Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction to Scikit Learn LDA
The following article provides an outline for Scikit Learn LDA. It is nothing but a linear discriminant analysis, the classifier by using linear decision boundary generated by fitting densities of class conditional for the data by using the Bayes rule. The model fits into the Gaussian density for every class, assuming that all classes share the covariance matrix. The fitted model also reduces the input projecting dimensionality for the most discriminative transformations.
Key Takeaways
- The scikit learn linear discriminant analysis tries to reduce the dimensions of the feature, and it is set while retaining the information that discriminates the output classes.
- It is finding the boundary of decisions around the cluster class of projects.
What is Scikit Learn LDA?
The scikit learn linear discriminant analysis is a linear classification of the machine learning algorithm. This algorithm involves developing a probabilistic model, which was classified by calculating the conditional probability of belonging to every class selected by the highest probability. It is a straightforward and probabilistic classification model that makes solid assumptions about the distribution of input variables; using this will violate compelling predictions.
A linear discriminant analysis algorithm is used to discover the topics present in the corpus. Multiple open-source libraries exist but suppose we are using python; the main one is genism. It is a handy library and scales well on large corpora. This is not including the matrix factorization; it is used to find the topics in the text. The NMF is different from the lda. The lda algorithm is based on probabilistic graphical modelling.
How to Create Scikit Learn LDA?
A linear discriminant analysis algorithm is an unsupervised machine learning used in topic modelling in natural language processing tasks. It is also a critical model to do this task; this algorithm is straightforward to understand.
Below steps shows how we can create the scikit learn lda as follows:
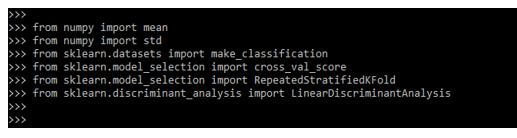
1. At the time of creating it, in the first step, we need to import the libraries as follows.
Code:
from numpy import mean
from numpy import std
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedStratifiedKFold
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysisOutput:
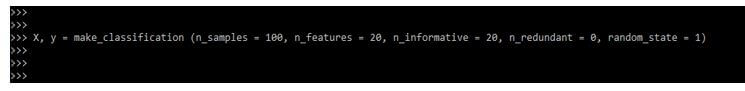
2. After importing the libraries and modules in this step, we define the dataset. We are representing the x and y datasets as follows.
Code:
X, y = make_classification (n_samples = 100, n_features = 20, n_informative = 20, n_redundant = 0, random_state = 1)Output:
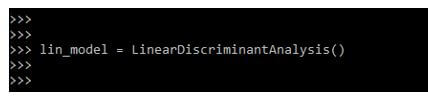
3. After defining the dataset now, we limit the model. We are defining the linear discriminant analysis model as follows.
Code:
lin_model = LinearDiscriminantAnalysis()Output:
4. After defining the linear discriminant analysis model, now, in this step, we are limiting the model evaluation method as follows. We are defining the k-fold method as follows.
Code:
lin_method = RepeatedStratifiedKFold (n_splits = 20, n_repeats = 3, random_state = 1)Output:
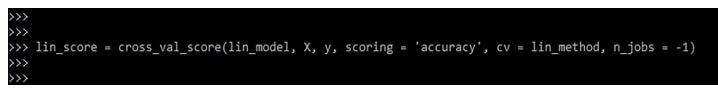
5. After defining the model evaluation method in this step, we evaluate the model; at the time of assessing the model, we give the variable name lin_score as follows.
Code:
lin_score = cross_val_score(lin_model, X, y, scoring = 'accuracy', cv = lin_method, n_jobs = -1)Output:
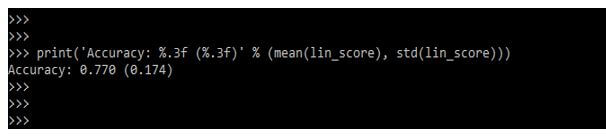
6. After evaluating the model in this step, we summarize the result of the accuracy matrix as follows.
Code:
print ('Accuracy: %.3f (%.3f)' % (mean(lin_score), std(lin_score)))Output:
How does Scikit Learn LDA Work?
The library of scikit contains built-in classes that perform LDA onto the dataset LDA will iterate each word and contain the best features. The main idea of lda is documented word combinations. Lda will use the two probabilities first probability is nothing but the phrase document assigned to the topic. The second topic is the assignment of the topic to all documents.
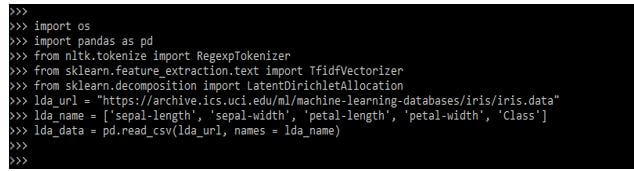
In the below example, we are loading the data from a csv file; we are using the age column from the csv file as follows:
Code:
import os
import pandas as pd
from nltk.tokenize import RegexpTokenizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.decomposition import LatentDirichletAllocation
lda_url = " "
lda_name = ['sepal-length', …., 'Class']
lda_data = pd.read_csv(lda_url, names = lda_name)Output:
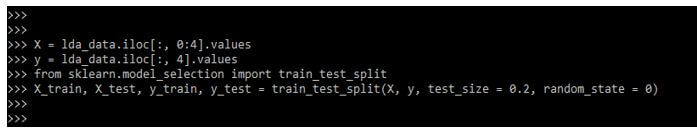
After loading the dataset, in the example below, we divide the dataset into features corresponding to the label and divide the datasets as follows.
Code:
X = lda_data.iloc [:, 0:4].values
y = lda_data.iloc [:, 4].values
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split()Output:
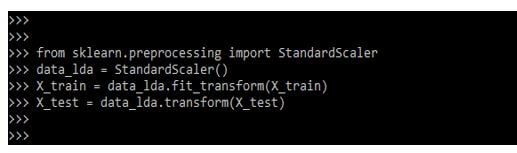
In the below example, we are defining the feature scaling; we are performing the feature scaling of lda as follows.
Code:
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
data_lda = StandardScaler()
X_train = data_lda.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = data_lda.transform(X_test)Output:
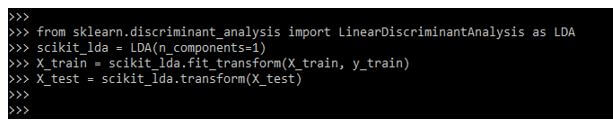
In the below example, we are performing the lda; the discriminant analysis library is used to perform the LDA.
Code:
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis as LDA
scikit_lda = LDA (n_components = 1)
X_train = scikit_lda.fit_transform(X_train, y_train)
X_test = scikit_lda.transform(X_test)Output:
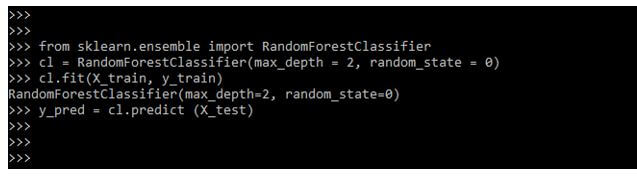
In the below example, we are making the predictions to define it and define the classifier as follows.
Code:
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
cl = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth = 2, random_state = 0)
cl.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = cl.predict (X_test)Output:
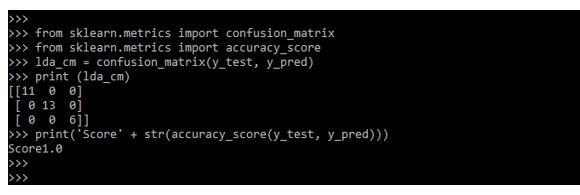
After defining the predictions in the below example, we are evaluating the performance of the scikit learn lda algorithm as follows.
Code:
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
lda_cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
print (lda_cm)
print('Score' + str(accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)))Output:
Examples of Scikit Learn LDA
Different examples are mentioned below:
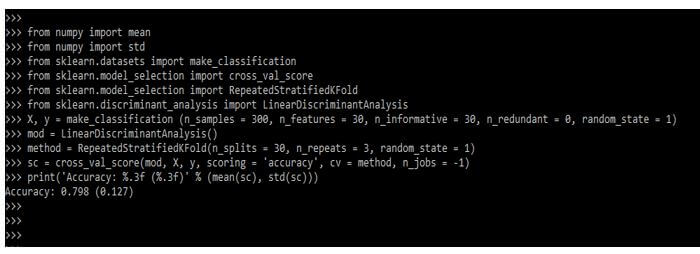
Example #1
The below example shows the scikit learn LDA algorithm as follows. In the below sample, we are predicting the accuracy as follows.
Code:
from numpy import mean
from numpy import std
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedStratifiedKFold
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
X, y = make_classification()
mod = LinearDiscriminantAnalysis()
method = RepeatedStratifiedKFold()
sc = cross_val_score(mod, X, y, scoring = 'accuracy', cv = method, n_jobs = -1)
print ('Accuracy: %.3f (%.3f)' % (mean(sc), std(sc)))Output:
Example #2
In the below example, we are using url as follows.
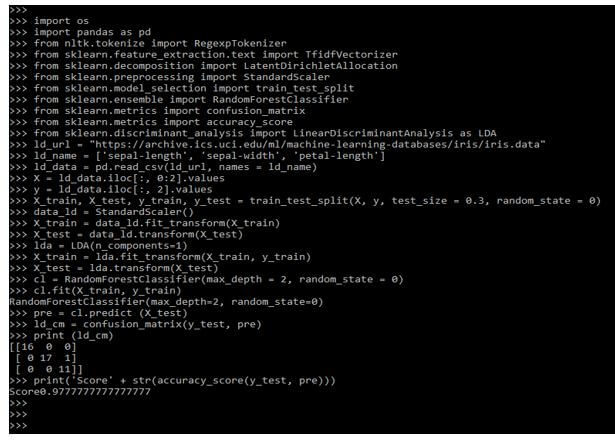
Code:
import os
import pandas as pd
ld_url = " "
ld_name = []
ld_data = pd.read_csv(ld_url, names = ld_name)
X = ld_data.iloc[:, 0:2].values
y = ld_data.iloc[:, 2].values
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split()
data_ld = StandardScaler()
X_train = data_ld.fit_transform (X_train)
X_test = data_ld.transform (X_test)
lda = LDA(n_components=1)
X_train = lda.fit_transform (X_train, y_train)
X_test = lda.transform (X_test)
cl = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth = 2, random_state = 0)
cl.fit(X_train, y_train)
pre = cl.predict (X_test)
ld_cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, pre)
print (ld_cm)
print('Score' + str(accuracy_score(y_test, pre)))Output:
FAQ
Other FAQs are mentioned below:
Q1. What is the use of scikit to learn LDA in python?
Answer:
The fitted model is used to reduce the dimensionality of the input by projecting the discriminative directions.
Q2. Which libraries are we using when working with scikit learn LDA?
Answer:
We use numpy, pandas, sklearn and tokenize library when working with scikit learn lda in python.
Q3. What is the difference between PCA and LDA in scikit learn in python?
Answer:
The PCA and LDA both are techniques of linear transformation. PCA is unsupervised, while LDA is a supervised technique.
Conclusion
The scikit learn linear discriminant analysis is a linear classification of the machine learning algorithm. Scikit learn lda is nothing but a linear discriminant analysis. Using the Bayes rule, the classifier uses the linear decision boundary generated by fitting class conditional densities for the data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Scikit Learn LDA. Here we discuss the introduction, working, examples, and steps to create scikit learn LDA with FAQ. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –