Updated March 28, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Get-Process
Get-Process cmdlet in PowerShell is used to retrieve the list of processes running in the system and also from the remote system(s). These processes can be applications or system processes. These are the same processes you can see in the task manager, in the Process tab.
Syntax
Get-Process
[[-Name] <String[]>]
-Id <Int32[]>
-InputObject <Process[]>
-ComputerName <String>
[-Module]
[-FileVersionInfo]
[-IncludeUserName]
[<CommonParameters>]
The above syntax can be used with different combinations. Not all the times all combinations work. For example, Module and FileversionInfo parameters don’t work together.
Parameters
Some of the parameters are given below:
- -Name: When -Name parameter is provided, PowerShell retrieves all the processes with that name. Wildcard character (*) is permitted. You can provide multiple process names separated by comma (,).
- -ID: The ID parameter defines the process ID. When specific process ID provided, PowerShell retrieves the information about that process ID. The process ID is always an integer. The process ID is a default with the Get-Process output. You can also get the PID from the Resource Manager.
- -Module: When this parameter is specified with the Get-Process, it shows all the modules that have been loaded by the processes. When PowerShell run as administrator, this parameter shows all the modules for all the users.
- You can run this command on a remote computer by providing system name in the -ComputerName parameter or by running the Invoke-Command.
- You can’t pipeline Stop-Process command with this parameter.
- -ComputerName: You can provide remote system name to retrieve the process running on remote computers. You can provide multiple computer names separated by comma (,).
- -IncludeUserName: When you add this parameter, Process output shows the column of username by which the particular process is running.
- -FileVersionInformation: This parameter provides the version of the file or application, responsible for the particular process. To get the list of all the processes file version information from different users, you need to run the PowerShell console as the administrator.
- You can retrieve the file version details from the remote computer using –ComputerName parameter or the Invoke-Command parameter
- -InputObject: It specifies the process object. When you create an advanced function, you can also specify the input object as the Pipeline or the variable that contains the process objects.
Examples of Get-Process in Powershell
The examples of PowerShell are shown below:
1. Simple Get-Process command
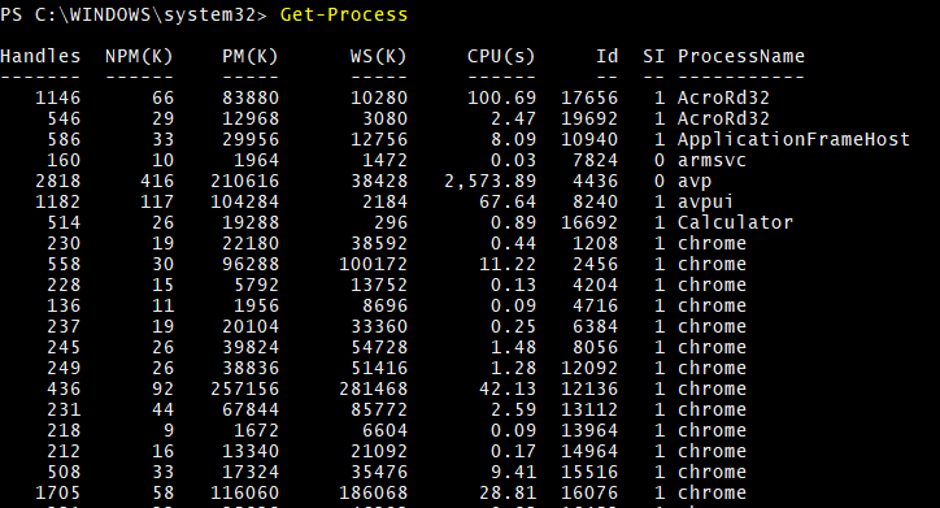
Get-Process
When you run above command only with no specific parameters, then below table output is the default.
Handle, NPM(K), PM(K), WS(K), Id, SI, ProcessName
Output:
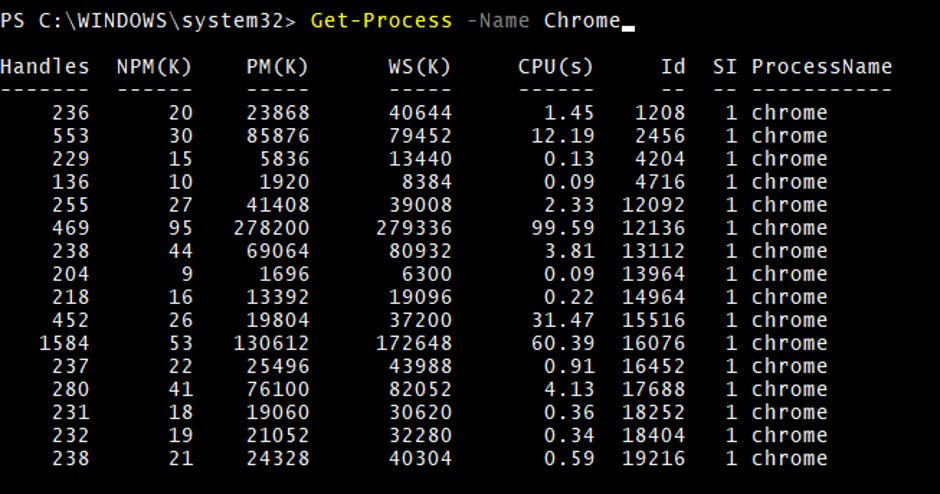
2. Get-Process with –Name parameter
Get-Process -Name chrome
Output:
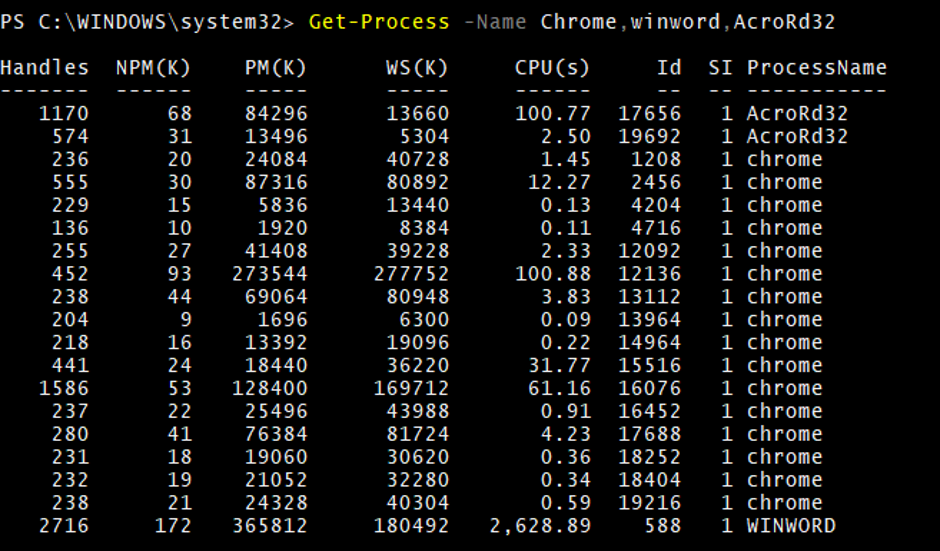
To filter multiple processes separate the process name with the comma (,).
Get-Process -Name chrome,WINWORD,AcroRd32
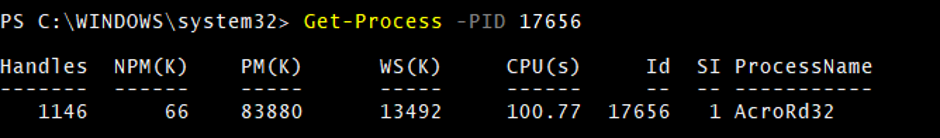
3. Get-Process with –ID parameter
Here ID means the Process ID (PID). You can use one of the parameters (ID or PID), both work the same way.
Get-Process -PID 17656
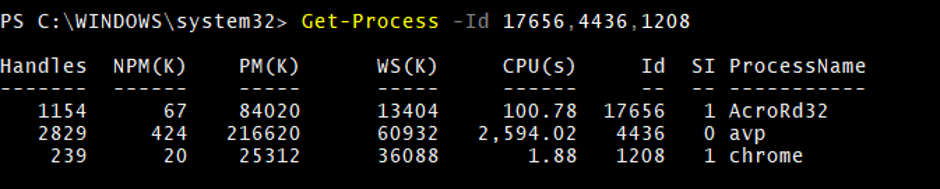
You can filter multiple PIDs as well.
Get-Process -Id 17656,4436,1208
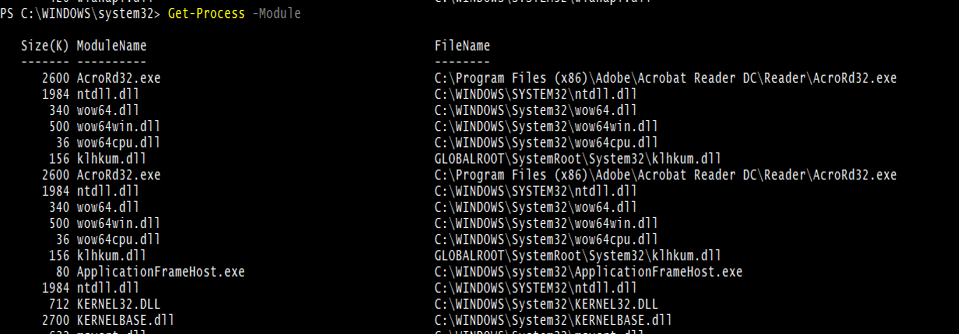
4. Get-Process with –Module parameter
Get-Process -Module
Output:
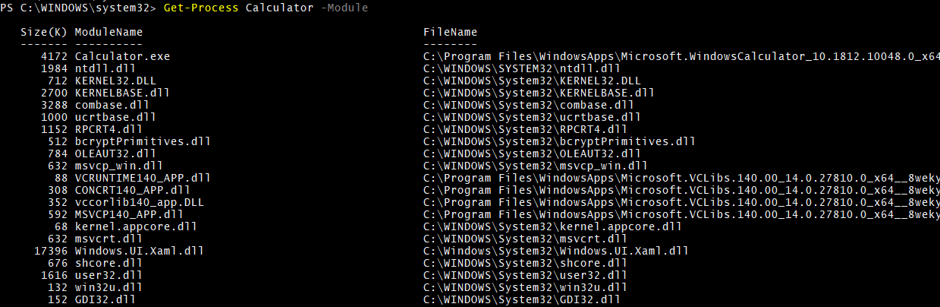
You can find the specific process module by providing the process name.
For example,
Get-Process Calculator -Module
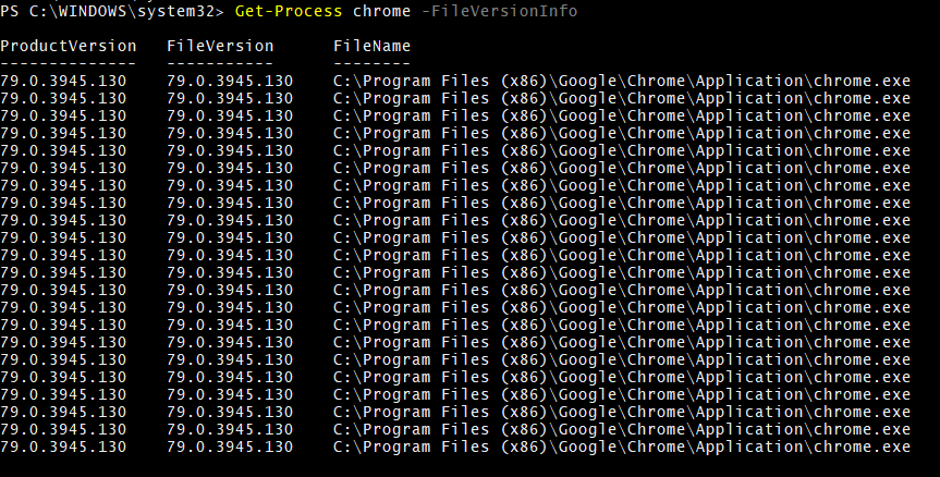
5. Get-Process with –FileVersionInformation
To get the File version of the specific process, use the below command.
Get-Process chrome -FileVersionInfo
Output:
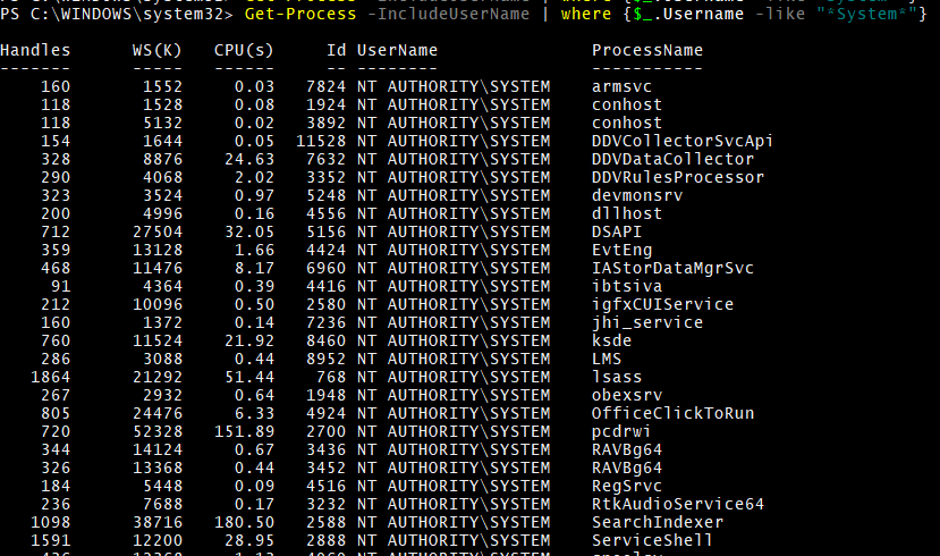
6. Get-Process with –IncludeUserName command
When you run the PowerShell with the administrator, you can see all the processes running with the different users.
Get-Process -IncludeUserName
To check the processes running with the specific user, you can filter the username.
For example, processes running by the System.
Get-Process -IncludeUserName | where {$_.Username -like "*System*"}
Output:
7. Get-Process with –ComputerName parameter
You can also use above all the commands for the remote system. To get the processes on the remote system, use –ComputerName parameter.
Get-Process -ComputerName Test-PC
To get the process with specific PID on a remote computer,
Get-Process –PID 12008 -ComputerName Test-PC
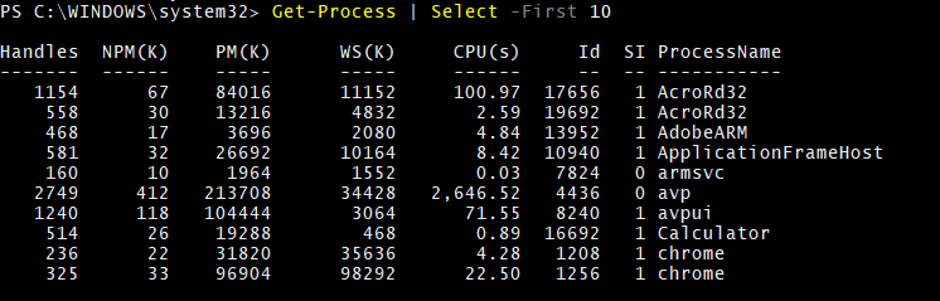
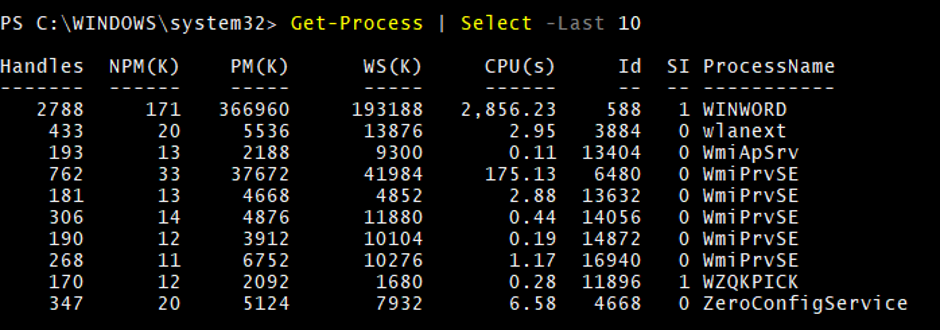
8. Restrict Get-Process displayed output
You can also restrict the number of processes to be displayed from the first and the last.
If you want to list out the first 10 processes then you can use the –First parameter with the Select command.
Get-Process | Select -First 10
Output:
To get the last 10 processes, use –the Last parameter.
Get-Process | Select -Last 10
Output:
9. Sorting Get-Process Output
You can sort the output of the Get-Process using, Sort-Object command.
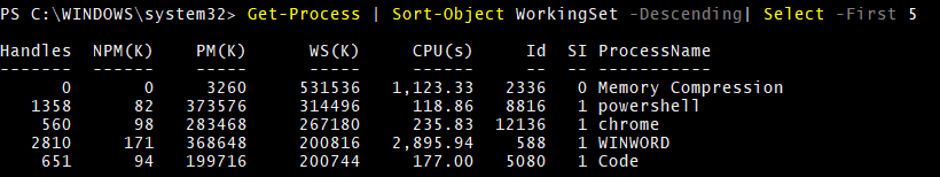
In the below examples, we will sort processes by its memory utilization (Working set) into Ascending and Descending orders and get the first 5 values.
Get-Process | Sort-Object WorkingSet | Select -First 5
The above output will be in ascending order. To sort the processes into descending order use –Descending parameter.
Get-Process | Sort-Object WorkingSet -Descending | Select -First 5
10. Group the processes
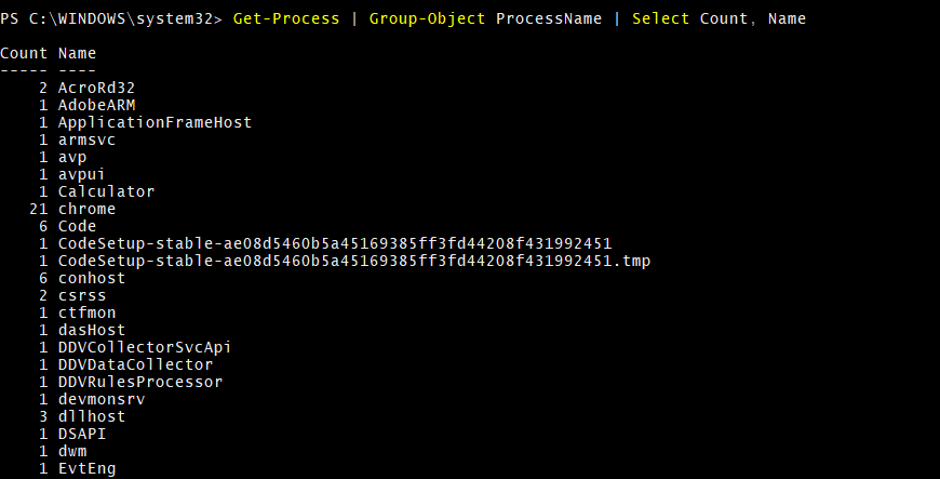
You can group similar processes with their name, so you can identify how many instances are running of the process.
Get-Process | Group-Object ProcessName | Select Count, Name
Conclusion
Get-Process is a great tool for system admins to monitor system performance. Admins can sort the output with CPU and memory utilization and with the command line, admins can find which processes are running by which particular application and the particular user. You can also pipeline Stop-Process command to stop the process(es).
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Get-Process. Here we discuss the introduction, Examples of Get-Process in Powershell and the Parameters along with Syntax & outputs. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –