Updated March 30, 2023
Introduction to python 3 write to file
Python 3 write to file method saves a string called str to a file. The string may not appear in methods of flush and closed because of buffering. As a result, understanding how to work with various file formats that store various sorts of data is very beneficial. The data is shortened and overwritten for an existing file. Append only is allows us to write to a file.
Overview of python 3 write to file
Reading, writing, or manipulating data is likely to be a part of any program we build. Below is the syntax of python 3 write to file are as follows.
Syntax:
Fileobject.write (str)In the above syntax, str is nothing but the string which is used to write the output in the file. The write method in python 3 is not returning any value. Fileobject is nothing but the object of file.
How to Create python 3 write to file?
- Text files, Each line of text in this type of file is terminated by the special character known as EOL (End of Line), which in Python is the new line character (‘n’).
- For a binary files, there is not any terminator, and the data is kept after it has been converted into machine-readable binary language.
- The kind of operations that can be performed on an opened file is determined by the access modes.
- It describes utilizing of the file after it has been opened. These modes additionally specify where the FileHandle should be in the file.
- A filehandle acts as a cursor, indicating where data should be written into the file. There are several access mechanisms for reading a file.
- Write and read of files is allows us to read and write to a file. Data is shortened and overwritten for an existing file. The handle is at the beginning of the document.
- For generating, writing, and reading files, Python provides built-in functions. Normal text files and binary files are the two types of files that can be processed by Python.
- The file’s handle is located at the very end. After the existing data, the data that is being written will be added at the end.
- Use the open function with creating, appending, and write parameters in Python to create a new file.
1) Create – creates a file, if the file already exists, it returns an error.
2) Append – If the chosen file does not exist, it will create new file.
3) Write – If the chosen file does not exist, Write will create one.
- We are using “x” letters to creating new file, “a” for append the file, and “w” for write a file.
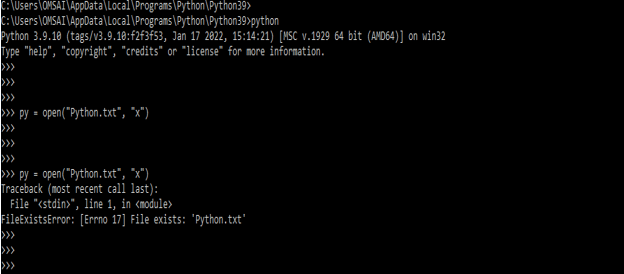
- In the below example, we are creating file by using open method. We are using “x” letter to create a new file in python 3 are as follows. In the first example we are creating new file, so it will creating a new file name as Python.txt. But in the second example we are trying to create same file, but it will showing the error message.
Code:
py = open("Python.txt", "x")
py = open("Python.txt", "x")Output:
- The below example shows create new file by using the append parameter. We are using “a” letter for appending the new file. In this example for executing the same command two times, it will not show an error even we are appending it into an old file.
Code:
py = open("Python1.txt", "a")
py = open("Python1.txt", "a")Output:
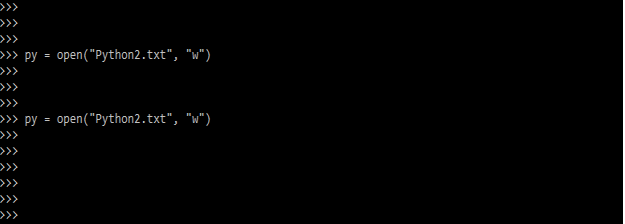
- The below example shows create new file by using write parameter. We are using “w” letter for creating the new file. In this example for executing the same command two times it will not showing error even we are writing into the old file.
Code:
py = open("Python1.txt", "w")
py = open("Python1.txt", "w")Output:
Python 3 write to file method
In python there are two ways to write into the file are as follows.
1. Write – This method is inserting a single string into a single line in a text file. Below syntax shows write method are as follows.
Fileobject.write (string)
2. Writelines – Each string is inserted into the text file for elements of string. Multiple strings can be inserted at once using this method. Below is the syntax of writelines method is as follows.
Fileobject.writelines (L) for L = [string1, String2, String3]The below example shows writing to file by using write and writelines method are as follows.
Code:
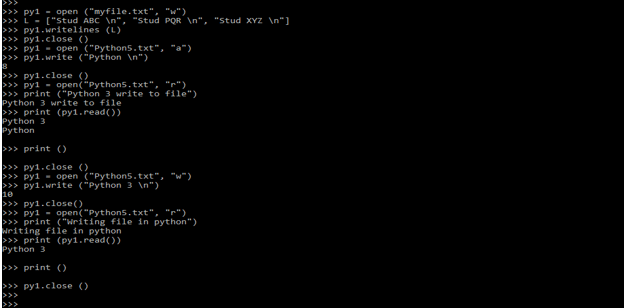
py1 = open ("myfile.txt", "w")
py1.writelines (L)
py1.close ()
py1 = open ("Python5.txt", "a")
py1.write ("Python \n")
py1.close ()
py1 = open("Python5.txt", "r")
print ("Python 3 write to file")
print (py1.read())
print ()
py1.close ()
py1 = open ("Python5.txt", "w")
py1.write ("Python 3 \n")
py1.close()
py1 = open("Python5.txt", "r")
print ("Writing file in python")
print (py1.read())
print ()
py1.close ()Output:
Examples
Below example shows python 3 write to file are as follows.
Example #1
In the below example, we opening the old file and appending the new content into the file.
Code:
py = open("Python1.txt", "a")
py.write ("Python 3 write to file")
py.close ()
py = open("Python1.txt", "r")
print (py.read())Output:
Example #2
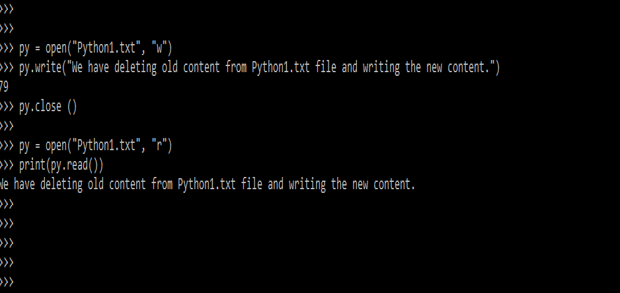
In below example, we are overwriting the content of old file which was edited last time. We are overwriting file name as Python1.txt are as follows.
Code:
py = open("Python1.txt", "w")
py.close ()
py = open("Python1.txt", "r")
print(py.read())Output:
Example #3
Below example, shows write content into file by using with statement. We are writing the statement into Python.txt file.
Code:
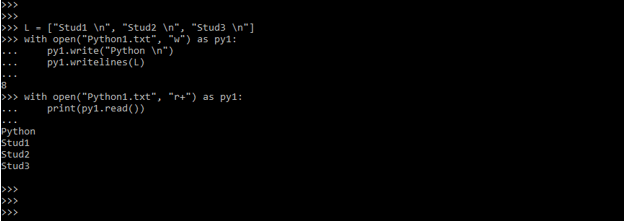
L = ["Stud1 \n", "Stud2 \n", "Stud3 \n"]
with open("Python1.txt", "w") as py1:
py1.write("Python \n")
py1.writelines(L)
with open("Python1.txt", "r+") as py1:
print(py1.read())Output:
Conclusion
For generating, writing, and reading files, Python provides built-in functions. Normal text files and binary files are two types of files that can be processed by Python. Python 3 write to file method saves string called str to a file. Append only is allows us to write to file.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Python 3 write to file. Here we discuss the definition, overview, How to create python 3 write to file, examples with code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-