Updated October 19, 2023
Introduction to Risk Management Process
The Risk Management Process is a systematic approach to defining and controlling risks. This process involves a series of methods and techniques that provide a reasonable defense mechanism against potential risks that an organization may face.
Risk Management training can be defined as a set of actions integrated into a company organization’s broader context. These actions are directed toward assessing and measuring possible risk management techniques.
Understanding the Risk Management Process
Every organization has a mission and a vision for its formation, and it must address the problem of protecting itself against potential risks that can harm the whole organization. In the past, companies faced different types of threats in a specific or unconnected manner. However, today, organizations elaborate on the risk management strategies necessary for managing these risks. Company risks are typically classified into three broad categories:
1. Risks inherent to the external context
- The emergence of unfavorable laws and regulations
- Significant changes in market conditions
- Technological innovations that favor competitors
2. Risks inherent to operative management
- Noncompliance with contractual requirements
- Possible loss of market share
- Possible loss of skills
- Possibility of physical damage to personnel
- Possible environmental pollution
3. Risks inherent to financial management
- Difficulty in collecting accounts receivables
- Unfavorable changes in exchange rates
- Imbalances in liquidity
Each risk management process may lead to direct or indirect damage to the organization, with economic implications in the short, medium, and long term. From this perspective, therefore, the attention given to Risk Management techniques, in terms of the quality and quantity of allocated resources, must be consistent. This not only applies to the type of risk management strategies but also to the potential negative event that could occur and the gravity of its consequences.
A complete risk management process aims to protect:
# Value already created by the organization
# Future opportunities
Phases of Risk Management Process
The Risk Management process is closely interconnected, so it cannot be handled in a fragmented manner. It is also not a task that can be assigned to a single department of an organization. A dedicated process that requires a structured organization and effective communication mechanisms is necessary. Traditionally, the phases of a Risk Management process are as follows:
- Context Definition
- Identification of Risks
- Risk Assessment
- Risk Control
- Communication
- Planning
- Checking and Supervision
- Process Review
Each phase must be fully integrated within the company organization to be effective.
1. Context Definition
Context definition emphasizes the following essential points:
- The first and foremost thing is to identify the areas of risk. Risks may arise due to a specific combination of market, product or service, manufacturing or distribution process, and other external factors.
- The next thing is to identify and define an assessment activity schedule.
- Based on that, organizing resources and defining duties and responsibilities becomes necessary.
2. Identification of Risks
The next phase of the Risk Management process is the Risk Identification Process. It is important to identify the potential risks and give their detailed description. Hence, all possible sources of risk management training, such as the stakeholders’ positions, market changes, manufacturing errors, or work accidents, should be thoroughly analyzed. The process of identifying potential risk management techniques must include the following:
- Objectives that the organization has set.
- Scenarios that the organization may face in carrying out its business.
- Procedures that the organization adopts for its management and operational purposes.
Effective risk identification finally requires the support of reasonable confirmations that state whether the risk analysis has been correct or not. These confirmations may be:
- A confirmation stating that the event has already occurred (Direct proof).
- A confirmation stating that the event has already happened in a similar situation. (Indirect evidence).
- A confirmation stating the cause-effect relationships stressing the probability of the event. (Deductive nature)
In this way, a “risk profile” is outlined specifically for each organization.
3. Risk Assessment
When risks have been identified, they must be assessed based on the following parameters:
- The probability of the adverse event occurring.
- The seriousness of the direct or indirect consequences of the event.
The assessment in such cases largely depends on the following:
- The criticality of the situation
- The relevance and availability of statistical data
- Confirmed analysis procedures.
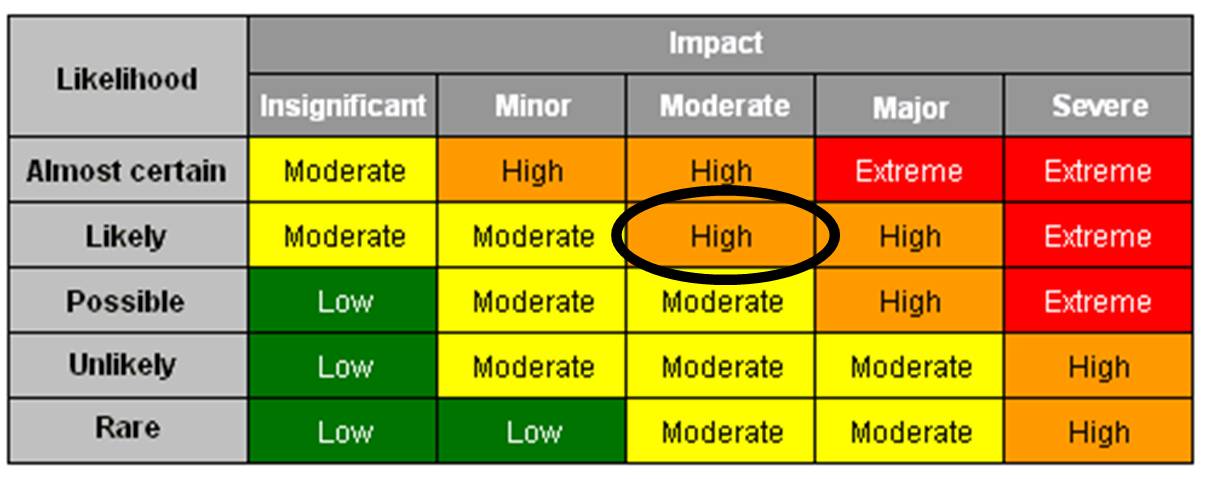
Another important aspect of this step in the risk management process is to assess the risk level, which helps develop an action plan for managing that specific risk.
| Extreme / High-Risk | Danger. Immediate action is required in this type of risk. Identify and implement controls to reduce the risk to as low as reasonably practical. The rules can be temporary or permanent. |
|---|---|
| Medium Risk | Moderate danger. Implement controls to reduce the risk to as low as reasonably practical as soon as possible. Actions can be for the short or long term. |
| Low Risk | Ranging from minor to negligible danger. Assess if further action can be taken. Steps should be taken to monitor the controls so that the hazard is maintained as “low” (if the risk cannot be eliminated). |
# Likelihood Scale
| Level | Likelihood | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | Very likely | It happens more than once a year in this industry |
| 3 | Likely | It happens about once a year in this industry |
| 2 | Unlikely | It happens every ten years or more in this industry |
| 1 | Very unlikely | It only happened once in this industry |
# Consequence scale
| Level | Consequence | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | Severe | Financial losses are greater than $50,000 |
| 3 | High | Financial losses between $10,000 and $50,000 |
| 2 | Moderate | Financial losses between $ 1,000 and $10,000 |
| 1 | Low | Economic losses are less than $1000 |
The following formula helps calculate risk rating:
For example, one may decide the likelihood of a fire is ‘unlikely’ (a score of 2), but the consequences are ‘severe’ (a score of 4). Then using the tables above, a fire has a risk rating of 8 (i.e., 2 × 4 = 8).
# Risk rating table
| Risk rating | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 12-16 | Severe | Needs immediate corrective action |
| 8-12 | High | Needs disciplinary action within one month |
| 4-8 | Moderate | Needs disciplinary action within three months |
| 1-4 | Low | Does not currently require corrective action |
Example: Crack in the Pathway of a company’s main office
The assessor rates the likelihood of the hazard as high (likely). This is because the pathway is frequently used by employees and visitors daily, making it highly probable that someone will be exposed to the hazard. The assessor also rates the consequences of a trip in this section of the pathway as moderate, with a sprain or break as the worst-case scenario. Therefore, the risk management process rating for this particular hazard was highly assessed.
In risk evaluation, one should consider the following:
- The importance of the activity to the business
- The amount of control one has over the risk
- Potential losses to the business
- Any benefits or opportunities presented by the threat.
4. Risk Control
In this phase of the risk management process, the decision-making process becomes particularly important. It includes one or more of the following conditions:
- Transfer of the risk
- Exclusion of the risk
- Reduction of the risk
- Acceptance of the risk or a certain amount of the risk
The option chosen from the above conditions will depend on the specific company situation. It should consider cost-benefit analysis, emphasizing quantitative aspects over short, medium, and long-term periods.
Risk transfer
Here, the company transfers the risk to another party willing to accept it. This generally includes insurance companies that offer risk management techniques. However, threats such as those of criminal liability cannot be transferred.
Risk exclusion
This condition involves the non-execution of activity with an unacceptable risk that cannot be transferred. Naturally, this results in a loss of opportunity that the action at-risk management training would have represented.
Risk reduction
Risk reduction considers managerial, technological, and behavioral actions that lower the probability of risk, thereby reducing the seriousness of its consequences.
Acceptance of an amount of the risk
Some risks that cannot be transferred or excluded are accepted. Acceptance applies when the threat has:
- A low probability of occurrence
- Consequences of little relevance
- Great benefits if successful
5. Communication
Communication of risks is another crucial step in the risk management process. In this step, the following aspects must be appropriately documented in detail in a Risk Management Report:
Communication of risk is another crucial step in the risk management process. In this step, the following things must be appropriately documented in detail in a Risk Management Report:
- The profile
- The matrix
- The risk treatment
- The control planning
The above aspects must be presented to all personnel who are involved in any way. Targeted training courses should be developed if necessary, making the Risk Management Report an effective management instrument. The Risk Management Report establishes the reference document for the entire Risk Management process.
6. Planning
The Planning step defines the risk control methods that are:
- Interpretation, transmission, or storage of incoming data for the control process
- Appropriate level and localization for the decisions and actions of the operational procedures and practices
- Control instruments
- Interpretation, transmission, or storage of output data from the control process.
The planning activity is documented in the Risk Management Strategies Plan. As the planning step is mainly directed toward coordinating all activities and their communication, it is recommended that the position of Risk Manager be created.
7. Checking and Supervision
One-time planning is not enough in the risk management process. It is essential that checking and supervision are carried out from time to time. The results of checking and maintenance must always be documented, evaluated, and recorded.
8. Process Review
The Risk Management Process is not one-time but dynamic. That is why it must be reviewed frequently enough. It should be based on experience gathered directly (within the organization) or indirectly (outside the organization). The purpose of such an activity should be:
- Evaluating possible evolutions that concern any phase of the process
- Assess the efficiency and effectiveness of the adopted Risk Management Plan
- Evaluation of the results of checking and supervision.
If revisions are made, another Risk Management Process Report must be created and updated concerning the changes made.
Conclusion
The Risk Management Process is crucial for any organization to identify, assess, and manage risks systematically. The three broad categories of company risks are inherent to external context, operative management, and financial management, which can cause damage with economic implications. There are 8 phases of the Risk Management process must be integrated within the company organization for effectiveness.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further related articles for expanding understanding: