Updated April 4, 2023
Introduction to RUP Methodology
RUP stands for Rational Unified Process. It is a popular and effective object-oriented software development process. RUP methodology is modified at Rational software and is widely practiced and adopted by various industries. RUP methodology can be a lightweight process that addresses the requirements of small projects to a more comprehensive process addressing the needs of large projects. As it performs early and continuous documentation of the urgent and probable risks by proper planning and keeping follow up, it helps in migrating the risks at early phases of software development. This methodology uses visualization methods like UML to build the models graphically to understand and ease the system’s complexity. For designing test cases, this methodology uses use cases.
Phases of RUP methodology
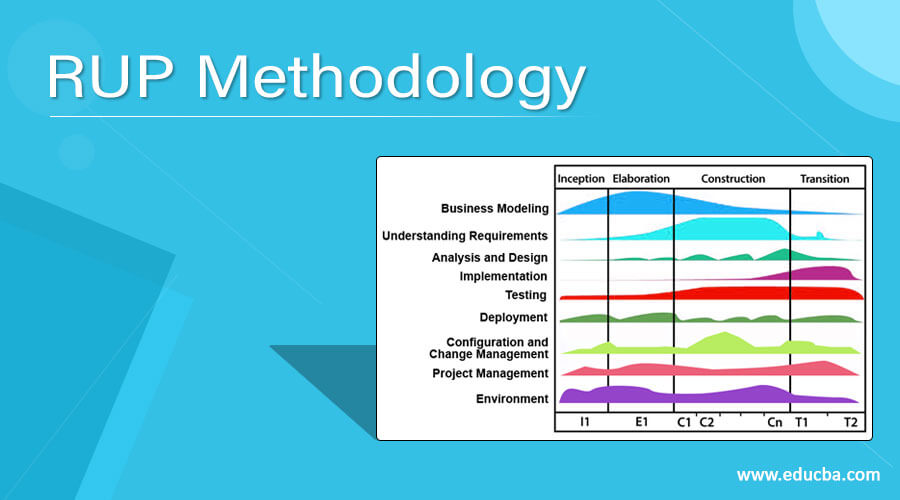
There are four phases involved in RUP – Inception, Elaboration, Construction, and Transition. Let’s discuss these phases one by one in detail.
- Inception: In the inception phase, the project is proposed. This phase aims to design a business model such as defining the problem, the system’s scope, initiating the project, etc. The objective of the project is stated so that the requirements of every stakeholder can be considered. Then scope and boundary conditions, entry-exit criteria, and other requirements are established. External entities with which the system will interact are identified. It also includes identifying the business cases, such as identifying the success criteria, risk, and estimation of the resources needed, and phase plan showing dates of major milestones. Then the working of the project starts. Use case model is 10% to 20% is complete.
- Elaboration: Elaborate means refinement. This phase aims to perform a detailed analysis of the problem. It constitutes of requirements, analysis, and design phases. It eliminates the highest risk elements of the project. Use case model is 80% complete. Additional requirements in this phase capture the nonfunctional requirements. It also captures the requirements that are not related to the specific use case. An executable architecture model is developed. The development plan for the whole project, including iterations and evaluation criteria for each iteration, also specifying the process to be used.
- Construction: In this phase, the manufacturing process is built. It constitutes implementation, i.e. detailed design and construction of source code. This phase aims to emphasize the resources and control the operations to optimize the costs, schedules, and quality. This phase is broken down into several iterations. During this phase, all remaining components and application features are developed. Then all these features are integrated into the product and tested as a whole system.
- Transition: In this phase, the product is delivered to end-users. It constitutes development, i.e. delivery of the system to the user community. It also involves issues related to marketing, packaging, user community, installation, etc. It performs beta testing to validate whether the new system meets the user’s requirements or not. The system run in parallel with the legacy system that it is replacing. It rolls out the product to the marketing, distribution, and sales team.
Advantages and disadvantages of RUP methodology
The advantages of the RUP methodology are as follows.
- Its main focus is on the software product itself and its quality.
- RUP does not pit the strong focus on the documentation.
- RUP emphasizes addressing high risks at the early stage of development.
- It does not assume a fixed set of firm requirements at the inception of the product but allows refining the requirements as the product evolves.
The disadvantages of the RUP methodology are as follows.
- RUP methodology fails to provide any clear implementation guidelines.
- IT leaves the tailoring entirely to the user.
- RUP methodology is not considered particularly agile, but recent studies have shown that by adopting the right essential artifacts, RUP is agile.
Workflows of RUP methodology
There are 9 workflows of RUP methodology in which 6 are core process, and 3 are supporting the process.
- Business modeling
- Understanding requirements
- Analysis and design
- Implementation
- Testing
- Deployment
- Configuration and change management
- Project management
- Environment
Six best practices
RUP methodology is built on six best practices which are as follows
- Develop iteratively: Software must be developed in small increment and short iteration
- Manage requirements: It allows accommodating requirements changes in the system development strategy.
- Use component architecture: It focuses on the early development and design of independent executable modules.
- Model Visually: Models that are used must be built using visualization methods like UML.
- Verify quality: Software’s quality is maintained by performing testing frequently.
- Control changes: Any changes occurred to requirements must be managed, and their effect on software should be tracked.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to RUP Methodology. Here we discuss Rational Unified Process, the various phases involved in it, and its advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –