Updated June 26, 2023
Introduction to SQL Clustered Index
The following article provides an outline for the SQL Clustered Index. A clustered index is an index that sorts the rows in a database table based on a specific column value and defines the manner in which the data in the table is stored on the disk. When we create a table with a primary key constraint, a clustered index is automatically created by default based on this primary key. A table can only have one clustered index. In order to create a new clustered index, we have to remove the previous one. For the uninitiated, an Index in relational databases is an additional data structure associated with a table that helps in faster retrieval of records from that table. An index is basically a key built based on the columns in the table and stored in B-Tree. B-Tree is a data structure that facilitates faster searches and access.
Syntax and Parameters:
The basic syntax used for creating a clustered index in SQL is as follows:
CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX index_name
ON schema.table_name(column_name);The parameters used in the above-mentioned syntax are as follows:
- index_name: Name of the index. There is convection which is followed while giving index names as IX_tablename_columnname.
- schema.table_name: Schema and the table name on which the said index has to be created.
- column_name: Name of the column which will act as a key for the index. That is the column on the basis of which records have to be sorted and stored.
Examples of SQL Clustered Index
Given below are the examples :
Example #1
Illustrating automatic creation of a clustered index on primary keys.
Here is an example to illustrate that a clustered index is created automatically when we create a primary key in a database table. In order to observe it, let’s create a table called “employees” with a primary key.
Code:
CREATE TABLE employees (
id integer IDENTITY (1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
name varchar (255),
role varchar (255),
department varchar (255)
);Output:
The table has been successfully created. Now, let’s check if the clustered index has been created on this table.
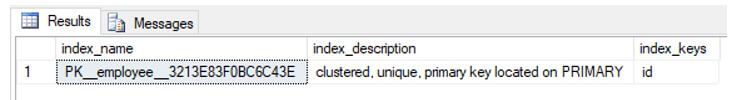
In SQL server, we have a system stored procedure called “sp_helpindex” that fetches all the information on indexes on a table. It returns the name of the index, a brief description, and the column on which the index has been created.
Code:
EXEC sp_helpindex 'dbo.employees'
GOOutput:
Example #2
Creating a clustered index on a table without a primary key.
An example to illustrate the creation of a clustered index on a table without any primary key. In order to see the example, let’s create a new table called “departments” without any primary keys. Here is the create table statement for the same.
Code:
CREATE TABLE departments (
department_id int NOT NULL,
department_name nchar(10) NULL,
location nvarchar(50) NULL
);Output:
The table has been successfully created.
Let’s move on to creating a clustered index using the following code snippet.
Code:
CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX IX_departments_id
ON dbo.departments(department_id);Output:
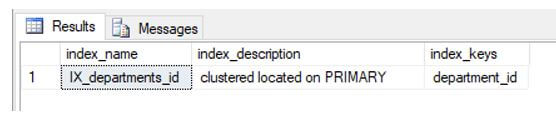
Using the sp_helpindex stored procedure, let’s fetch details on the newly created index.
Code:
EXEC sp_helpindex 'dbo.departments'
GOOutput:
The clustered index has been successfully created.
Example #3
Creating a clustered index from SQL server management studio.
Now, all this has been using a query tool. Let’s try creating a clustered index using SQL Server Management Studio.
Follow the following steps:
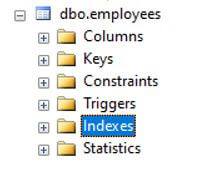
Step 1: In the object explorer, move to the database table on which you wish to create an index. From the table, move to Indexes.
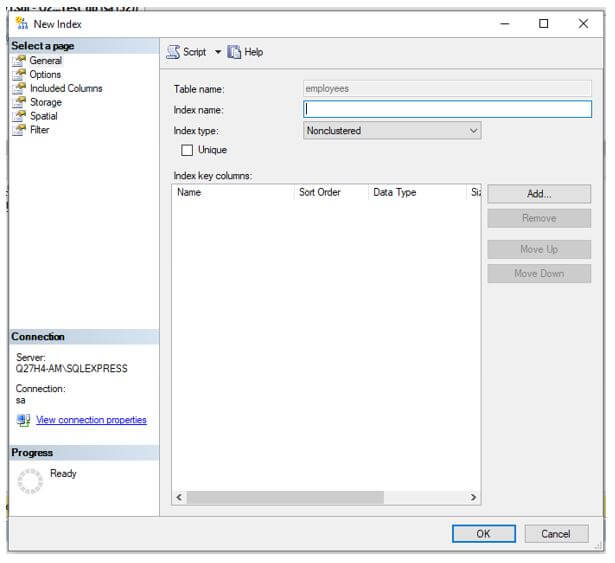
Step 2: Select a new index from the extended menu and a dialog box as shown below will appear.
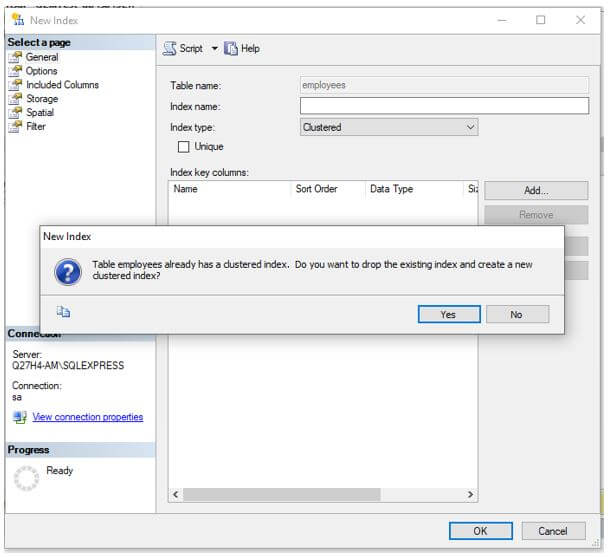
Step 3: On the dialog box, choose index type as “clustered”. Wait what just happened!! Yes, right as we saw above, we can only have one clustered index on a table. Ergo, the server is prompting us to delete the previous index. If you wish to create a new index then click on ‘Yes’.
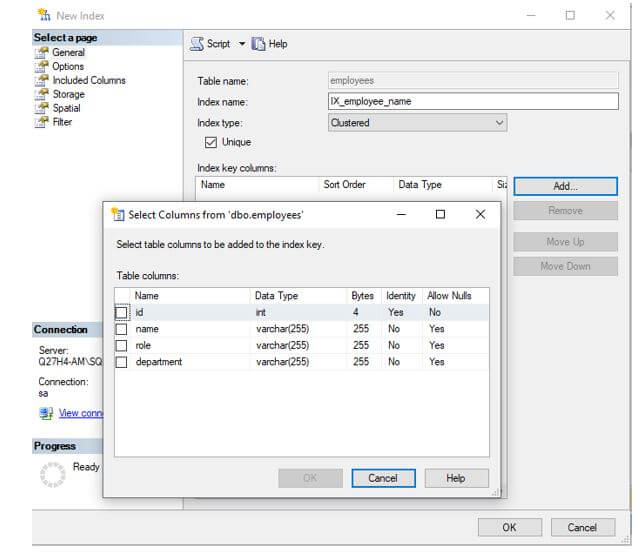
Step 4: Once you have clicked on yes, move to Index Key Columns and Click on Add. A new dialog box will appear as shown below. Tick on the columns based on which you wish to create an index.
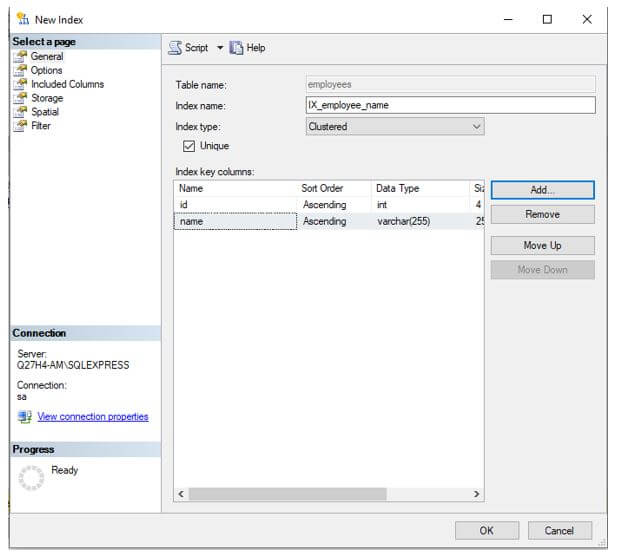
Step 5: Click on Ok and you will see that the desired columns have been added as key columns.
Step 6: Click on Ok and you are good to go.
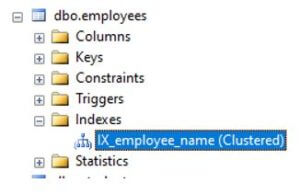
Now, in order to see if the index has been successfully created or not, move to indexes and you will observe the name of the newly created index as shown below.
Example #4
Dropping or deleting a clustered index.
The basic syntax for deleting indexes in SQL Server is as follows:
DROP INDEX table_name.index_name;Here is an example to delete the IX_departments_id index.
Code:
DROP INDEX departments.IX_departments_id;Output:
The IX_departments_id index on the department’s table has been successful.
Conclusion
A clustered index is an index that is created by default on the primary key in the SQL server. It sorts the records in the table based on the primary key and stores data on the disk with the primary key as an index. We can only have one clustered index on a table. If you wish to store data differently then delete the previous index and create a new one.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Clustered Index” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.