Updated February 28, 2023

Introduction to PowerShell Grep
Grep command is not a PowerShell cmdlet. It is a command used in Linux/Unix which allows the user to filter based on various patterns. The same is achieved in PowerShell via the Select-String cmdlet. It can be considered as the GREP equivalent in windows. Select-String is used for comparing text and patterns in both files as well as input string. It uses regular expression for matching purposes. It searches for patterns on a line by line basis. Whenever a match is found on a line, corresponding file name, line number and the match are printed. While searching, if the user wants a encoding to be used for comparison even that can be specified.
Syntax
The below is the syntax of Select-String:
NAME
Select-String
SYNTAX
Select-String [-Pattern] <string[]> [-Path] <string[]> [-SimpleMatch] [-CaseSensitive] [-Quiet] [-List] [-Include <string[]>] [-Exclude <string[]>] [-NotMatch]
[-AllMatches] [-Encoding {unicode | utf7 | utf8 | utf32 | ascii | bigendianunicode | default | oem}] [-Context <int[]>] [<CommonParameters>]
Select-String [-Pattern] <string[]> -InputObject<psobject> [-SimpleMatch] [-CaseSensitive] [-Quiet] [-List] [-Include <string[]>] [-Exclude <string[]>] [-NotMatch]
[-AllMatches] [-Encoding {unicode | utf7 | utf8 | utf32 | ascii | bigendianunicode | default | oem}] [-Context <int[]>] [<CommonParameters>]
Select-String [-Pattern] <string[]> -LiteralPath<string[]> [-SimpleMatch] [-CaseSensitive] [-Quiet] [-List] [-Include <string[]>] [-Exclude <string[]>] [-NotMatch]
[-AllMatches] [-Encoding {unicode | utf7 | utf8 | utf32 | ascii | bigendianunicode | default | oem}] [-Context <int[]>] [<CommonParameters>]
ALIASES
sls
Parameters
Below are the different parameters of PowerShell Grep
1. -AllMatches: This denotes that all matching patterns in each line must be returned. Without this, Select-String matches only the first matching pattern in a line. Its type is switch parameter. Its default value is false. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters are not accepted.
2. -CaseSensitive: It denotes that a case sensitive match must be performed. By default, the matches are case-insensitive. Its type is switch parameter. Its default value is false. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters are not accepted.
3. -Context: This captures the number of lines before a match is found and the number of lines that there after the match. If only a single number is mentioned, that number determines the lines before and after the match. If two numbers are mentioned, first number denotes the number of lines before the match and the number of lines after the match is determined by the second number. Its type is int32[]. Its default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters are not accepted.
4. -Culture: It denotes the culture name to be used for matching purpose. To get a list of available cultures the Get-Culture -ListAvailable cmdlet can be used. It was first introduced with PowerShell 7. Its type is string. Default value is the culture value of the current PS session. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters are not accepted.
5. -Encoding: It denotes the target files encoding type. The default encoding type is UTF8NoBOM. The other accepted values are ASCII, BigEndianUnicode, OEM, Unicode, UTF7, UTF8, UTF8BOM, UTF8NoBOM, UTF32. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters are also not accepted.
6. -Exclude: This denotes the list of items that needs to be excluded from matching. It can be a path or a pattern. Its type is String []. Its default value is none. It can accept wild card characters whereas pipeline input is not allowed.
7. -Include: This denotes the list of items that needs to be included for matching. It can be a path or a pattern. Its type is String []. Its default value is none. It can accept wild card characters whereas pipeline input is not allowed.
8. -InputObject: It denotes the text to be searched. It can either be a variable that holds a text or an expression. Its type is PSObject. Its default value is none. It accepts pipeline input whereas wild card characters are not accepted.
9. -List: When this is used, only the first instance of matching is considered and returned for each file. Its type is switch parameter. Its default value is false. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters are also not allowed.
10. -LiteralPath: It denotes the path of the files to be searched. The value is same as how it is typed. No wild card characters are allowed, if the path has special characters it must be enclosed in single quotes. Its type is string []. Its aliases are PSPath and LP. Its default value is none. It accepts pipeline input, but wild card characters are not accepted.
11. -NoEmphasis: Select-String by default that matches the search pattern, to disable the highlighting this parameter is used. This was first introduced in PowerShell 7. Its type is switch parameter. Its default value is false. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters are not accepted.
12. -Pattern: This denotes that pattern that needs to be searched for. Its treated as a regular expression. Its type is String []. Its default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters are also not allowed.
13. -Path: It denotes the path of the files to be searched. Its default value is current directory. It accepts pipeline input; also, wild card characters are accepted.
14. -NotMatch: It is used to find the non-matching occurrence. Its type is switch parameter. Its default value is false. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters are also not allowed.
Example of PowerShell Grep
Given below is the example:
Code:
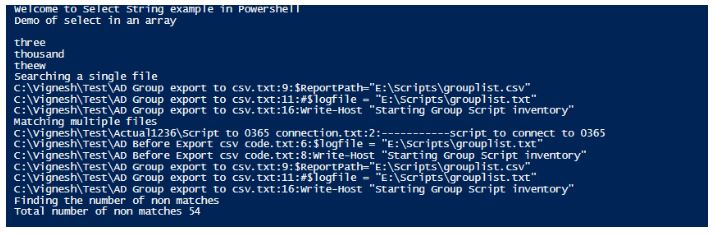
Write-Host "Welcome to Select String example in Powershell"
$input=@("one","two","three","four","ttt","thousand","theew")
Write-Host "Demo of select in an array"
$input| Select-String -Pattern 'th'
Write-Host "Searching a single file"
Select-String -Pattern Scri -Path "C:\Vignesh\Test\AD Group export to csv.txt"
Write-Host "Matching multiple files"
Get-ChildItem C:\Vignesh\Test\*.txt -Recurse |Select-String -Pattern Scri
Write-Host "Finding the number of non matches"
$result=Select-String -Pattern Scri -NotMatch -Path "C:\Vignesh\Test\AD Group export to csv.txt"
Write-Host "Total number of non matches" $result.Count
Output:
Conclusion
Thus, the article explained in detail how grep can be achieved in PowerShell using Select-String cmdlet. It explained about the various types of parameters that are available for the cmdlet along with appropriate example.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Grep. Here we discuss the introduction and example of PowerShell Grep. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

