Updated July 12, 2023
What is Return on Average Equity?
The term “return on average equity” or ROAE refers to the performance metric that assesses the ability of a company to generate a profit on the basis of the capital investment made by the company’s shareholders in the form of equity.
In other words, ROAE measures the dollar profit yielded by each dollar of the shareholder’s equity during a certain period of time, usually a year. The calculation of ROAE uses average shareholder’s equity, which is the average of the equity value at the start and the end of the year. As such, it mitigates the impact of a sudden change in the equity value during the year.
ROAE is a very important metric for investors as it can be used for either peer or industry benchmarking. Typically, a company with a higher ROAE than its peers is considered a more favorable investment option. Further, ROAE gives you a peek into a company’s operational and financial management capability and ability to grow business by leveraging its capital structure.
Formula
The formula for return on average equity can be derived as net income divided by average shareholder’s equity which is then expressed in percentage. Mathematically, it is represented as,
Please note that the average shareholder’s equity is the average value of the equity at the start and end of the period.
Examples of Return on Average Equity (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of Return on Average Equity in a better manner.
Example #1
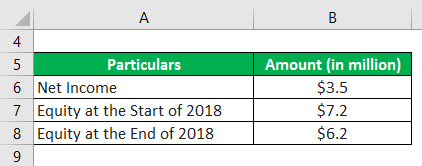
Let us take the example of a company named DFG Inc., which is a multi-tied agent and broker for various insurance products. During 2018, the company clocked revenue of $55.2 million and booked a net income of $3.5 million. Also, the company’s equity at the start of 2018 was $6.2 million, and it infused equity of $1.0 million during the year to end up with total equity of $7.2 million. Calculate the ROAE of DFG Inc. based on the given information.
Solution:
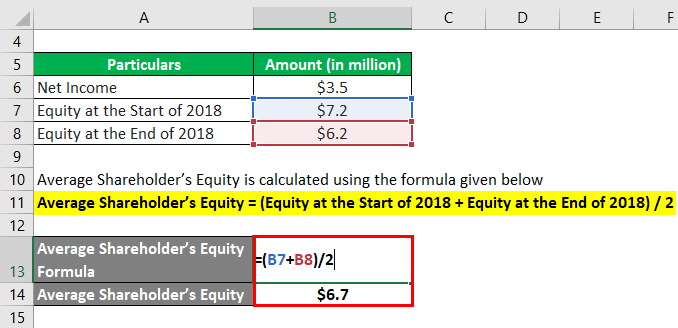
Average Shareholder’s Equity calculate using the formula given below
Average Shareholder’s Equity = (Equity at the Start of 2018 + Equity at the End of 2018) / 2
- Average Shareholder’s Equity = ($6.2 million + $7.2 million) / 2
- Average Shareholder’s Equity = $6.7 million
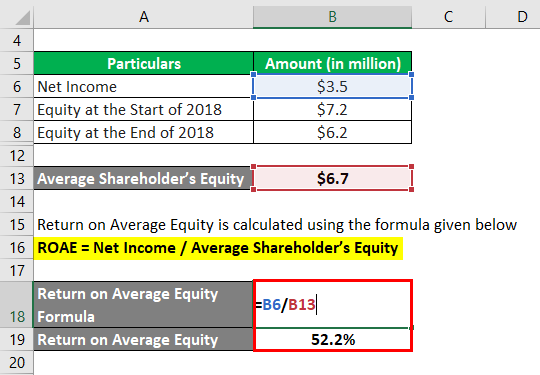
Return on Average Equity calculate using the formula given below
ROAE = Net Income / Average Shareholder’s Equity
- ROAE = $3.5 million / $6.7 million
- ROAE = 52.2%
Therefore, DFG Inc. generated ROAE at 52.2% during the year 2018.
Example #2
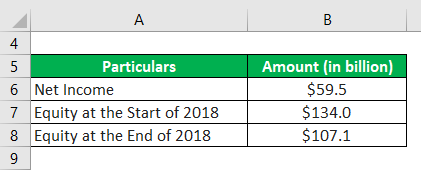
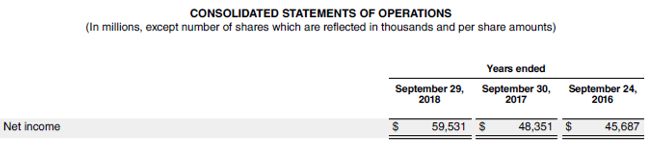
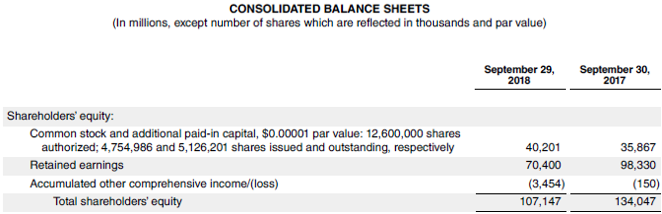
Now, let us take the example of Apple Inc. to demonstrate ROAE calculation. During 2018, Apple registered a net income of $59.5 billion, while its shareholder’s equity at the start of the year was $134.0 billion, reduced to $107.1 billion by the end of the year. Calculate Apple Inc.’s ROAE for the year based on the given information.
Solution:
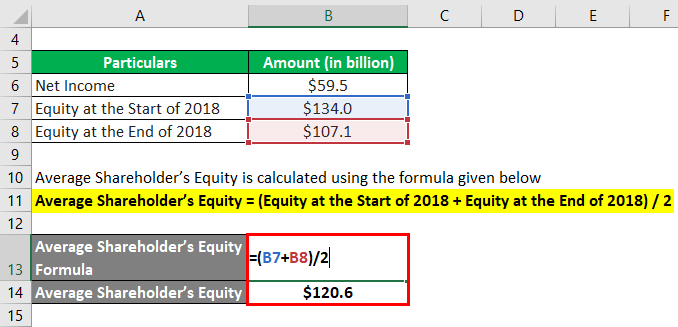
Average Shareholder’s Equity calculate using the formula given below
Average Shareholder’s Equity = (Equity at the Start of 2018 + Equity at the End of 2018) / 2
- Average Shareholder’s Equity = ($134.0 billion + $107.1 billion) / 2
- Average Shareholder’s Equity = $120.6 billion
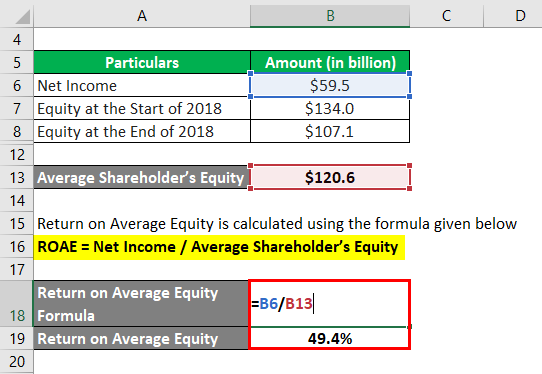
Return on Average Equity calculate using the formula given below
ROAE = Net Income / Average Shareholder’s Equity
- ROAE = $59.5 billion / $120.6 billion
- ROAE = 49.4%
Therefore, Apple Inc. generated ROAE at 49.4% in 2018.
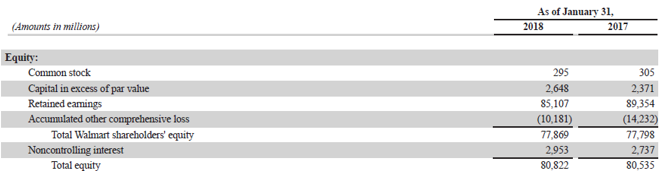
Screenshot of the income statement/ balance sheet used for calculation.
Source: Walmart Annual Reports (Investor Relations)
Example #3
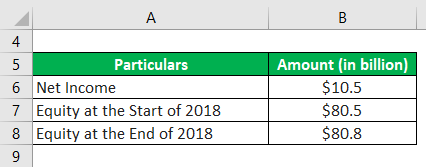
Now, let us take the example of Walmart Inc. According to its 2018 annual report, the company booked a net income of $10.5 billion, while its shareholder’s equity value was $80.5 billion at the start of the year, which ended up at $80.8 billion by the end of the year. Calculate Walmart Inc.’s ROAE for the year based on the given information.
Solution:
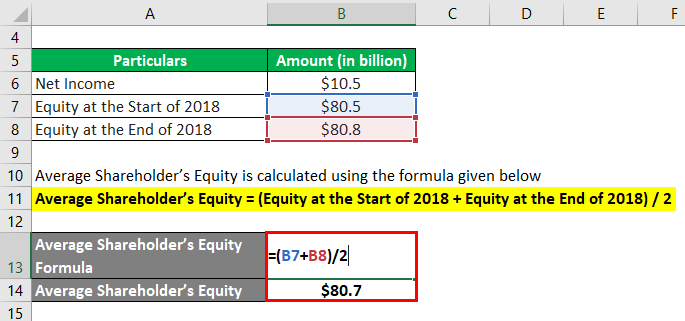
Average Shareholder’s Equity calculate using the formula given below
Average Shareholder’s Equity = (Equity at the Start of 2018 + Equity at the End of 2018) / 2
- Average Shareholder’s Equity = ($80.5 billion + $80.8 billion) / 2
- Average Shareholder’s Equity = $80.7 billion
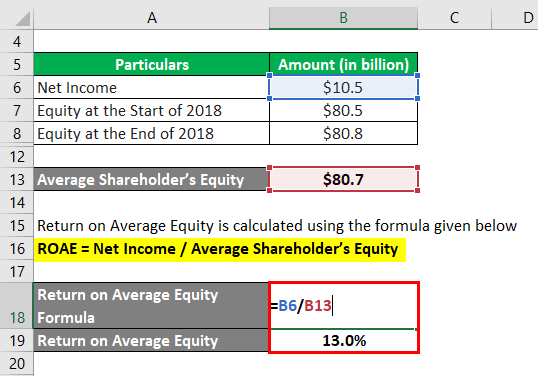
Return on Average Equity calculate using the formula given below
ROAE = Net Income / Average Shareholder’s Equity
- ROAE = $10.5 billion / $80.7 billion
- ROAE = 13.0%
Therefore, Walmart Inc.’s ROAE was 13.0% during the year 2018.
Screenshot of income statement/ balance sheet used for calculation
Source: Walmart Annual Reports (Investor Relations)
Advantages of ROAE
Some of the major advantages of return on average equity are:
- It helps equity investors to assess the performance of their investment during a given period of time.
- It overcomes the shortcomings of return on equity (ROE) by computing the profitability based on average shareholder’s equity.
Limitations of ROAE
Some of the major limitations of return on average equity are:
- Companies with high financial leverage (lower proportion of equity in capital employed) can report relatively higher ROAE, but it may not be sustainable in the long run.
- It doesn’t capture the impact of intermittent change in equity during the year, as it only focuses on its starting and ending value.
- Companies can manipulate net income by using accounting caveats like reducing depreciation rates, reporting lower provisions, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Return on Average Equity. Here we discuss how to calculate Return on Average Equity and practical examples. We also provide a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –