Updated April 7, 2023
Introduction to PyTorch repeat
In deep learning, we need to repeat the tensor along with the required dimensions at that time we can use PyTorch repeat. tensor. repeat should suit our necessities yet we want to embed a unitary aspect first. For this we could utilize either tensor. reshape or tensor. unsqueeze. Since unsqueeze is explicitly characterized to embed a unitary aspect we will utilize that. In deep learning, it plays a more important role because sometimes we need to change the dimension of the tensor in the training dataset so at that time we can use the repeat method to change the dimension of the tensor and utilize it whenever we require it.
What is PyTorch repeat?
tensor. repeat should suit your necessities yet you really want to embed a unitary aspect first. For this, we could utilize either tensor. reshape or tensor. unsqueeze. Since unsqueeze is explicitly characterized to embed a unitary aspect we will utilize that.
Fundamentally, PyTorch gives the reshape usefulness to the client, in profound learning it is a significant part. The Squeeze in PyTorch is used for controlling a tensor by dropping all of its components of wellsprings of data having size 1. Presently in the under code scrap, we are using the devastating limit of PyTorch. As it might be seen, the tensor whose wellsprings of information are having the part of size 1 is dropped. PyTorch unsqueeze work is used to make one more tensor as yield by adding one more component of size one at the best position. For instance, here we take a tensor of 2x2x2 and use PyTorch level ability to get a tensor of a singular estimation having size 8.
First, let’s try to understand what deep learning is. Deep Learning is a subfield of AI where concerned calculations are enlivened by the construction and capacity of the mind called Artificial Neural Networks. Profound learning has acquired a lot of significance through administered taking in or gaining from marked information and calculations. Every calculation in profound learning goes through the same interaction. It incorporates the progression of nonlinear change of information and utilizations to make a factual model as yield.
AI process is characterized utilizing the following advances:
1. Recognizes important informational indexes and sets them up for examination.
2. Picks the sort of calculation to utilize.
3. Fabricates a logical model dependent on the calculation utilized.
4. PyTorch – Universal Workflow of Machine Learning
5. Trains the model on test informational indexes, reexamining it on a case-by-case basis.
6. Runs the model to create test scores.
So we need to use different functions such as reshape (), shape, etc, to achieve the above-mentioned point. Pytorch also provides one more function that we can utilize with the reshape() function that is the repeat function. It avoids the duplication of tensors that means we can use existing tensors with specified dimensions to get the predicted outcome as well as it also provides the support to reduce the complexity and we can implement tensors in an efficient way in deep learning.
How to repeat a new dimensions in PyTorch?
Now let’s see how we can create a new dimension with a repeat as follows.
Syntax
Specified torch.repeat(specified dimension)Explanation
In the above syntax, we use repeat function as shown, here specified torch means the actual variable name of tensor and specified dimension means the required dimension that we need to change.
The repeat function has different parameters as follows.
- Input: It is used to indicate the input tensor.
- repeat: This is a function, used to repeat the shape of the tensor as per our requirement.
- Dimension: This is an optional parameter of the repeat function, if we can’t provide the dimension at that time it takes the default dimension.
PyTorch repeat Examples
Now let’s see a different example of Pytorch repeat for better understanding as follows.
Example #1
First, we need to create the tensor to implement the repeat by using the following code as follows.
Code:
import torch
x = torch.randn(5, 2, 220, 220)
y = x.repeat(3, 2, 1, 1)
print(y.shape)Explanation
In the above example, we try to implement the repeat function with shape as shown, in this example first we created a tensor by using a random function. After that we use repeat with a new specified dimension as shown, finally, we print the result. The final result of the above program we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see another example of repeat () as follows.
Example #2
Code:
import torch
x = torch.tensor([[5, 2, 4], [6, 2, 3]])
print(x)Explanation
In the above example first, we need to import the torch package, after that, we created a tensor as shown. The final result of the above program we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
After the successful creation of the tensor, we use the cat function to repeat the tensor, here we repeat the tensor 4 times as shown in the following code as follows.
y = torch.cat(4*[x])
print(y)Explanation
The final result of the above program we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
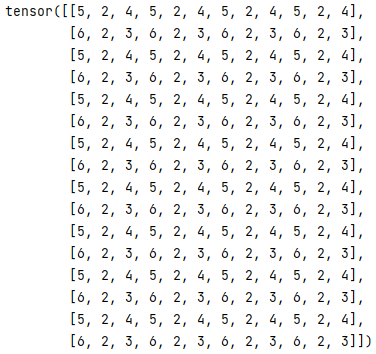
Now we use the repeat function as shown in below code as follows.
z = y.repeat(2, 4)
print(z)Explanation
The final result of the above program we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see one more example of repeat with size function as follows.
Example #3
Code:
import torch
A = torch.tensor([2, 3, 5])
A.repeat(3, 5)
B =A.repeat(3, 1, 2).size()
print(B)Explanation
In the above example first, we need to import the torch as shown, after that we created a tensor. In this example, we use repeat () with the size function as shown. The final output of the above program we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
One important thing about the repeat () function is that it is totally different from the nump. repeat but at the same time is more similar to NumPy.tile.
So in this way we can implement the PyTorch repeat, moving towards deep learning if we need to speed up the code or suppose we need to perform an arithmetic operation at that time we can use the repeat function in our model as per requirement.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you learn more about the PyTorch repeat. From the above article, we have taken in the essential idea of the PyTorch repeat and we also see the representation and example of the PyTorch repeat. From this article, we learned how and when we repeat PyTorch.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PyTorch repeat” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.