Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to Spark Transformations
A transformation is a function that returns a new RDD by modifying the existing RDD(s). The input RDD is not modified as RDDs are immutable. All transformations are executed by Spark in a lazy manner- The results are not computed right away. The computation of the transformations happens only when a certain action is performed on the RDD.
Types of Transformations in Spark
They are broadly categorized into two types:
1. Narrow Transformation: All the data required to compute records in one partition reside in one partition of the parent RDD. It occurs in the case of the following methods:
map(), flatMap(), filter(), sample(), union() etc.
2. Wide Transformation: All the data required to compute records in one partition reside in more than one partition in the parent RDDs. It occurs in the case of the following methods:
distinct(), groupByKey(), reduceByKey(), join() , repartition() etc.
Examples of Spark Transformations
Here we discuss the types of spark transformation with examples mentioned below.
1. Narrow Transformations
Below are the different methods:
1. map()
This function takes a function as a parameter and applies this function to every element of the RDD.
Code:
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("testApp")
val sc= SparkContext.getOrCreate(conf)
sc.setLogLevel("ERROR")
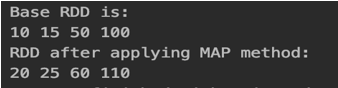
val rdd = sc.parallelize(Array(10,15,50,100))
println("Base RDD is:")
rdd.foreach(x =>print(x+" "))
println()
val rddNew = rdd.map(x => x+10)
println("RDD after applying MAP method:")
rddNew.foreach(x =>print(x+" "))Output:
In the above MAP method, we are adding each element by 10 and that is reflected in the output.
2. FlatMap()
It is similar to map but it can generate multiple output items corresponding to one input item. Thus, the function has to return a sequence instead of single item.
Code:
val conf= new SparkConf().setAppName("test").setMaster("local")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
sc.setLogLevel("WARN")
val rdd= sc.parallelize(Array("1:2:3","4:5:6"))
val rddNew = rdd.flatMap(x =>x.split(":"))
rddNew.foreach(x =>print(x+" "))Output:
This function passed as a parameter splits each input by “:” and returns an array and the FlatMap method flattens out the array.
3. filter()
It takes a function as a parameter and returns all elements of the RDD for which the function returns true.
Code:
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("testApp")
val sc= SparkContext.getOrCreate(conf)
sc.setLogLevel("ERROR")
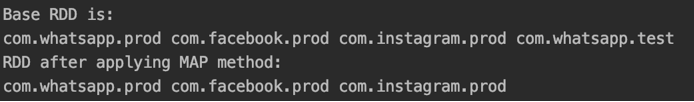
val rdd = sc.parallelize(Array("com.whatsapp.prod","com.facebook.prod","com.instagram.prod","com.whatsapp.test"))
println("Base RDD is:")
rdd.foreach(x =>print(x+" "))
println()
val rddNew = rdd.filter (x => !x.contains("test"))
println("RDD after applying MAP method:")
rddNew.foreach(x =>print(x+" "))Output:
In the above code, we are taking strings that don’t have the word “test”.
4. sample()
It returns a fraction of the data, with or without replacement, using a given random number generator seed (This is optional though).
Code:
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("test").setMaster("local")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
sc.setLogLevel("WARN")
val rdd = sc.parallelize(Array(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,10,11,12,15,20,50))
val rddNew = rdd.sample(false,.5)
rddNew.foreach(x =>print(x+" "))Output:
In the above code, we are getting random samples without replacement.
5. union()
It returns the union of the source RDD and the RDD passed as a parameter.
Code:
val conf= new SparkConf().setAppName("test").setMaster("local")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
sc.setLogLevel("WARN")
val rdd= sc.parallelize(Array(1,2,3,4,5))
val rdd2 = sc.parallelize(Array(-1,-2,-3,-4,-5))
val rddUnion = rdd.union(rdd2)
rddUnion.foreach(x=>print(x+" "))Output:
The resultant RDD rddUnion contains all the elements from rdd and rdd2.
2. Wide Transformations
Below are the different methods:
1. distinct()
This method returns the distinct elements of the RDD.
Code:
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("testApp")
val sc= SparkContext.getOrCreate(conf)
sc.setLogLevel("ERROR")
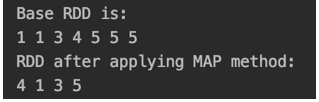
val rdd = sc.parallelize(Array(1,1,3,4,5,5,5))
println("Base RDD is:")
rdd.foreach(x =>print(x+" "))
println()
val rddNew = rdd.distinct()
println("RDD after applying MAP method:")
rddNew.foreach(x =>print(x+" "))Output:
we are getting the distinct element 4,1,3,5 in the output.
2. groupByKey()
This function is applicable to pair-wise RDDs. A pair-wise RDD is one who’s each element is a tuple where the first element is the key and the second element is the value. This function groups together all the values corresponding to a key.
Code:
val conf= new SparkConf().setAppName("test").setMaster("local")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
sc.setLogLevel("WARN")
val rdd= sc.parallelize(Array(("a",1),("b",2),("a",3),("b",10),("a",100)))
val rddNew = rdd.groupByKey()
rddNew.foreach(x =>print(x+" "))Output:
As expected all the values for keys “a” and “b” are grouped together.
3. reduceByKey()
This operation is also applicable to pair-wise RDDs. It aggregates the values for each key according to a supplied reduce method which has to be of the type (v,v) => v.
Code:
val conf= new SparkConf().setAppName("test").setMaster("local")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
sc.setLogLevel("WARN")
val rdd= sc.parallelize(Array(("a",1),("b",2),("a",3),("b",10),("a",100),("c",50)))
val rddNew = rdd.reduceByKey((x,y)=>x+y )
rddNew.foreach(x =>print(x+" "))Output:
In the above case, we are summing up all the values of a key.
4. join()
The join operation is applicable to pair-wise RDDs.The join method combines two datasets based on the key.
Code:
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("testApp")
val sc= SparkContext.getOrCreate(conf)
sc.setLogLevel("ERROR")
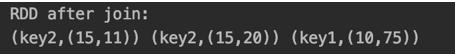
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(Array(("key1",10),("key2",15),("key3",100)))
val rdd2 = sc.parallelize(Array(("key2",11),("key2",20),("key1",75)))
val rddJoined = rdd1.join(rdd2)
println("RDD after join:")
rddJoined.foreach(x =>print(x+" "))Output:
5. repartition()
It reshuffles the data in the RDD randomly into a number of partitions passed as parameters. It can both increase and decrease the partitions.
Code:
val conf= new SparkConf().setAppName("test").setMaster("local")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
sc.setLogLevel("WARN")
val rdd= sc.parallelize(Array(1,2,3,4,5,10,15,18,243,50),10)
println("Partitions before: "+rdd.getNumPartitions)
val rddNew= rdd.repartition(15)
println("Partitions after: "+rddNew.getNumPartitions)Output:
In the above case, we are increasing the partitions from 10 to 15.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Spark Transformations. Here we discuss the introduction and two types of Spark Transformations along with examples and methods. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –