Updated March 30, 2023
Definition of Python 3 URLlib
Python 3 urllib handling module is contained in the Urllib package. It’s used to get URLs from the Internet, it makes use of the URL open function to retrieve URLs over a variety of protocols. Urllib is a collection of modules for working with URLs, including URLs, urllib. parse for parsing URLs. For processing robot.txt files raised urllib. robotparser. Use the code below to install urllib if it isn’t already installed in our environment.
What is Python 3 URLlib?
- The urllib request module assists in the definition of URL-opening functions and classes (mostly HTTP).
- The urllib parse module aids in the definition of functions for manipulating URLs and their constituent elements, in order to construct or deconstruct them. It mainly focuses on breaking down a URL into individual components or combining several URL components together to form URL strings.
- This module assists in raising exceptions whenever a URL is not successfully retrieved.
- URL error is thrown when there are mistakes in URLs or when requesting. It provides a reason field that explains to the user why the error occurred.
- HTTP Error is thrown when there are unusual HTTP errors, such as authentication request errors. It belongs to the URLError subclass. ‘404’ (page not found) and ‘403’ are common errors.
- Urllib RobotFileParser class is part of the robotparser module. This class responds to the question of whether a specific user can access a URL that contains robot.txt files.
- Webmasters used Robots.txt file their pages. The robot.txt file instructs the web scraper.
- In Python 3, the urllib module allows us to access websites from our program. This provides as many opportunities for our programs as the internet does for us.
- Although urllib in Python 3 is different in Python 2, they are basically the same. We can use urllib to parse data, change headers, and perform any GET and POST requests we need.
- URLs can be retrieved using the urllib request Python module. The URL open method provides a fairly straightforward interface. This can retrieve URLs over a variety of protocols. It also has a little more complicated interface for dealing with typical scenarios such as basic authentication, cookies, and proxies.
- Objects known as handlers and openers provide these services. Urllib requests may fetch URLs via their corresponding network protocols for multiple “URL schemes” identified by the string preceding the “:” in URL.
- The HTTP protocol is built on requests and replies, where the client sends queries and the server responds. This is mirrored by urllib request, which uses a Request object to represent the HTTP request. In its most basic form, we create an object that defines the URL to be retrieved. When we use this Request object to call URL open, we will get a response object.
Python 3 URLlib Module
- Request objects in HTTP allow us to do two additional things. We can send data to the server by first passing data to it. Second, we can send the server additional information about the request as HTTP headers.
- Urllib is a Python 3 library that allows us to interact with websites by utilizing their URLs to access and interact with them. It has a number of URL-related modules.
- For blocking actions such as connection attempts, the optional timeout argument provides a timeout in seconds. Only HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP connections are supported by this.
- A SSL Context instance that describes the different SSL options. More information is available at HTTPS Connection.
- For HTTPS queries, the cafile and capath options are optional trustworthy CA certificates. Capath refers directory of hashed files, whereas cafile refers to a single file holding bundle of CA certificates.
- An opener is used when retrieving a URL. Normally, we use the default opener, which is urlopen, but we can make our own. Handlers are used by openers.
- The handlers do all of the “hard lifting.” Each handler understands how to open URLs using a specific URL scheme or how to deal with specific components of URL opening.
Below are the modules of the python 3 urllib module are as follows.
1. Urllib.request
When we use urllib.request with urlopen, we can open the supplied URL. The below example shows urllib. requests are as follows.
Code:
from urllib.request import urlopen
url = urlopen("https://www.python.org/")
print(url.read())Output:
2. Urllib parse
The protocol scheme utilized, the network location netloc, and the route to the webpage are all separated from the URL.
Code:
from urllib.parse import urlparse
url = urlparse ('https://www.python.org/')
print (url)Output:
3. Urllib. error
- This module is responsible for catching URLs. request exceptions. These errors, or exceptions, are categorized as follows.
- At the time our URL is wrong or there is a difficulty with internet connectivity, the URL Error is raised.
- HTTP Error, which is triggered by HTTP errors like 404 and 403. The following code shows how to use urlib. error.
Code:
from urllib.request import urlopen, HTTPError, URLError
try:
myURL = urlopen("'https://www.python.org/")
except HTTPError as e:
print('Error code: ', e.code)
except URLError as e:
print('URL error: ', e.reason)
else:
print('We have not found any error in URL.')Output:
The URLError exception is thrown when a request for https://www.python.org/ is made; the URL is invalid. Experiment with the exceptions by visiting other URLs.
Examples of Python 3 URLlib
The below example shows python 3 urllib is as follows. In the below example, we are using the get method and we are reading the content from the python page.
Code:
import urllib.request
res = urllib.request.urlopen ('https://www.python.org')
print (res.read())Output:
The below example shows the python urllib header request.
Code:
import urllib.request
res = urllib.request.urlopen('https://www.python.org')
print(res.read())Output:
The below example shows python urllib rest are as follows.
Code:
import urllib.request
res = urllib.request.urlopen('https://www.python.org')
print(res.read())Output:
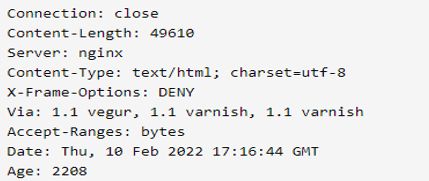
The below example shows python urllib header responses are as follows. The response headers can be obtained by invoking the info function on the response object.
Because this provides a dictionary, we may extract specific header info from the response as well.
Code:
import urllib.request
res = urllib.request.urlopen('https://www.python.org')
print (res.info())
print ('Content Type = ', res.info()["content type"])Output:
Conclusion
The classes for urllib request exceptions are defined in the urllib.error module. Python 3 urllib is used to get URLs from the Internet, it makes use of the URL open function to retrieve URLs over a variety of protocols. Python 3 urllib handling module is contained in the Urllib package.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Python 3 URLlib. Here we discuss the definition, What is Python 3 URLlib, modules and Examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –