Introduction to PowerShell Get-ADUser
The Get-ADUser cmdlet is used to fetch information about one or more active directory users. A user can be identified by using several parameters like his distinguished name, the corresponding GUID in active directory, Security Identifier, or SAM(Security Account Manager) name. To fetch multiple user’s information Filter or LDAPFilter can be used. PowerShell expression language is used by the filter parameters to fetch information from the Active Directory. This article will cover in detail about this cmdlet along with appropriate explanations and examples.
Syntax and Parameters
Syntax and parameters of Powershell get-ADUser are given below:
Syntax:
Get-ADUser [-AuthType <ADAuthType>] [-Credential <PSCredential>] -Filter <String> [-Properties <String[]>] [-ResultPageSize <Int32>] [-ResultSetSize <Int32>] [-SearchBase <String>] [-SearchScope <ADSearchScope>] [-Server <String>] [<CommonParameters>]
Get-ADUser [-AuthType <ADAuthType>] [-Credential <PSCredential>] [-Identity] <ADUser> [-Partition <String>] [-Properties <String[]>] [-Server <String>] [<CommonParameters>]
Get-ADUser [-AuthType <ADAuthType>] [-Credential <PSCredential>] -LDAPFilter <String> [-Properties <String[]>] [-ResultPageSize <Int32>] [-ResultSetSize <Int32>] [-SearchBase <String>] [-SearchScope <ADSearchScope>] [-Server <String>] [<CommonParameters>]
Parameters:
Parameters of Powershell get-aduser are
- -AuthType: This denotes the authentication method to be used to connect to Active directory. It can be either of two values, negotiate also can be referred to as 0 or Basic otherwise can be referred to as 1. Negotiate is the default used authentication mode. For basic authentication to work, an SSL connection is required. The type of param is ADAuthType. It doesn’t accept pipeline input; wildcard characters are also not allowed.
- -Credential: This refers to the user account that will be used to run the cmdlet. By default, the credentials of the current user are considered unless the cmdlet is run from the drive of the Active Directory. In such a scenario, the account that is associated to the drive is considered. Either username or PSCredential object is supplied as value to the parameter. In case if a username is specified, a prompt is given for a password. The account specified should have directory-level permission else the cmdlet will fail throwing an error. Its type is PSCredential. The parameter can not accept pipeline input and wild card characters are also not allowed.
- -Filter: This denotes the query that is used to fetch the objects from the active directory. It uses the syntax of PowerShell express language. PowerShell express language has good type-conversion support. Its type is a string and the default value is none. This parameter doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters are also not supported.
- -Identity: This is a mandatory parameter. This denotes the Active directory user whose details should be fetched. The following values can be passed as the identity parameter. A unique name, GUID of the user in the Active directory, SID or SAM account name. The type of this parameter is ADUser. Its default value is none. This parameter accepts pipeline input but doesn’t permit wild card characters.
- -LDAPFilter: This denotes the LDAP query that is used for filtering purposes. The filter parameter is like LDAP syntax. Its type is a string. Both the input pipeline and wild card characters are not supported by this parameter.
- -Partition: This refers to an Active Directory partition. It must be the name of one of the current directory servers. This partition is searched to identify the object that is referred by the identity parameter. If no value is specified, the default value is used. If the value passed to the identity parameter is a distinguished name, the default value is automatically generated from this and treated as the partition name. If the cmdlets are run from the active directory provider, the current path in the drive is treated as the default value of the partition. The data type for this parameter is a string and the default value is none. Both pipeline input and wild card characters are not accepted by this parameter.
- -Properties: This denotes the list of properties of the Active Directory object to be returned. To retrieve multiple properties, separate them using a comma. To retrieve all properties, use the *. The data type of this parameter is a string[]. The default value is none. Both pipeline input and wild card characters are not accepted by this parameter.
- -ResultPageSize: This denotes the number of objects to be present in a single page of the query results. Its type is int32. The default is 256. Both pipeline input and wild card characters are not accepted by this parameter.
- -ResultSetSize: This denotes the maximum number of objects that should be returned by the query. If all the properties need to be returned, the null value must be passed to this parameter. Its data type is int32. Both pipeline input and wild card characters are not accepted by this parameter.
- -SearchBase: This denotes the AD path under which the search for the specified object must occur. If the cmdlet is run from the active directory drive, the current path of the drive is considered as the default value. If the cmdlet is run from outside, then the targets drive is taken as default value. The data type is a string and the default value is none. Both pipeline input and wild card characters are not accepted by this parameter.
- -SearchScope: This denotes the scope of the search for the AD object. It has three values. Base or 0, one level or 1 and subtree or 2. Base scope searches only for the mentioned user. One level search for the children of an object, subtree searches for all children of the mentioned object.
- -Server: This denotes the active directory to connect to. The domain values can be either of FQDN or netbios name. The default value can be either the domain where the cmdlet is run or the active directory drive server or the one that is passed to the parameter.
Example of PowerShell Get-ADUser
Example of Powershell get-aduser are given below:
Input:
Write-Host "Welcome to the Get user from ad example"
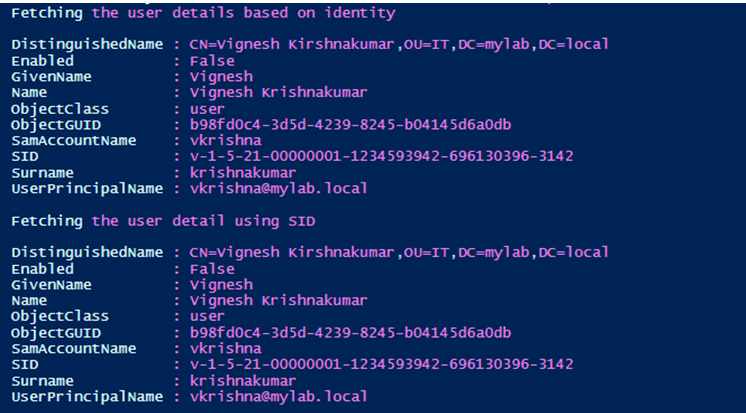
write-host "Fetching the user details based on identity"
Get-ADUser -Identity vkrishna
Write-Host "Fetching the user detail using SID"
Get-ADUser -Identity 'v-1-5-21-00000001-1234593942-696130396-3142'
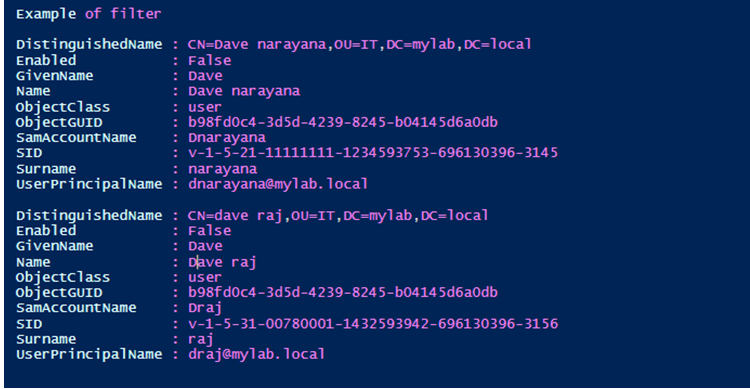
write-host "Example of filter"
Get-AdUser -Filter "givenName -eq 'Dave'"
Output:
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Get-ADUser. Here we also discuss the syntax and parameters of Powershell get-aduser along with an example and its code implementation. you may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –