Updated July 3, 2023
Difference Between REST vs RESTful
REST denotes a server that shares the JSON files with a client over HTTP. It is a complete version that doesn’t seem completely dependent on JSON, XML, or HTTP. A Restful is an advanced web exchange server that shares other documents or JSON to develop new applications. The REST represents the Representational State Transfer, which uses an architectural pattern for creating new web services and implementing that architectural pattern; RESTful services are implemented. In this article, we will see a difference between REST vs RESTful.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between REST vs RESTful (Infographics)
Below are the top 6 comparisons between REST vs RESTful:
Key Differences Between REST vs RESTful
Let us discuss some key differences between REST vs RESTful:
- Architecture: The REST application architecture has a client-server, stateless, cacheable, layer system, and uniform interface. But in RESTful web applications, it has combined architecture as the same as REST, but it is built with unique features. REST applications have an individual system that handles application information. This REST server interacts with a client-server that manages the user’s interaction. It defines the update and improvement in independent tracks.
- Stability: The REST servers don’t maintain any client state where the client manage all the application stage. The request to the server comprises all the mandatory data needed to process them. If there are any fluctuations in the RESTful APIs, the client replies to the system for storage. Fetching the particular contrast data from REST with infrastructure that utilizes distributed objects to hinder the information from other components. But in REST systems, the client and server exchange knowledge about the state and data. In RESTful services, data concealing doesn’t occur; it only hides the implementation.
- Cache Ability: The REST system must represent the response as cacheable or not cacheable. So the clients and infrastructure can store them when it is possible to increase performance. It can displace the non-cacheable data when no client utilizes the stored data. In RESTful applications, the undeviating state and cacheable information are accessible to the client anywhere and anytime.
- Undeviating Interface: It is the most well-known rule based on user requirements. The central feature segregates the REST’s architecture from another network-dependent panache as it embeds an undeviating interface between devices. The REST services offer data as a resource with a unique and individual namespace.
- Multi-Layered Architecture: In REST, the devices in the system cannot view beyond the layer. So it can simply augment load balancers and make some proxy to enhance performance and security. But in the RESTful API, the layered architecture is built on the client-server where the stateless limits are merged to develop an application with strong boundaries, and the separation between the boundaries is clear and distinct. The data flow between the layers is based on the client’s requirements. The client manipulates the data or displays it.
- Remote Procedure Call on Web Services: If the user mentions that a service is not in REST, it searches for URI working or services on HTTP verbs. It is referred to as the uniform set of resources and is a structural representation of REST data. So this segregation between every frame or layer is called REST on remote procedure calls. The web services for addition, scheduling, and removing any objects from an inventory or e-commerce database can be made by RPC on REST. The single URL link with a query on HTTP POST and HTTP GET is used to interact with services by posting a file and configuring the content to complete the requirement. The popular commands used to perform HTTP actions used by REST and RESTful services are PUT, DELETE, GET, POST, and PATCH, with all specific limitations. The structured APIs can return unique codes according to the client’s requirements.
- Maturity Model by Richardson: The URI resources utilize HTTP, which makes the user predict API. But if it is unpredictable, the user can approach REST services and hypertext. The inventory application comprises many links for removing, editing, entering, or configuring the resource’s inventory database, through which every object can be returned. Files explain that before any RESTful service, it should give hypertext content as a portion of API. But many web services didn’t meet this demand and called REST. Many sites divide the rules into minor portions, and the Richardson model creates a REST with many levels of compliance with advanced security. This model offers suitable and effective guidelines for designing and creating new applications.
Comparison Table of REST vs RESTful
The table below summarizes the comparisons between REST vs RESTful:
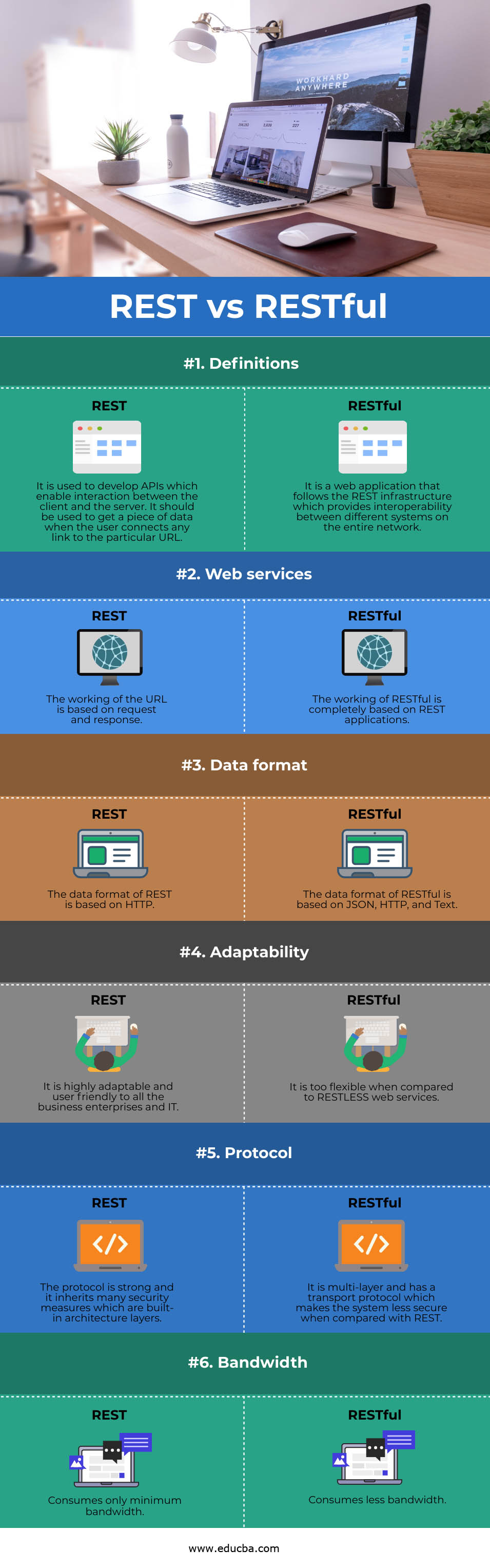
| Attributes | REST | RESTful |
| Definition | It is used to develop APIs that enable interaction between the client and the server. It should be used to get data when the user connects any link to a particular URL. | It is a web application that follows the REST infrastructure, which provides interoperability between different systems on the entire network. |
| Web Services | The working of the URL is based on request and response. | The working of RESTful is completely based on REST applications. |
| Data Format | The data format of REST is based on HTTP. | The data format of RESTful is based on JSON, HTTP, and Text. |
| Adaptability | It is highly adaptable and user-friendly to all business enterprises and IT. | It is too flexible when compared to RESTLESS web services. |
| Protocol | The protocol is strong and inherits many security measures, including built-in architecture layers. | It is multi-layer and has a transport protocol, making the system less secure when compared with REST. |
| Bandwidth | It Consumes only minimum bandwidth. | Consumes less bandwidth. |
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “REST vs RESTful” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.