Updated February 18, 2023
Introduction to Redis FLUSHALL
Redis FLUSHALL is one of the mechanisms to delete all the keys which are existed on the redis databases by using CLI commands. In order to execute these flush database modifications and gather N number of threads, it must delete the keys associated with the mapped nodes.. FLUSHALL is database synchronous to configure the directive on the flush mode changes to reflect it.
Key Takeaways
- Not just the currently selected database, but all the existing databases’ keys should be deleted.
- The default flush mode is now asynchronous when the lazy free-lazy-user-flush configuration directive is set to “yes”.
- The ASYNC keyword uses asynchronously flushes the databases.
- The SYNC keyword flushes the databases synchronously.
- Only keys that were present at the time the asynchronous FLUSHALL command was issued are deleted. Keys generated during an asynchronous flush won’t be impacted.
What is Redis FLUSHALL?
Redis FLUSHALL purges all keys from all active databases, not just the one that is presently being used. This instruction will always work and remove all of the keys from all of the presently active databases, not just those we have selected. All the databases will be simultaneously flushed using FLUSHALL by default. And the latest version of the Redis will be able to use the default flush mode, for now, asynchronous when the lazy free-lazy-user-flush configuration directive is set to “yes” value. Mainly Asynchronous will flush the databases by using the Async keyword and the Sync keyword will flush the databases by using the synchronous mode.
How to Flush Redis Cache and Delete?
We can utilize the data clearing feature on the DCS interface, for the FLUSHDB command on Web CLI, or the FLUSHALL command in redis-cli to clear the data of a DCS Redis version 4.0, 5.0 instance. To Run the FLUSHDB or FLUSHALL command on each share of a Redis Cluster instance for helping to clear all its data which associated with the specific key areas. It is designed for deleting all the keys in all of the appropriate databases that can be mapped on the server. Use the below command to erase or destroy all the keys stored on the databases.
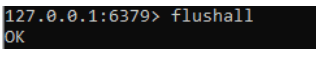
Redis-cli flushallThe above code is the syntax to remove all the keys. We can also remove the databases by using the syntax.
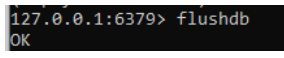
redis-cli flushdbThe above screenshot shows to flush the databases and flushall for removing all the keys also. Based on the scenario it may vary the redis cluster deploy the primary and secondary instances. Generally, the clusters will configure the database services like AWS, Azure, Google cloud, etc. For clustered redis database cache.
How to Use Delete All Keys in Redis?
We know that Redis is one of the free, open-source key-value pair databases. Because it keeps the data in memory, it is incredibly quick and well-liked in high-performance settings. It is utilized by small to large apps, like Twitter, GitHub, Stack Overflow, and many more which will use the Redis cache on each cluster. In other ways circumstances, we need to reset all the databases stored in the Redis cluster which starts over the indexes.
Async Delete
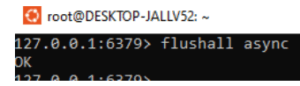
Blocking is the FLUSHALL command that implies performing any additional server-side operations, like waiting thread for the flushing process to complete the task. However, as of Redis version 4.0 and other latest versions, it can conduct a non-blocking flush operation using the ASYNC argument.
The flush process is made to operate in the background without slowing down the server via the ASYNC argument. Delete Keys from the Currently Selected Database use the flushdb command to only delete keys from the currently selected database. We delete all the keys in the presently selected database, database 10 version. And almost the database version is the main part of the redis cache that selected the keys on every column value. To select which database to run the flushdb command on, use the -n argument.
Time complexity where N is the number of keys that will be eliminated; hence the answer is O(N). The individual complexity for a key to remove that has a value other than a string is O(M), where M is the total number of elements in the list, set, sorted set, or hash. It is O to remove a single key that contains a string value (1). Redis is single-threaded, so using keys cmd is extremely risky for performance and is strongly discouraged in production environments when the number of keys is greater. Since keys cmd will block all other operations on redis and all clients will have to wait for it to finish, this method can only be used when the number of keys in redis (use DBSIZE to know the count) is lower.
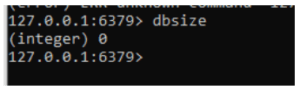
Here the DB Size default is 0 we can also increase the size by manually entering the keys.
How to Use FLUSHALL Command in Redis?
Following are the steps to use the flushall command in the redis cache.
Steps to use the flushall command:
1. Link to Redis.
2. Select your database (with the command select “Index”) and then perform the command flushdb.
3. If redis-cli is running on port 6379, you can use that command; otherwise, you must specify the port number.
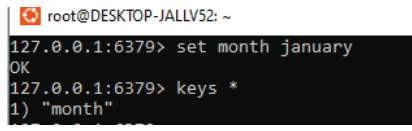
4. Here we have created and checked the number of keys in redis.
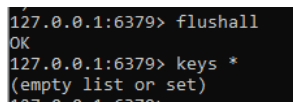
It has 1 key called month now we are using the flushall command, after executing this command the list shows empty.
Example of Redis FLUSHALL
Given below is the example mentioned:
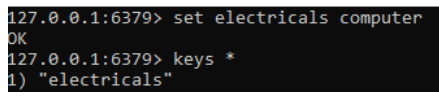
set electricals computerKeys *FlushallFAQ
Given below are the FAQs mentioned:
Q1. What is redis flushall?
Answer:
Delete every key from every database that is currently in use, not just the one we have selected.
Q2. What are the two types of flushes in Redis databases?
Answer:
- ASYNC
- SYNC
Q3. Define lazyfree-lazy-user-flush.
Answer:
Version >= 6.2.0 the default flush behavior is customizable using the lazyfree-lazy-user-flush configuration option.
Conclusion
A specific database or a Redis cluster helps to understand the FLUSHALL command and the flushdb command. Redis, and the redis-cli command interface which is used for devops like docker and other technologies which maintain the data in many Redis databases and for how to clear one or more of them using the flush commands.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Redis FLUSHALL. Here we discuss the introduction, how to flush redis cache, and delete. run the FLUSHALL command & examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –