Updated July 17, 2023
Round-Tripping Meaning
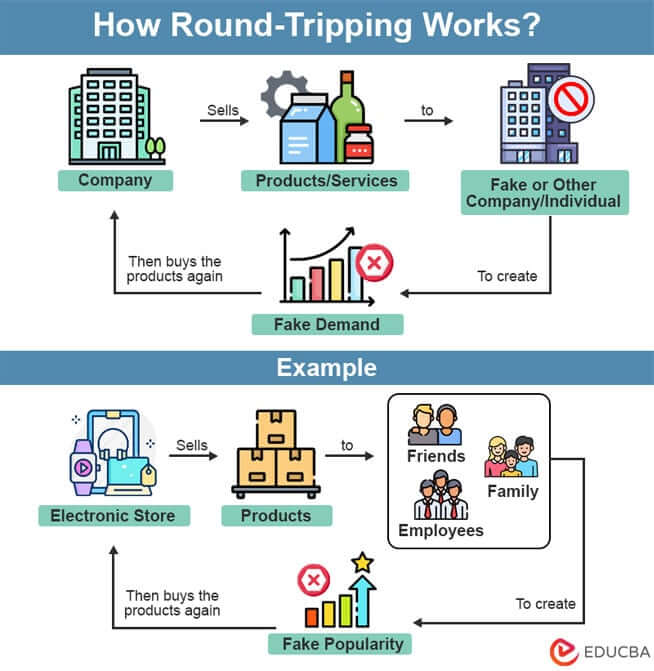
Round-tripping is when a company uses fake transactions, i.e., fake buying and selling of products/services, to show they have higher sales and their product is in demand. The main company does this by either creating a subsidiary or a fake company or working with another company they know.
Here, the main company sells its products/services to these other companies in exchange for money and records the transaction in its accounting books. However, later on, they get back their products and return the money. It means the transaction never actually happened, but they have proof (recorded transaction) to show that their company is successful and popular.
For example, imagine you open a new electronic store in a competitive area. To promote your business and attract more customers, you ask your friends, family, and employees to buy your products. This makes your store look popular, leading to more actual customers buying from your store. However, you give your friends their money back, and they return the product. So there was no actual sale, but you made customers believe that your shop is famous. This is how round-tripping works.
Table of Contents
Why Do Companies Use Round-Tripping?
Round-tripping transactions create an illusion of high trade activities without a real impact on the financial outcomes (net income or earnings). Here are some reasons why companies use this practice:
- Report more transactions than competitors to increase popularity in the market and show that the company is growing faster than its competitors.
- Attract investors by showing fake financial statements with increased sales and revenue.
- Avoid taxes by sending money or products to shell (fake) companies present in some other countries.
- Convert black money into legal money by dividing it among different investors who will invest the same money in the company through legal ways like shares, etc.
Round-Tripping Examples
Example #1: Round-Tripping for Tax Evasion
A company based in Australia wants to avoid paying taxes, so they create a fake company in Hong Kong, where taxes are very low. The company sends $10 million of its profits to a fake company in Hong Kong, proving that it has invested in a foreign business.
Then, they return the $10 million to Australia’s business and show it as a genuine company that has invested in their business. By doing this, they deceive the tax authorities in Australia into thinking they made less profit and manage to avoid paying a significant amount of taxes.
Example #2: Round-Tripping through Assets
A technology company in Silicon Valley wants to create a fake asset sale transaction. It has a subsidiary company in New York, so the main company of Silicon Valley will sell a piece of equipment for $25 million to this subsidiary. The company can skip sending the equipment to the New York company because it can just mention the transactions in the accounts. Later the main company will purchase the equipment back at the same amount. Therefore, the accounts will show physical proof of sale and purchase transactions without the actual sale of the equipment.
Features
Some of the main characteristic features of round-tripping transactions are as follows:
1. No Extra Taxes: Although there is a constant exchange of money and product, there is no actual profit. Therefore, the company won’t have to pay any extra tax.
2. No Real Impact: The fake transactions just circulate the money but don’t generate any real income for the company.
3. Unethical Practice: Showing false transactions to show a fake profit is a dishonest practice. It tricks people into thinking there are continuous buying and selling transactions, even if it’s not true.
4. Possible Legal Problems: Although it’s not illegal if someone uses it to launder money or avoid taxes, there can be an investigation, and authorities can take legal action.
5. Incorrect Economic Information: When companies record huge amounts of fake transactions, the income information and transaction history can be misleading.
6. Company’s Reputation: It can damage the company’s reputation and existing customers’ trust and push their sales lower than before.
7. Market Fluctuations: Recording false transactions with large amounts of money can make the markets unstable and unpredictable due to no actual financial gain.
8. Focusing on Short-Term Gains: Continuous buying and selling will show the company’s popularity in the short term, but the company will ignore real investments and actual growth.
Q2. What is not an example of a round-tripping?
Answer: Although round-tripping is usually about creating fake transactions, not all transactions fall into this category. For instance, you buy 20 company shares for $5 per share and sell them later when the stock price increases, making a profit. It is a genuine transaction because the purpose here is to make a profit, which is different from round-tripping.
Q3. Is round-tripping illegal?
Answer: Round-tripping that involves money laundering and tax evasion is illegal. The guilty person may have to pay fines or even face prison charges. The consequences depend on the intensity of the fraud under laws like the Money Laundering Control Act and the Internal Revenue Service.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to what round-tripping is. Here, we mention its definition, features, reasons, and advantages and disadvantages. We have also added a real-life example for your understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –