Updated April 11, 2023
Introduction to RabbitMQ Routing Key
Routing Key is of significant importance in a RabbitMQ system. A Routing Key is generated by the producer and is a part of the message along with the payload (actual data that is to be transmitted). An exchange looks at the Routing Key while deciding how the message has to be routed. A Routing Key is simply a word or a number of words separated by dots.
What is Routing Key?
RabbitMQ is quite popular because of its powerful routing capabilities and the routing key plays an important role in it. An exchange is given the responsibility to route messages to different queues and it uses the routing key to route messages to various queues. Messages are generated by an external application known as a producer. It has to figure out what messages need to be sent and what should be the routing key. After the messages are constructed by the producer, these are sent to exchanges, which in turn reads the routing key and routes the messages to appropriate exchanges or queues. Now the question arises is that the exchange compares the routing key to what: The answer is binding key.
How Routing is Done?
To understand the process better let’s understand the binding key as well. A binding denotes a relationship between a queue and an exchange. The binding key is specified while adding a queue to an exchange. Now, how exactly the routing key is compared against the binding key depends on the type of exchange. Let’s discuss the various exchange types and how they route the messages:
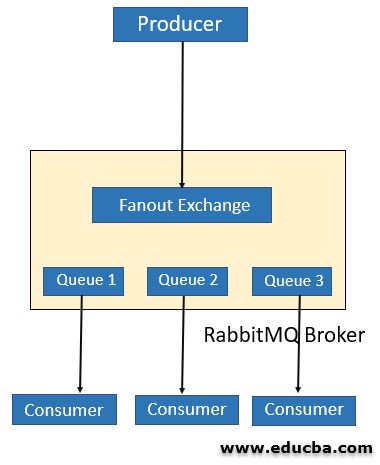
1. Fanout Exchange
It routes messages to all the available queues without discrimination. A routing key, if provided, will simply be ignored. This exchange is useful for implementing the pub-sub mechanism. While using this exchange, different queues are allowed to handle messages in their own way, independently of others.
As shown in the diagram above, the messages are routed to all the queues. Fanout Exchange doesn’t provide any flexibility with routing – it just capable of broadcasting without discrimination.
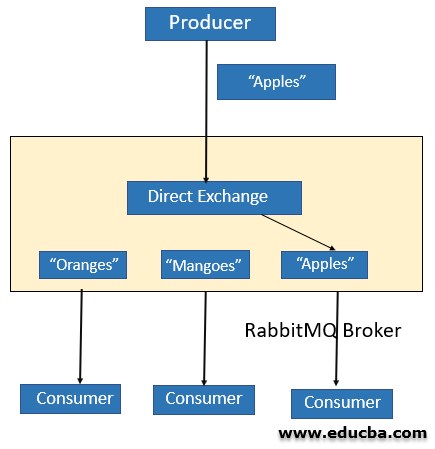
2. Direct Exchange
It routes messages on the basis of the routing key that the message carries. Routing Key is a short string generated by the Producer of the messages. The messages are routed to the exchanges/queues having the Binding Key that exactly matches the routing Key.
As shown in the above diagram, the routing key is “Apples” and the messages are delivered to only one queue whose binding key is “Apples”. Multiple queues are allowed to use the same binding key. In the above example, if we add another queue with binding key as “Apples” then the messages will be delivered to this queue as well.
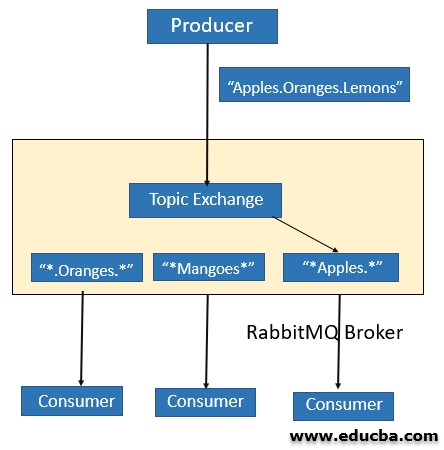
3. Topic Exchange
It routes messages on the basis of the complete or partial match with the routing key. In this case, the messages are published in such a way that the routing key consists of dot-separated series of words (like word1.word2.word3 ). Patterns can have an asterisk(*) that can match word at a certain position of the routing key or a hash that can match zero or more words.
In the above case, the routing key is “Apples.Oranges.Lemons” and the messages are routed to two queues: one having pattern as “*.Oranges.*” and others with the pattern “Apples.*”.
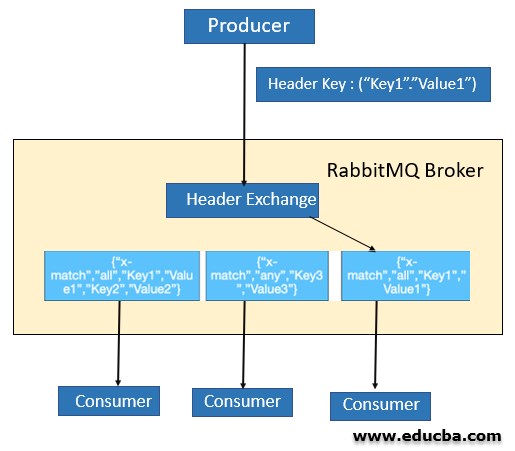
4. Headers exchange
Messages are routed based on the message headers. The message headers are matched against headers specified by binding queue and if matched then messages are sent to that queue. A special argument called “x-match” is added in the binding between an exchange and a queue. Now, this takes can have two values “any” or “all”, where “all” is the default value. “all” signifies that all header pairs must match, whereas “any” signifies that at least one of the header pairs must match.
In the above case, messages are routed to one queue for which the “x-match” is set as “all” and all of its key-value pairs (only 1 in this case) match with that in the message header.
5. Consistent Hashing
This type of exchange hashes either the routing key or the message header in order to route the messages to one queue only. This finds useful in cases where we have to guarantee that messages are Consumed in the same order as published.
Conclusion
In this article, we have understood how the routing key provides powerful routing capabilities to RabbitMQ. We have also checked how different exchanges route messages to queues or other exchanges based on the routing key and the binding key.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to RabbitMQ Routing Key. Here we discuss how the routing key provides powerful routing capabilities to RabbitMQ. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –