Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to Powershell Parameter
A parameter is nothing but an input provided to a function or any cmdlet. Every parameter will have a name and a data type associated with it. It is always not necessary that parameters are mandatory. Some parameters may also have default values, and these values are used when a value for the parameter is not explicitly mentioned. For a function, the parameters are defined with the Param block. Mandatory parameters are defined using the [Parameter (Mandatory)] attribute. It is also possible to validate the value passed to each parameter using the ValidateSet property. Parameter names are always preceded by a hyphen (-), which denotes the PowerShell that the word after (-) is a parameter. This article will explain in detail about the parameters and their types in PowerShell, the various types of parameters, how to pass parameters to a function, etc., in detail.
Syntax of Powershell Parameter
The following example shows how to pass parameters to a cmdlet
Get-ChildItem -Path “C:\vignesh\test”
In the above example, the path is a parameter for the cmdlet, and the corresponding value of the parameter is enclosed within “”.
To define parameters for a function, the below format is used
param(
[Parameter()]
[string]$Testparameter1
[Parameter()]
[string]$Testparameter2
[Parameter()]
[int]$Testparameter3
)
Identifying the various parameters associated with a cmdlet:
To identify the various parameters that are available for a cmdlet, the below cmdlet can be used.
Get-Help CmdletName -Parameter *
Example:
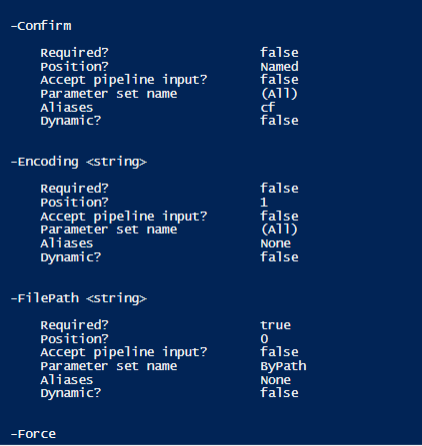
Get-Help out-file -Parameter *
Output:
The above shows the various parameters that are associated with the Out-File cmdlet. It also shows whether a parameter is a mandatory one, its position, aliases.
Attributes of a parameter
Here are the attributes of a parameter mentioned below
-Required
This denotes whether the parameter is a must for running this cmdlet. If this value is true for a parameter, then it means that this is a mandatory one. An error will be thrown if the appropriate value for that parameter is not passed.
-Position
Positional parameters are parameters that have its position set to a positive integer. When using this type of parameter, the parameter name is not required, but the parameter value must be mentioned in the appropriate position. If the position value is 0, then the parameter name is not required, but its value should be the first to appear after the cmdlets name. If the position setting is excluded, it can be defined anywhere in the cmdlet.
-Type
It denotes the type of the parameter like string, int, switches, etc.
-Default Value
This denotes the default value of the parameter when another value is not specified. For a required parameter, there is never a default value and is always supplied by the user. For many optional parameters, there are no default values as optional parameters don’t have much significance.
-Accepts Multiple Values
This denotes whether a parameter can accept multiple values. In case if multiple values are allowed, they are typed in a comma-separated and passed, or the values can be saved in a comma-separated way in a variable, and that variable can be passed as a value to the parameter.
-Accepts Pipeline Input
This denotes whether the pipeline can be passed as input to the parameter. If its value is false, it denotes the parameter doesn’t accept the pipeline for an input.
-Accepts Wildcard Characters
This denotes whether the parameter can use the wildcard to match characters.
Validation of Parameters
Below are some ways of validating the value that is passed to a parameter.
1. Making a parameter Mandatory and allowing Null Value
The mandatory parameter is used to denote whether a parameter compulsorily requires a value or not. AllowNull attribute is used to allow null values as a value.
Example:
Param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[AllowNull()]
[String]
$UserName
)
In the above, UserName is a mandatory parameter, and it accepts null for a value.
2. AllowEmptyString validation attribute
This attribute is used to allow empty string as a value to the mandatory parameter. The Allow Empty collection attribute is used to allow empty collection as a value to a mandatory string parameter.
Example:
Param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[AllowNull()]
[AllowEmptyCollection()]
[String]
$UserName
)
ValidateCount attribute is used to validate the number of values that can be passed to a parameter.
ValidateLenght attribute is used to specify the minimum and maximum length of the value that is passed to a parameter.
Validatepattern is used to match a regular expression with the value that is passed to the parameter.
ValdiateRange specifies a range in which the value of the variable must be.
ValidateSet denotes a set of values from which one of the values must be passed for the parameter. Value outside this set can’t be set to the parameter.
ValidateDrive is used to validate the value of a path parameter to a certain drive
Example:
Param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[AllowNull()]
[AllowEmptyCollection()]
[ValidateCount(5,50)]
[ValidateLength(10,20)]
[ValidatePattern("[1-9][0-4][4-9][1-4]")]
[ValidateDrive("C", "Function", "Drive")]
[String]
$UserName
)
Example:
Input:
Write-Host "Welcome to parameter example"
function test1()
{
Write-Host "Demo of function without any parameter"
Write-Host "Function without parameters is called"
}
#calling test1 function
test1
function test2($username)
{
Write-Host "Demo of Function with a single parameter"
Write-Host "the value of username supplied is" $username
}
#calling test2 function with parameter
test2 -username "Viki"
function test2
{
Param(
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[ValidateLength(1,30)]
[String]
$Name,
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[Int]
$age,
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[ValidateSet("Chennai", "Mumbai", "Delhi")]
[String]
$City
)
Write-Host "Demo of fucntion with multiple parameters"
Write-Host "The name supplied is" $Name
Write-Host "the age supplied is "$age
Write-Host "The city passed is " $City
}
#function calling
test2 -Name "Vignesh" -age 28 -City Chennai
function test3
{
Param(
[parameter(position=1)]
[ValidateLength(1,30)]
[String]
$Name,
[parameter(position=2)]
[Int]
$age,
[parameter(position=3)]
[ValidateSet("Chennai", "Mumbai", "Delhi")]
[String]
$City
)
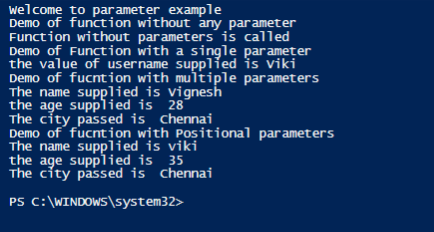
Write-Host "Demo of fucntion with Positional parameters"
Write-Host "The name supplied is" $Name
Write-Host "the age supplied is "$age
Write-Host "The city passed is " $City
}
#function calling
test3 "viki" 35 "Chennai"
Output:
Conclusion – Powershell Parameter
Thus, the article covered in detail about parameters in PowerShell. It covered various types of parameters, various attributes that are associated with a parameter, different parameter types, mandatory and non-mandatory parameters, validation of parameters, etc. To learn more in detail about the parameters, it is advisable to write sample scripts and execute them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Powershell Parameter. Here we discuss the attributes of a parameter and some ways of validating the value that is passed to a parameter. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –