SELECT *
FROM Medicine
WHERE place = "shelong"
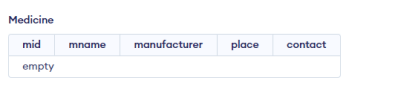
);CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS medicine (
mid int, mname varchar(50),
manufacturer text,
place varchar(50),
contact int(15)
);Output:
Utilizing the Construct TABLE AS command, we can also create a table using the data from any other existing table.
The PRIMARY KEY constraint gives each item in a table a special identification. A database can only contain one primary key, and this primary key may be made up of one or more columns.
SQL Table Six Columns
Columns and rows are used to structure tables. Each column can be looked at as reflecting a part of the record that each row represents. The sample that follows makes a table. The field name and data types are as follows.
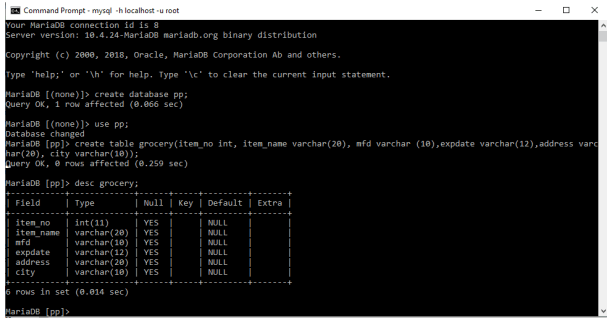
In the below example, we have created six columns with 6 datatypes.
SQL code is given here:
Code:
create table grocery(item_no int, item_name varchar(20), mfd varchar (10),exp date varchar(12),address varchar(20), city varchar(10));To see the structure of a code we can use Describe table name.
Output:
SQL Server Create Table Examples
A table with a primary key in SQL Server can be created with Transact-SQL or SQL Server Management Studio. A distinct clustered index that corresponds to a primary key is generated automatically, as is a non-clustered index if one is given.
Code:
CREATE TABLE [Schema name].[tableName](
[Col_1] [Datatype](Length),
[Col2] [Datatype](Length) [Constraint_Name] ,
[Col3] [Datatype](Length),
…. . . . .
) ON [Group]Example:
Code:
CREATE TABLE [Courses].[Course](
[COurse_ID] [bigint] IDENTITY(1,1),
[COurse _code] [varchar](50),
[COurse _name] [varchar](50),
[Communication] [varchar](25),
[City] [varchar](50),
[EnrollmentDate] [datetime],
) ON [PRIMARY]Create Table With a Foreign Key:
The table with the main key is referred to as the parent table, while the table with the foreign key is referred to as the child table.
Code:
CREATE TABLE bookOrders (
Order_no int NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
Orderitem int NOT NULL,
PID int FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES user(userID)
);FAQ
Given below are the FAQs mentioned:
Q1. How do I make a primary key table?
Answer:
Code:
CREATE TABLE marksheet (
rollno int,
sname varchar(50),
sgrade text,
email varchar(50),
phone varchar(10),
PRIMARY KEY (rollno)
)Q2. What are constraints?
Answer:
Constraints can occasionally be database-specific, which means that the keywords can differ from one database to another.
Q3. Write a SQL statement to create a simple table India including columns state_id,state_name and state_regions.
Answer:
Code:
Create table india( state_id integer, state_name varchar(10),state_regions(5));Q4. What does “Primary key” mean?
Answer:
- A column (or group of columns) or a set of columns that uniquely identifies each entry in the table is known as a primary key in SQL.
- No null values are permitted.
Conclusion
The CREATE TABLE SQL statement, its syntax, and the column parameters that must be set are all been covered in this article.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQL Create Table. Here we discuss the introduction, how to create SQL table? using IF NOT EXIST in create table, examples and FAQ. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –