Updated March 3, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Delete File
In PowerShell Delete File, to delete items in a PowerShell the Remove-Item cmdlet can be used. This cmdlet is used not only to remove files but also folders, functions, registry keys, etc. One of the most important works of a system administrator is to ensure that there is enough space on the drive and this process is referred to as housekeeping. These kinds of activities can be automated using a script that will delete files based on certain conditions. This article will cover in detail how the files can be deleted using Remove-Item cmdlet and how it can be automated.
Syntax
Below is the syntax of PowerShell Delete File:
Remove-Item[-Path] <String[]>[-Filter <String>][-Include <String[]>][-Exclude <String[]>][-Recurse][-Force] [-Credential <PSCredential>][-WhatIf][-Confirm][-Stream <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>]
Remove-Item-LiteralPath <String[]>[-Filter <String>][-Include <String[]>][-Exclude <String[]>][-Recurse][-Force][-Credential <PSCredential>][-WhatIf] [-Confirm][-Stream <String[]>][<CommonParameters>]
Parameters
Below are the Parameters:
Confirm: An affirmation is appeared to the client before running the cmdlet. The information sort of this parameter is a switch. It is alluded by the assumed name cf. The default esteem is none. The parameter doesn’t acknowledge pipeline input and wild card characters are moreover not allowed.
Exclude: The values provided to this parameter will not be considered while executing the cmdlet. This is generally considered as the path parameter’s value. It allows wild card characters to be passed. This can be used only when the cmdlet is run using a wild card and not for a specific file or item. The information sort of this parameter is String[]. The default esteem is none. The parameter doesn’t acknowledge pipeline input whereas wild card characters are allowed.
Filter: This is used to filter the objects against which the cmdlet can be run. This is efficient because it applies the filter in the beginning rather than after fetching all the objects. The information sort of this parameter is String. The default esteem is none. The parameter doesn’t acknowledge pipeline input whereas wild card characters are allowed.
Force: Powers the cmdlet to evacuate things that cannot something else be changed, such as covered up or read-only records or read-only nom de plumes or factors. The cmdlet cannot evacuate variables and aliases which have constant values. The implementation differs based on the provider. Indeed, utilizing the Drive parameter, the cmdlet cannot abrogate security limitations. The information sort of this parameter is the switch. The default esteem is none. The parameter doesn’t acknowledge pipeline input and wild card characters are not permitted.
Include: The values provided to this parameter will only be considered while executing the cmdlet. This means the objects that are represented by this parameter only will not be deleted. This can be used only when the cmdlet is run using a wild card and not for a specific file or item. The information sort of this parameter is String[]. The default esteem is none. The parameter doesn’t acknowledge pipeline input whereas wild card characters are allowed.
LiteralPath: Indicates a way to one or more locations. The esteem of LiteralPath is utilized precisely because it is written. Single quotes are used to differentiate the escape sequences. The value of this parameter should be provided as to how it appears in its properties. The information sort of this parameter is String[]. It is alluded by the assumed namesPSPath and LP. The default esteem is none. The parameter acknowledges pipeline input and wild card characters are not allowed.
Path: This refers to the path in which the items to be deleted are present. The information sort of this parameter is String[]. The default esteem is none. The parameter acknowledges pipeline input and wild card characters are also allowed.
Recurse: If the specified path has some folders and subfolders, this denotes that those child items also need to be considered while performing the operation. This however doesn’t work well with include parameter which is a known one. The information sort of this parameter is a switch. The default esteem is none. The parameter doesn’t acknowledge pipeline input and wild card characters are also not allowed.
Stream: This parameter is only used within file system drives. The information sort of this parameter is a string[]. The default esteem is none. The parameter doesn’t acknowledge pipeline input whereas wild card characters are allowed.
Examples to Implement PowerShell Delete File
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Code:
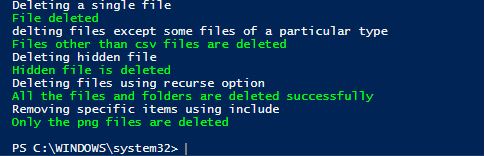
Write-Host "Deleting a single file"
#Remove-Item -Path "C:\Vignesh\Test\AD Group export to csv.txt"
Write-Host "File deleted" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host "delting files except some files of a particular type"
#Remove-Item -Path "C:\Vignesh\Test\*" -Exclude *.csv
Write-Host "Files other than csv files are deleted" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host "Deleting hidden file"
#Remove-Item -Path "C:\vignesh\Test\Path.csv" -Force
Write-Host "Hidden file is deleted" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host "Deleting files using recurse option"
#Remove-Item -Path "C:\vignesh\Test" -Recurse
Write-Host "All the files and folders are deleted successfully" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host "Removing specific items using include"
#Remove-Item -Path "C:\Vignesh\New folder\*" -Include *.png
Write-Host "Only the png files are deleted" -ForegroundColor Green
Output:
Example #2
Automating files to be deleted:
Code:
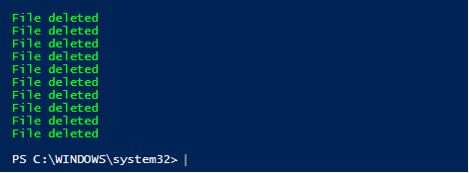
Write-Host"Deleting files greater than 60 days"
Get-ChildItem–Path"C:\logs"-Recurse|Where-Object {($_.LastWriteTime -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-60))} |Remove-Item
Write-Host"File deleted"-ForegroundColorGreen
Write-Host"Deleting files that are greater than 1000 mb"
$path="C:\vignesh\logs"
$allowedsize=1000
$fsize= (Get-ChildItem$path|Measure-Object-propertylength-sum)
$Sizeinmb="{0:N2}"-f ($fsize.sum /1MB) +"MB"
if ($Sizeinmb-ge$allowedsize) {
Get-ChildItem$path-Recurse|Remove-Item–Force
Write-Host"File deleted"-ForegroundColorGreen
}
Output:
Explanation: The above script deletes files that are older than 60 days and files that are greater than 1000 MB. The above script can be automated to run daily by creating a task in the task scheduler.
Conclusion
Thus, the article explained in detail about deleting files in PowerShell. It also explained the various scenarios of include and exclude that can be used while deleting files. It also showed how to automate the delete operation using a script and task scheduler. To learn more in detail it is advisable to write sample programs and practice them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Delete File. Here we discuss an introduction to PowerShell Delete File, syntax with parameters, examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –