Updated March 6, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell XML Parsing
The following article provides an outline for PowerShell XML Parsing. The XML parsing is the library or the process to connect to your XML document and read the document’s content, filtering out specific XML documents, navigating to the nodes, and validating the XML document. PowerShell uses the Select-XML command line to parse the document. In turn, it uses the XPath (XML path) method and another method called the .Net method to parse the XML document for ease of XML document search and readability.
Syntax of PowerShell XML Parsing
Given below are the syntax mentioned:
Select-Xml
[-Xml] <XmlNode[]>
[-XPath] <String>
[-Namespace <Hashtable>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Select-Xml
[-Path] <String[]>
[-XPath] <String>
[-Namespace <Hashtable>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Select-Xml
-LiteralPath <String[]>
[-XPath] <String>
[-Namespace <Hashtable>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Select-Xml
-Content <String[]>
[-XPath] <String>
[-Namespace <Hashtable>]
[<CommonParameters>]
The above 4 different mentions that only one pair can be used at a time. Like we can not use the -LiteralPath and -Content parameter at the same time. They can be used in the same combination as mentioned.
How to Perform XML Parsing in PowerShell?
As we know, XML parsing is analyzing the XML documents, syntax, and navigating nodes. XML uses Select-XML command line or .Net method for it.
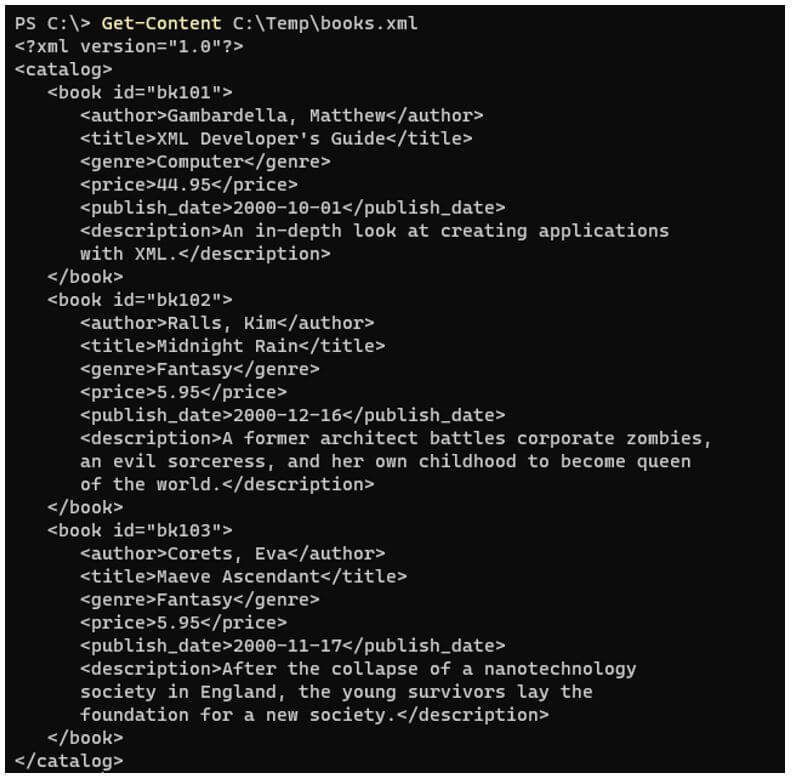
Suppose we have a sample XML file shown below:
Part of the sample XML file has been taken from the MS website.
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/desktop/ms762271(v=vs.85)
Code:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<catalog>
<book id="bk101">
<author>Gambardella, Matthew</author>
<title>XML Developer's Guide</title>
<genre>Computer</genre>
<price>44.95</price>
<publish_date>2000-10-01</publish_date>
<description>An in-depth look at creating applications
with XML.</description>
</book>
<book id="bk102">
<author>Ralls, Kim</author>
<title>Midnight Rain</title>
<genre>Fantasy</genre>
<price>5.95</price>
<publish_date>2000-12-16</publish_date>
<description>A former architect battles corporate zombies,
an evil sorceress, and her own childhood to become queen
of the world.</description>
</book>
<book id="bk103">
<author>Corets, Eva</author>
<title>Maeve Ascendant</title>
<genre>Fantasy</genre>
<price>5.95</price>
<publish_date>2000-11-17</publish_date>
<description>After the collapse of a nanotechnology
society in England, the young survivors lay the
foundation for a new society.</description>
</book>
</catalog>
To work with the XML content, we first need to content to be passed in XML format. If we use the simple Get-Content command, it won’t be in actual XML format but the raw content.
Code:
Get-Content C:\Temp\books.xml
Output:
To work with the Select-XML method or DotNet method, we need to convert the raw file into XML format.
There are two ways to convert a file into XML.
- Type Conversion
$xmldoc = [xml](Get-Content C:\Temp\books.xml)
- With Add-Type Method
$xml = New-Object -TypeName XML
$xml.Load('C:\Temp\books.xml')
When we use the Select-XML method, XPath is mandatory.
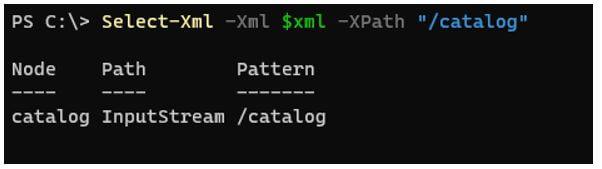
To select the root node (catalog) using XPath.
Code:
Select-Xml -Xml $xml -XPath "/catalog"
Output:
The other way to navigate is using the DotNet method.
Code:
$xml.catalog
book
----
{book, book, book}
Examples of PowerShell XML Parsing
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Expand the root node.
With Select-XML method to expand the root or the first parent node (catalog).
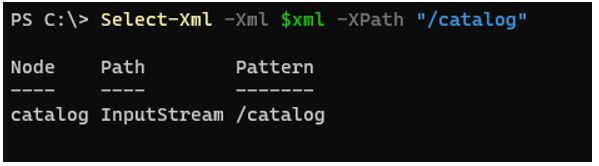
Code:
$xmldoc = [xml](Get-Content C:\Temp\books.xml)
Select-Xml -Xml $xmldoc -XPath "/catalog"
Output:
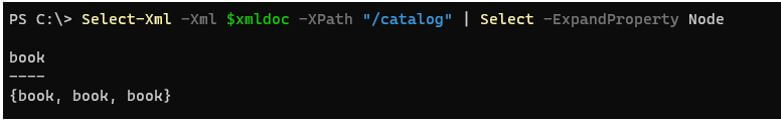
Once we get the above output, we need to expand the Node property.
Code:
Select-Xml -Xml $xmldoc -XPath "/catalog" | Select -ExpandProperty Node
Output:
Example #2
Using the SelectNodes method.
Instead of using the Select-XML method, we can use the SelectNodes method to search from the XML file.
Code:
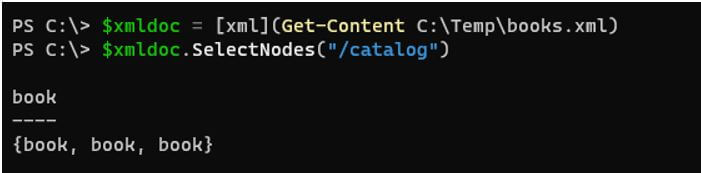
$xmldoc = [xml](Get-Content C:\Temp\books.xml)
$xmldoc.SelectNodes("/catalog")
Output:
In the above example, ‘/’ mentions the select from the root node. At the root node, we have only the ‘Catalog’ node available. If we use the ‘Book’ node instead, it won’t give any output because it is not at the root level.
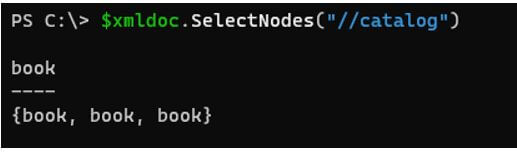
When we use the ‘//’ syntax in the xPath method, it selects that node from the entire document no matter where they are.
Code:
PS C:\> $xmldoc.SelectNodes("//catalog")
Output:
This will search for all the catalog nodes.
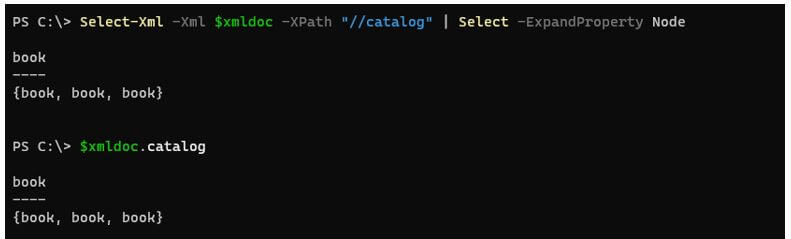
The above command is similar to.
Code:
Select-Xml -Xml $xmldoc -XPath "//catalog" | Select -ExpandProperty Node
And
Code:
$xmldoc.catalog
Output:
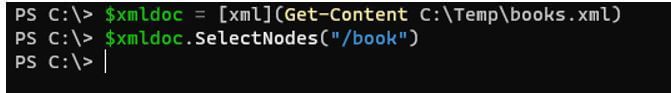
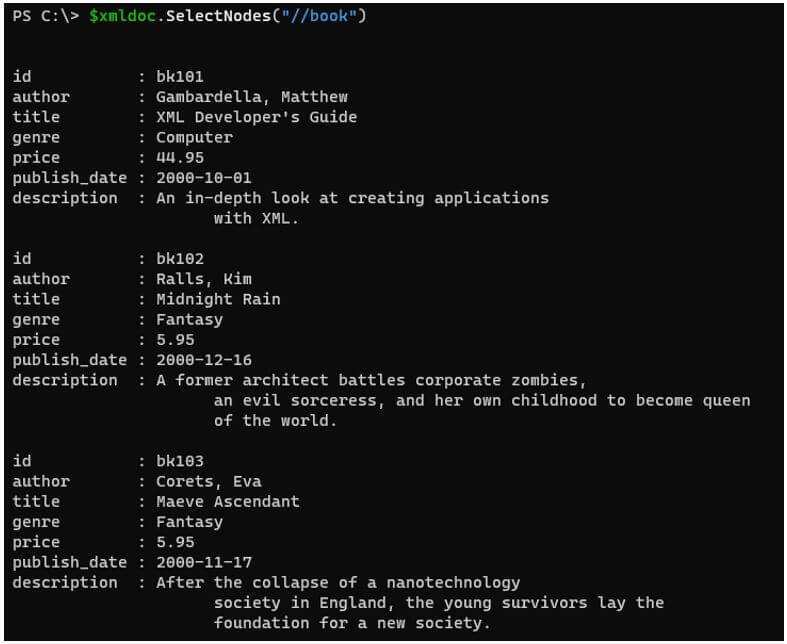
To select all the books from the XML file.
Code:
$xmldoc.SelectNodes("//book")
Output:
Similar commands
Code:
Select-Xml -Xml $xmldoc -XPath "//book" | Select -ExpandProperty Node
And
Code:
$xmldoc.catalog.book
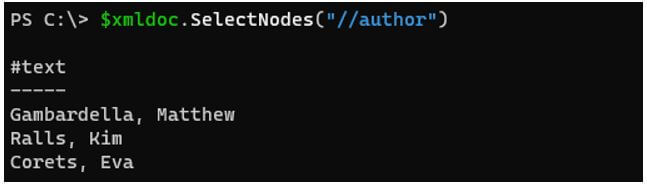
To select all the authors from the file.
Code:
$xmldoc.SelectNodes("//author")
Output:
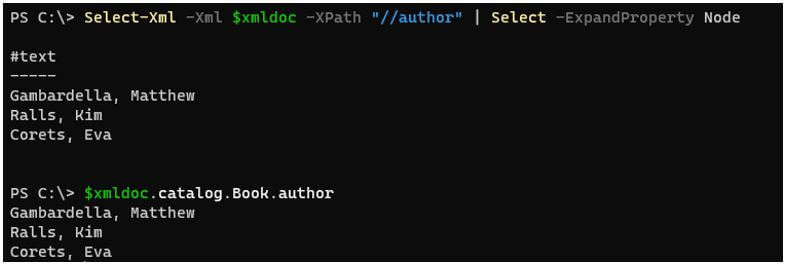
Similar commands
Code:
Select-Xml -Xml $xmldoc -XPath "//author" | Select -ExpandProperty Node
And
Code:
$xmldoc.catalog.Book.author
Output:
Example #3
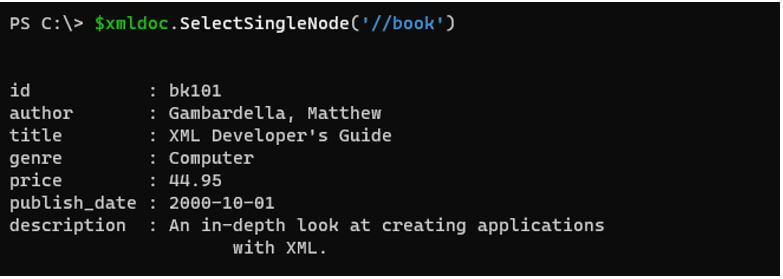
Using SelectSingleNode method.
SelectSingleNode method is to get the particular node output. By default, this command selects the first output from the array if the index is not mentioned and the index starts from 1 in XML.
Code:
$xmldoc.SelectSingleNode('//book')
Output:
This command is similar to,
Code:
$xmldoc.SelectSingleNode('//book[1]')
Or
Select-Xml -Xml $xmldoc -XPath "//book[1]" | Select -ExpandProperty Node
Or
$xmldoc.catalog.book[1]
- To select another node:
Suppose we want to select the second book author then, we can use below example.
Code:
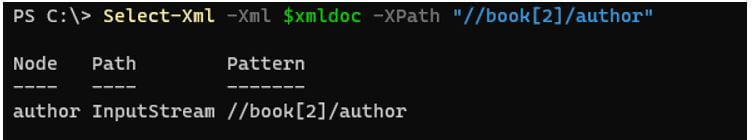
$xmldoc.SelectSingleNode("//book[2]/author")
Select-Xml -Xml $xmldoc -XPath "//book[2]/author"
Output:
Alternate commands
Code:
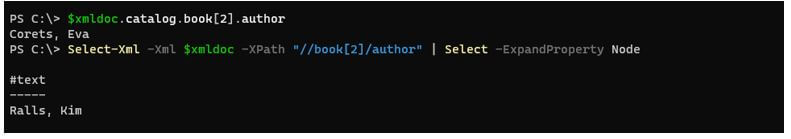
$xmldoc.catalog.book[2].author
Or
Select-Xml -Xml $xmldoc -XPath "//book[2]/author" | Select -ExpandProperty Node
Output:
Example #4
Selecting a particular attribute.
In this example, we will select a particular attribute. We need to select here the node which has book id: bk103.
Code:
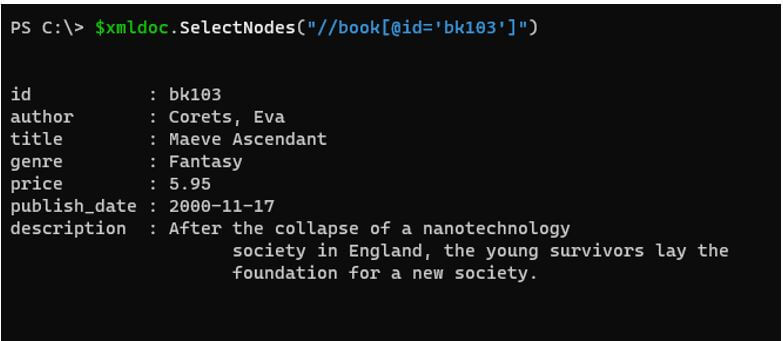
$xmldoc.SelectNodes( "//book[@id='bk103']" )
Output:
You can also use the alternate commands for Select-XML and dotnet method, as shown below.
Code:
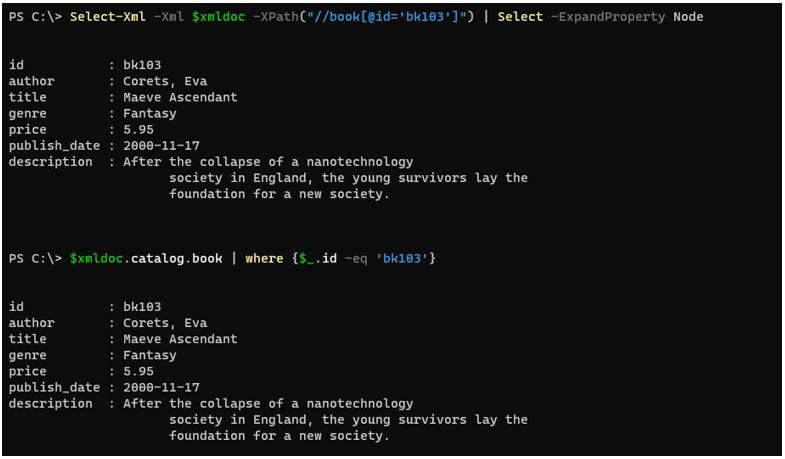
Select-Xml -Xml $xmldoc -XPath("//book[@id='bk103']") | Select -ExpandProperty Node
Or
$xmldoc.catalog.book | where {$_.id -eq 'bk103'}
Output:
Example #5
Selecting multiple elements.
To select multiple elements, we can use the below command.
Code:
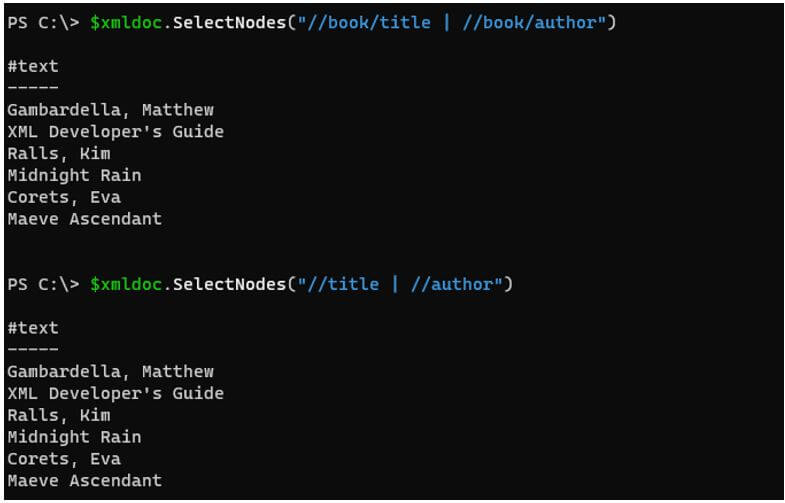
$xmldoc.SelectNodes("//book/title | //book/author")
Or
$xmldoc.SelectNodes("//title | //author")
The above command selects the title and author from the XML file.
Output:
Similar commands
Code:
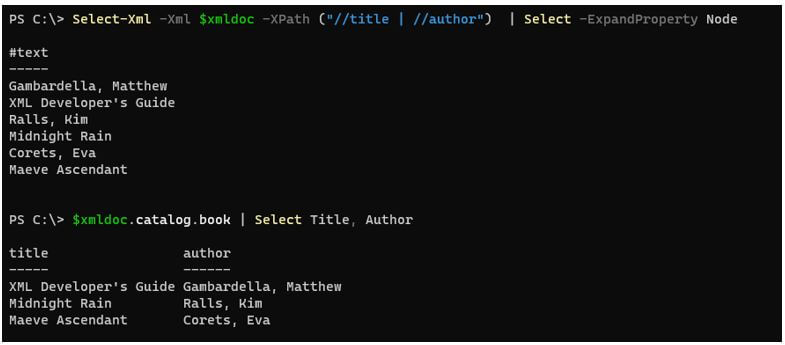
Select-Xml -Xml $xmldoc -XPath ("//title | //author") | Select -ExpandProperty Node
$xmldoc.catalog.book | Select Title, Author
Output:
Example #6
Single and Double dot syntax Xpath.
In the XPath syntax, Dot (.) represents the current node while double dot (..) represents the parent of the current node.
Code:
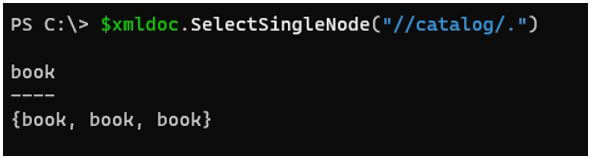
$xmldoc.SelectSingleNode("//catalog/.")
Output:
The above example represents the current node.
Code:
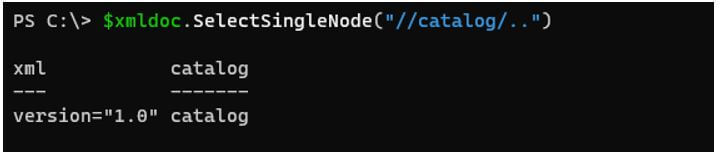
$xmldoc.SelectSingleNode("//catalog/..")
Output:
The above example represents the parent node.
Conclusion
PowerShell XML parsing methods are useful while working with the XML documents, so once it is used in the application, it can be easier for applications to search and navigate the larger documents quickly, and also it is very fast for web processing.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell XML Parsing. Here we discuss the introduction, how to perform XML parsing in PowerShell? and examples respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –