Introduction to Remote PowerShell
PowerShell not only helps the administrators run commands on the local system or a server to manage the environment, but it also allows users to connect to remote servers or machines. PowerShell’s one of the major strengths lies in its remote computing ability using various technologies. PowerShell remoting allows users to execute PowerShell cmdlets or execute a script or perform any other operation on any windows systems using a remote connection. PowerShell core supports and uses technologies like Windows Management Instrumentation(WMI), Secure Shell(SSH), or WS- Management to perform tasks in a remote system. This article will cover in detail about using PowerShell to execute commands in a remote system and the various ways in which a connection to a remote computer can be established.
Steps Involved in Connection to a Remote system
The first step involved in order to connect to a remote system is to enable PowerShell Remote facility on the target machine. The above is achieved by opening the windows PowerShell in administrative mode and running the following cmdlet.
Enable-PSRemoting -Force
The above cmdlet starts the WinRM service. This will allow incoming connections to the system and creates a firewall rule to achieve that. If you don’t want to be prompted for each step, run the cmdlet with the force parameter.
The above step alone is required if the source and target machine are in the same domain.
In case if the systems are not connected to the same domain, a few more steps are needed to be done. Prior to which Remoting must be enabled on the machine to which the source will connect.
For PowerShell remoting feature to work, it must be ensured that the network must be a private network and not as a public one.
Then the trust between computers(the source and destination) must be established using the Trusted Host Settings on the computer
The above step can be achieved using the following cmdlet
Set-Item wsman:\localhost\client\trustedhosts
Next to trusted hosts, we should specify the IP addresses of the computers to which a connection needs to be listed in a comma-separated manner. If you want to allow all computers to connect then you should use the wild card character “*”. Once the above cmdlet is run, the WinRM service must be restarted in orders for the settings to take effect. That can be achieved using the following cmdlet
Restart-Service WinRM
- Both the cmdelts must be run on all the source and target machines.
- Once the configuration is done, the connection to a remote computer can be verified by running the below cmdlet:
Test-WsMan <RemoteCOMPUTERName>
- Specify the computer name to which the connection must be established in the above cmdlet
- If the connection is successful, then the status of the WiRM Service of the target system is returned.
There are few cmdlets that can be executed on remote computers without having remoting configuration enabled. This is because those cmdlets have Computer Name as a parameter. These types of cmdlets have certain communication protocols and work on all Windows machines.
Following are some cmdlets of the mentioned type
- Restart-Computer
- Get-WmiObject
- Get-WinEvent
- Test-Connection
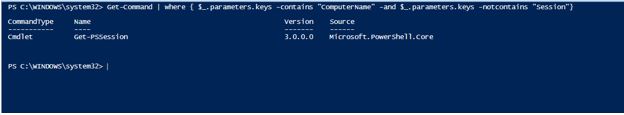
To find such cmdlets in our session, the following cmdlet can be used
Code:
Get-Command | where { $_.parameters.keys -contains "ComputerName" -and $_.parameters.keys -notcontains "Session"}
Output:
Testing the connection
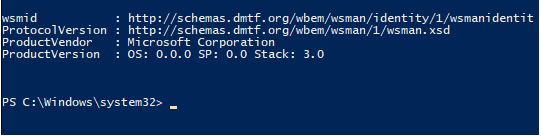
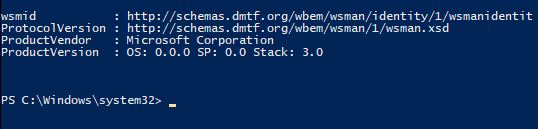
To test the status of the remoting configuration, we can try to connect to the remote computer using the following cmdlet. The test-was man cmdlet can be used to check if the WinRM service is running on the target machine. If the service is enabled a success message is displayed along with the target machines details else an error message is thrown. The cmdlet can be used with either the target systems’ name or ip address. To test the status of the WinRM service in local Test-WSMan can be used.
Test-WSMan 10.20.20.22
Test-WSMan
Connecting and ending a session
To start a session with a remote computer, a session needs to be established. Once the session is established the command prompts display name is changed to the display name of the machine to which the session is established. After that commands that are run on the local are executed on the remote machine and the results are displayed in the local computer.
Enter-PSSession TestComputer.
To end the session, the below cmdlet is used
Exit-PSSession
Running commands on Remote computer
In some cases, it may be required to run the same command on multiple remote systems. It would be tedious to establish a session for each and execute them. In that case, the invoke-command cmdlet can be used. This cmdlet can take multiple computer names or IP addresses as input parameters and executed those commands and display the output.
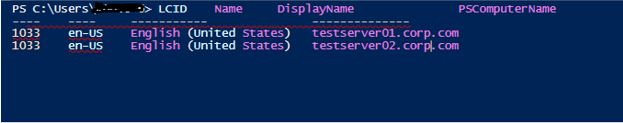
Code:
Invoke-Command -ComputerName testserver1, testserver2 -ScriptBlock {Get-UICulture}
Output:
Running a script
It is also possible to execute scripts on the remote computer from out local system. The same invoke-command can be used to perform the same. The script should be either on the local system in which the command is being run or can be on a network drive.
Invoke-Command -ComputerName testServer01, testServer02 -FilePath c:\Scripts\test.ps1
In the above command, the script is run on the mentioned two servers.
If the session objects are stored in a variable, then any commands can be run on them. Since the sessions are saved then the input of one command can be passed to another command. In this case, the session is not on the local computer.
$test=New-PSSession -ComputerName testServer01, testServer02
Invoke-Command -Session $test {$test1 = Get-HotFix}
Advanced remoting can be established using WSMan Provider.
Code:
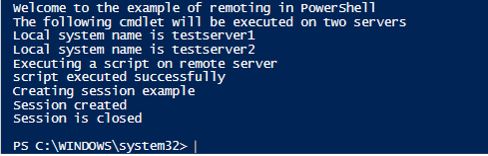
Write-Host "Welcome to the example of remoting in PowerShell"
Write-Host "The following cmdlet will be executed on two servers"
Invoke-Command -ComputerName testserver1,testeserver2 -ScriptBlock {Write-Host "Local system name is" $localhost}
Write-Host "Executing a script on remote server"
Invoke-Command -ComputerName Server01, Server02 -FilePath c:\Scripts\DiskCollect.ps1
Write-Host "script executed successfully"
Write-Host "Creating session example"
$cr=Get-Credential
$se = New-PSSession -Credential $cr -ComputerName testserver1,testserver2
Enter-PSSession $se
Write-Host "Session created"
Exit-PSSession
Remove-PSSession $sess
write-host "Session is closed"
Output:
Conclusion
Thus, the article covered in detail about remoting in PowerShell. It explained how a connection needs to be established, the prerequisites that need to be done before connecting to remote computers. It also explained with various examples how to run commands on the remote systems, how to execute scripts etc. To learn more in detail it is advisable to work on sample scripts.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Remote PowerShell. Here we discuss an introduction to Remote PowerShell, steps to connect to a remote system, with respective examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –