Updated October 4, 2023
Introduction to Timestamp to Date in SQL
In SQL, the timestamp is a function that retrieves the current date and time of the SQL server without the database timezone offset. In SQL, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP is used to extract the current date and time. It takes no argument and returns the DateTime value. However, retrieving, storing, and comparing the 2 date and time values in practical situations is necessary and making decisions accordingly. So, it is essential to convert the obtained timestamp in the format according to the requirements. There are various functions provided in the SQL languages which allow the user to handle the above situation.
Table of Content
- Introduction to Timestamp to Date in SQL
- Why Convert Timestamps to Dates
- How to Convert Timestamp to Date in SQL with Syntax
- Examples of Timestamp to Date in SQL
- Best Practices
Why Convert Timestamps to Dates
- Simplicity and Readability: By removing the time complication, timestamps are converted to dates, simplifying the data and making it easier to read.
- Aggregation and Grouping: Dates are better suited for aggregating data over time intervals, such as days, months, or years, which helps simplify analysis.
- Filtering and Querying: Dates make it easier to filter and query SQL for specific date periods.
- Consistency: For consistent data, converting timestamps to dates ensures consistency and eliminates extraneous temporal details.
- Compatibility: Because some tools need data in date format, conversion ensures they work with these products.
- Reducing Complexity: Dates are easier to manipulate, which minimizes the possibility of errors in data manipulation and comparison jobs.
Some common uses of time-series data
- Stock price movement
- Sensor tracking (e.g., weather tracking)
- Rental services (e.g., bike or scooter rentals)
How to Convert Timestamp to Date in SQL with Syntax
A timestamp data type also exists in SQL, which has nothing to do with the date and time values. Instead, it exposes the uniquely generated binary numbers in the database whose value keeps changing on any update/insert. The data type timestamp has been deprecated now. Instead, the row version is used nowadays to deal with such things.
But, here, the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP function retrieves the current date and time values. And to convert this timestamp in the required date and time values formats. In addition, SQL provides CONVERT and CAST functions that the programmer can use to perform the desired conversion task.
1. CONVERT
In SQL, the CONVERT () function converts any data type’s value into the required data types (as mentioned by the user in the query). To convert the current timestamp to the desired date and time values, the required datatype, expression, and ‘code’ (used to define the required format of date and time to be obtained) are taken as a parameter.
- There are already defined date and time format codes in SQL ranging from 0-141, specifying the date and time values in different formats.
- It is suitable for the coder to learn a few frequently used in the query to perform the task efficiently. However, all the codes are available on the internet easily.
Some of the codes are given below to give you an overview of the formats provided by them:
| Sr. No | Code | Format |
| 1 | 0 | mon dd yyyy hh: mm AM/PM |
| 2 | 9 | mon dd yyyy hh:mm:ss:nnn AM/PM |
| 3 | 13 | dd Mon yyyy hh:mm:ss:nnn AM/PM |
| 4 | 20 | yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm: ss |
| 5 | 21 | yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss:nnn |
| 6 | 22 | mm/dd/yy hh:mm: ss AM/PM |
| 7 | 25 | yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss:nnn |
| 8 | 100 | mon dd yyyy hh: mm AM/PM |
| 9 | 113 | dd Mon yyyy hh:mm:ss:nnn |
| 10 | 126 | yyyy-mm-ddThh:mm:ss:nnn |
| 11 | 2 | yy.mm.dd |
| 12 | 5 | dd-mm-yy |
| 13 | 7 | Mon dd, yy |
| 14 | 8 | hh:mm: ss |
As seen above, to retrieve the current timestamp of the SQL server function which is used is:
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP;
(takes no arguments)Syntax of the CONVERT function of the SQL server to convert the above timestamp:
convert(data_type(length), expr, code) ;Where,
- data_type: It is the data type to convert the input expression to. It can be varchar, char, bigint, smallint, datetime, binary, text, image, etc.
- expr: It is an expression that needs to be converted. In the above query, the expression should be the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP retrieved before.
- code: The date style code is the format in which we want the desired result. Some of the codes are already mentioned in the above table.
2. CAST
The CAST() function performs the same way as CONVERT(), i.e., it converts any data type’s value into the desired data type. Thus, this function can convert the retrieved current timestamp into the date and time values. The CONVERT and CAST function performs the same task, the only difference being that CAST() is a part of ANSI-SQL, whereas CONVERT() is not. But one advantage of the CONVERT() function is that it takes an extra parameter of ‘code’ in which we can style the date and time in the ‘n’ number of formats by passing the style code as a parameter.
Syntax of the CAST function to convert the above timestamp value in the required date and time format:
cast (expr AS data_type(length);Where,
- data_type: It is the data type to convert the expression to. It can be int, bigint, datetime, char, varchar, text, image, etc.
- expr: It is an expression that needs to be cast. It can be an integer, varchar, string, date, etc. But in the above query, the expression should be the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP retrieved before using CURRENT_TIMESTAMP to perform the desired task.
3. DATE
The DATE function extracts the date portion (year, month, and day) from a timestamp or date expression. It is often used when you want to ignore the time portion of a timestamp and work with only the date component. Here’s how you can use it:
SELECT DATE(timestamp_column) AS date_only
FROM your_table;In this example, timestamp_column contains timestamp values, and DATE(timestamp_column) extracts the date portion from each timestamp. The result will be a new column with only the date.
4. EXTRACT
The EXTRACT function retrieves specific components (e.g., year, month, day, hour, minute) from a timestamp or date. It allows you to access various parts of a timestamp. Here’s how you can use it:
SELECT EXTRACT(YEAR FROM timestamp_column) AS year,
EXTRACT(MONTH FROM timestamp_column) AS month,
EXTRACT(DAY FROM timestamp_column) AS day,
EXTRACT(HOUR FROM timestamp_column) AS hour,
EXTRACT(MINUTE FROM timestamp_column) AS minute
FROM your_table;In this example, we use EXTRACT to extract the year, month, day, hour, and minute components from the timestamp_column. To suit your needs, you can replace these components with SECOND, QUARTER, WEEK, or DOW (day of the week).
Combining DATE and EXTRACT
You can also combine the DATE and EXTRACT functions to extract specific components from the date portion of a timestamp. For example, to extract the month and day from the date part of a timestamp:
SELECT EXTRACT(MONTH FROM DATE(timestamp_column)) AS month,
EXTRACT(DAY FROM DATE(timestamp_column)) AS day
FROM your_table;This query extracts the date part from timestamp_column using DATE and then uses EXTRACT to retrieve the month and day components from that date.
Examples of Timestamp to Date in SQL
Below are some examples using different functions:
1. DATE Function
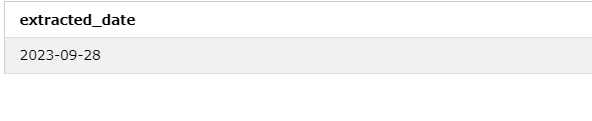
Suppose you want to create a date from a given timestamp, ‘2023-09-28 14:30:00’.
The DATE function extracts the date part from a timestamp or datetime value.
Query:
SELECT DATE('2023-09-28 14:30:00') AS extracted_date;Output:
2. CAST Function
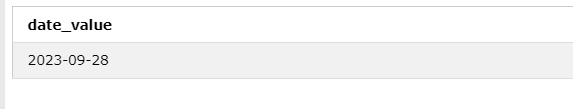
Suppose you have a string ‘2023-09-2,8’ and want to cast it to a date data type.
The CAST function converts one data type into another.
Query:
SELECT CAST('2023-09-28' AS DATE) AS date_value;Output:
3. EXTRACT Function
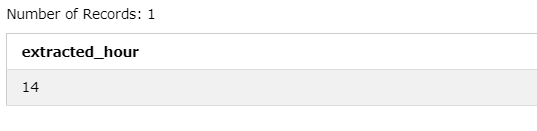
Let’s say you have a timestamp ‘2023-09-28 14:30:0,0’ and want to extract the hour from it.
The EXTRACT function retrieves a specific component (e.g., hour, day, month) from a timestamp or datetime.
Query:
SELECT EXTRACT(HOUR FROM '2023-09-28 14:30:00') AS extracted_hour;4. CAST Function for Date to String Conversion
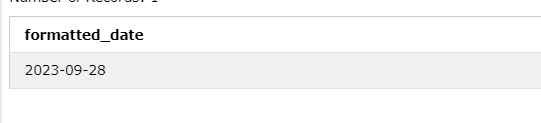
Suppose you have a date ‘2023-09-28’ and want to cast it to a string in a specific format.
The CAST function can also convert date or timestamp values to strings with custom formatting.
Query:
SELECT CAST('2023-09-28' AS VARCHAR(10)) AS formatted_date;Output:
Best Practices for Timestamp-to-Date Conversion in SQL
Converting timestamps to dates in SQL involves handling date and time data efficiently. Here are some best practices for timestamp-to-date conversion in SQL:
1. Use Explicit Casting
When converting a timestamp to a date, use explicit casting functions like CAST or CONVERT. This makes your intention clear and helps prevent data type mismatches.
SELECT CAST(timestamp_column AS DATE) AS converted_date
FROM your_table;2. Be Mindful of Time Zones
Consider the time zone of your data when converting timestamps to dates. SQL databases often store timestamps with time zone information. If necessary, adjust for time zone differences during conversion.
SELECT CAST(timestamp_column AT TIME ZONE 'UTC' AS DATE) AS converted_date
FROM your_table;3. Handle Null Values
Check for and handle null values in the timestamp column to avoid errors or unexpected results during conversion.
SELECT
CASE
WHEN timestamp_column IS NOT NULL THEN CAST(timestamp_column AS DATE)
ELSE NULL
END AS converted_date
FROM your_table;4. Use Indexed Columns for Filtering
When filtering data based on converted dates, consider indexing the converted date column for faster query execution.
CREATE INDEX idx_converted_date ON your_table (CAST(timestamp_column AS DATE));Conclusion
The above description clearly explains how the timestamp function works in SQL and the practical implementation of converting a timestamp to date. Although for a DBA working on SQL queries, there arise various scenarios when we want the data of date and time in the desired format, we cannot change the table schema every time to satisfy each requirement, so it is essential to understand the conversion clearly to proceed further quickly.
FAQs
Q1. What’s the Difference Between a Timestamp and a DateTime?
Answer: Although they are closely connected, a timestamp and a datetime may differ slightly depending on the situation and the database system. The word “timestamp” is used in many database systems to describe a datetime that also contains information about the time that a particular event happened, making it appropriate for storing events or transactions. The more general term “datetime” describes any date and time, including timestamps.
Q2. How Can I Convert a Timestamp to a Human-Readable Format?
Answer: You can use functions or techniques made available by your database system to transform a timestamp into a human-readable format. CAST, CONVERT, and formatting functions like TO_CHAR (in Oracle) and FORMAT (in SQL Server) are examples of common functions. You can extract and format the date and time components using these functions in the way that suits you best.
Q3. Why Timestamps are Important in Data Management?
Answer: Timestamps are essential to data management for several reasons.
- Temporal Accuracy: Timestamprecord accurate data, preserving events’ chronological order.
- Data versioning: You can track data changes across time using timestamps for version control.
- Timestamps are essential for auditing and logging processes because they show when specific events or actions took place.
- Data Analysis: Timestamps make it possible for data analysts to conduct time-based analysis, which includes spotting trends, patterns, and anomalies throughout time.
Q4. How Do I Handle Time Zones When Working with Timestamps?
Answer: To ensure accurate representation of time, especially in applications with international users, it is crucial to handle time zones with timestamps. You can standardize specific time zones for your data or utilize timestamps containing time zone information. Consider translating timestamps to the user’s local time zone before presenting them to users.
Q5. How Are Timestamps Stored in Databases?
Answer: Timestamps are frequently recorded in databases as a data type that combines date and time components. The storage format may change depending on the database system. Still, it typically contains year, month, day, hour, minute, and sec data. Some databases also include timestamps with time zone information to maintain accuracy across multiple locations.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Timestamp to Date in SQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.