Introduction to Spark Executor
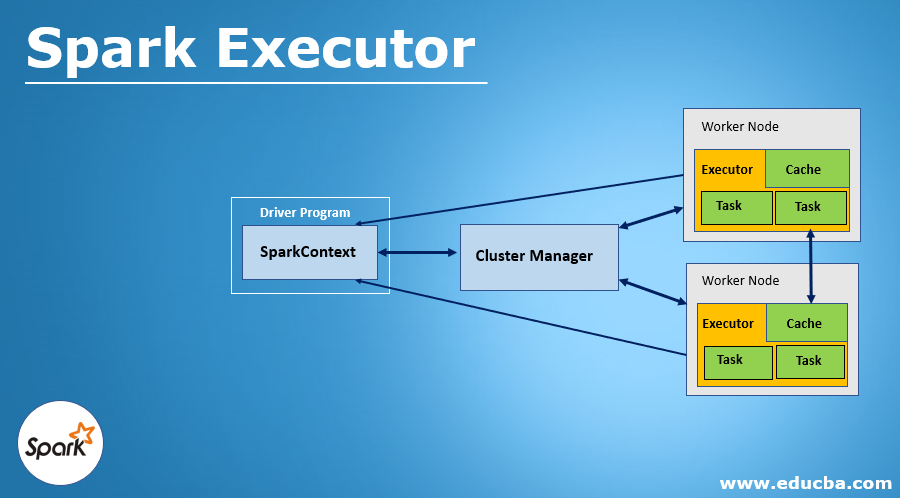
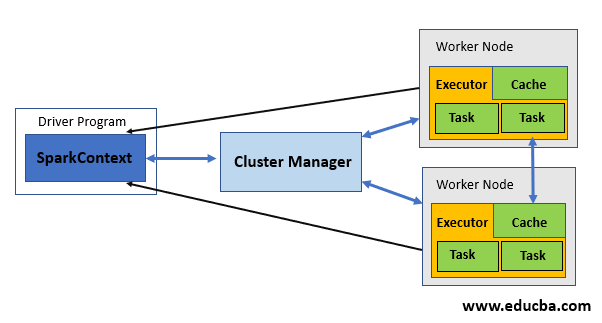
There is a distributing agent called spark executor which is responsible for executing the given tasks. Executors in Spark are the worker nodes that help in running individual tasks by being in charge of a given spark job. These are launched at the beginning of Spark applications, and as soon as the task is run, results are immediately sent to the driver. In-memory the storage provided by executors for Spark RDD and are cached by programs by the user with block manager. Run the application for a complete lifespan, by which executor’s static allocation is inferred.
How Apache Spark Executor Works?
The executor starts over an application every time it gets an event. Spark on YARN is used while using this executor and this is generally not compatible with Mesos. Using Spark executor can be done in any way like in start running applications of Sparkafter MapR FS, Hadoop FS, or Amazon S# destination close files. Each time the Hadoop FS destination closes a file, the spark application each time, can convert Arvo files into Parquet. In an external system, the Spark application is started. It does not wait for the monitoring application nor complete. Additional processing is done after submitting the application successfully.
Client or cluster mode can be used to run an application by it. But Client mode is used only when the use of resources is not a deal to be considered. Make sure you perform the task prerequisite before using the Spark executor. The number of worker nodes has to be specified before configuring the executor. Enabling dynamic memory allocation can also be an option by specifying the maximum and a minimum number of nodes needed within the range. Also, by specifying the minimum amount of memory required, used by executor and application driver one can pass additional cluster manager properties to it.
Specify the custom Java home and Spark directories and a proxy user of Hadoop and also the Kerberos credentials. Language can be specified which is used to write applications and then the properties as per specific language defined. Executors can generate the events for a variant event stream which can also be configured.
Conditions in creating a Spark Executor
When the message – RegisteredExecutor is received, by coarseGrainedExecutorBackend. And this happens only in YARN.
When the registration of MesosExecutorBackend in Mesos in Spark.
For local mode, a local endpoint will be created.
Code:
at org.apache.spark. SparkContext$Sanonfun$assertNoOtherContextIsRunning$2.appl Que
at org.apache.spark.SparkContext anonfun$assertNoOtherContextIsRunning$2.apply(SparkContext.scala:245
at scala.Option.foreach
at org.apache.spark.SparkContext.assertNoOtherContext IsRunning
at org.apache.spark.SparkContext.mark Partially Constructed
at org.apache.spark. SparkContext.<init>
scala
sc.stop
val conf = new SparkConf.
setAppName("testing").
setMaster("yarn").
set("spark.executor.instances", "2") conf: org.apache.spark.SparkConf - org.apache.spark. SparkConfe69d7b1f9
val sc = new SparkContext(conf) sc: org.apache.spark. SparkContext - org.apache.spark. SparkContext e31b4e1
sc.stop
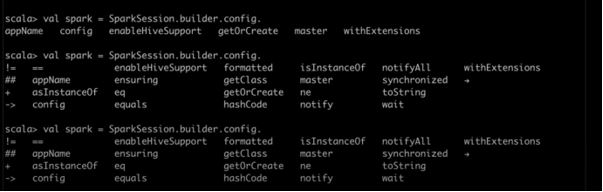
scala import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession SparkSession SparkSession Extensions
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
scala val spark Spark SparkConf SparkContext SparkSession
scala val spark SparkSession.
Builder clearActiveSession getactiveSession builder clear Default Session getDefault Session
spark = SparkSession.builder.
appName config enableHiveSupport getorCreate
val spark
SparkSession.builder. // hit tab
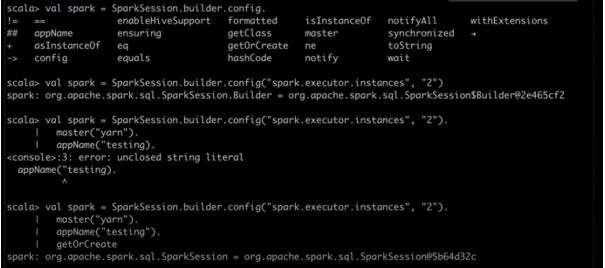
val spark = SparkSession.builder.config("spark.executor.instances", "2".
master("yarn").
appName("testing).
val spark = SparkSession.builder.config("spark.executor.instances", "2").
master("yarn").
appName("testing").
getOrCreate
Output:
Advantages and uses to be noted about Apache Executor in Spark
1. Every application has its own process of execution while the application is running in a task of multiple threads.
2. To the underlying cluster manager, the spark executor is agnostic. meaning as long as the process is done, communication with each other is done.
3. Acceptance of incoming connections from all the other executors.
4. The executor should run closer to the worker nodes because the driver schedules tasks on the cluster. These can be preferably run in the same local area network.
Conclusion
We have seen the concept of Spark Executor of Apache Spark. I also saw key points to be remembered and how executors are helpful in executing the tasks. And as a conclusion, it can be said that the Spark executors in Apache Spark can enhance the performance of the system.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Spark Executor. Here we discuss an introduction to Spark Executor, how does it work, conditions, advantages, and uses. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –