Updated May 23, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Count
The following article provides an outline for PowerShell Count. In our day-to-day activities, there are multiple scenarios in which we need to find out the count. It might be anything from how many files are kept in a location to the number of active and inactive users, the amount of error messages reported in a day, files older than a date, and so on. In any of these instances, the count can be obtained using the Measure-Object or the count method.
Syntax of Measure Object
The measure-object cmdlet calculates the number of lines, characters, and words in a file, along with the numerical properties of objects. It can perform three types of calculations based on the parameters available as part of a cmdlet. It can count the number of things or objects of a specific category. It can perform arithmetic operations like minimum, maximum, and average numbers. If the object is of string value number of characters or words can be calculated.
Example:
Code:
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\vignesh\Test | Measure-Object -Property LastAccessTime
Output:
Parameters:
- Allstate: This denotes all the data of the mentioned properties. The data type of this parameter is the switch parameter, and the default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wild card characters are also not specified.
- Average: This parameter calculates the average value of the mentioned properties. Its type is the switch parameter. The default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wild card characters are also not specified.
- Character: This parameter returns the number of characters in the specified input objects. Its type is the switch parameter. The default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wild card characters are also not specified.
- IgnoreWhiteSpace: To avoid utilizing this parameter, white spaces are taken into account when determining the number of characters by default. Its type is a switch. The default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wild card characters are also not specified.
- Input Object: It denotes the measurement items. When this parameter is provided, the input objects are processed as a single entity instead of being given to the pipeline. PSObject is its type. None is the default value. Pipeline input is accepted, but wild card characters are not.
- Line: This will return the number of lines in the specified input. Its type is the switch parameter. The default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wild card characters are prohibited.
- Maximum: This will return the maximum value of the mentioned properties or objects. Its type is the switch parameter. The default value is none.
- Minimum: This will return the minimum value of the mentioned properties or objects. Its type is the switch parameter. The default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wild card characters are prohibited.
- Property: This denotes the specified properties to measure. If no properties are specified, all the properties are returned. The data type is PSPropertyExpression[]. The default value is none.
- Standard deviation: This will return the average deviation value of the mentioned properties or objects. Its type is the switch parameter. The default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wild card characters are prohibited.
- Sum: This will return the properties or objects’ total value. Its type is the switch parameter. The default value is none. It does not accept pipeline input and does not allow wildcard characters.
- Word: This will return the total number of words in the input. Its type is the switch parameter. The default value is none. It does not accept pipeline input and does not allow wildcard characters.
Example of PowerShell Count
Given below is the example mentioned:
Code:
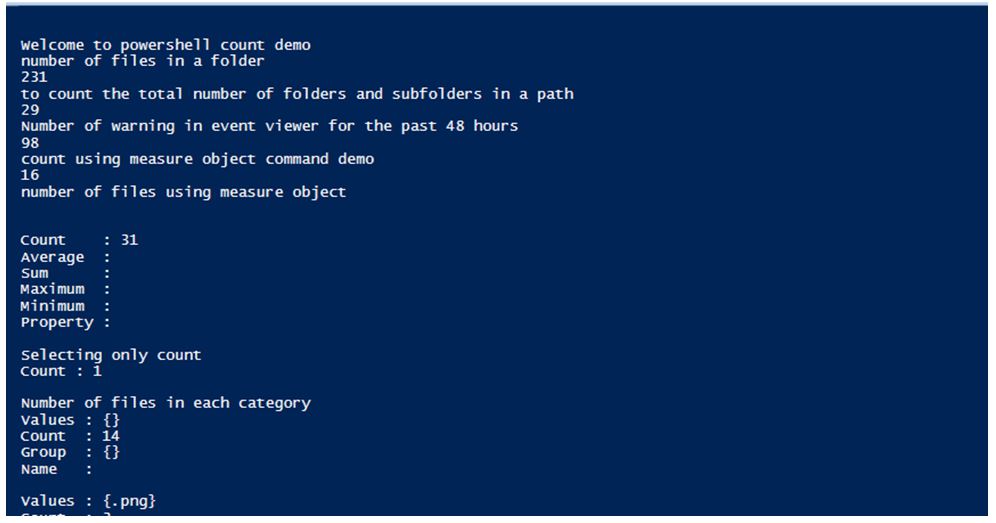
Write-Host "Welcome to powershell count demo"
Write-Host "number of files in a folder"
(Get-ChildItem -Path C:\vignesh -Recurse | Where-Object{ $_}).count
Write-Host "to count the total number of folders and subfolders in a path"
(Get-ChildItem -Path C:\vignesh -Recurse | Where-Object{ $_.PSIsContainer }).count
Write-Host "Number of warning in event viewer for the past 48 hours"
(Get-EventLog -LogName System -After ((Get-Date).AddDays(-2)) | Where-Object {$_.EntryType -eq "Warning"}).count
Write-Host "count using measure object command demo"
(Get-ChildItem -Path "C:\vignesh\test" | Measure-Object | Select-Object Count).count
Write-Host "number of files using measure object"
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\vignesh\Test -Recurse | Where-Object{ !($_.PSIsContainer) } | Measure-Object
Write-Host "Selecting only count"
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Vignesh\Test\Actual1239 | Measure-Object | Select-Object Count
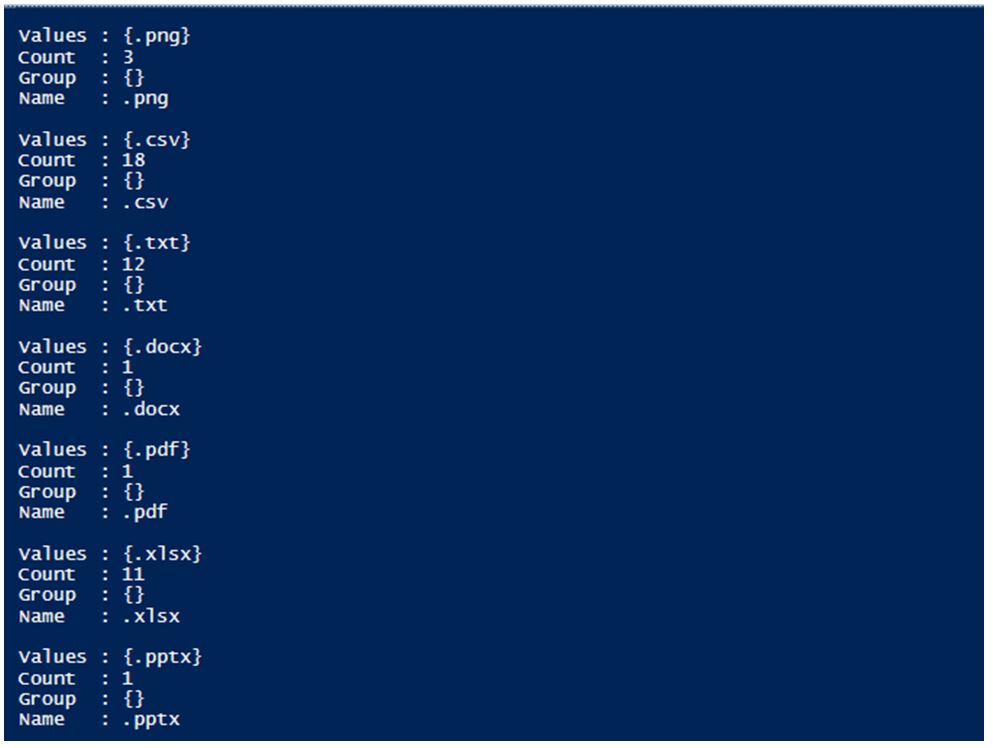
Write-Host "Number of files in each category"
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\vignesh | Group-Object Extension -NoElement
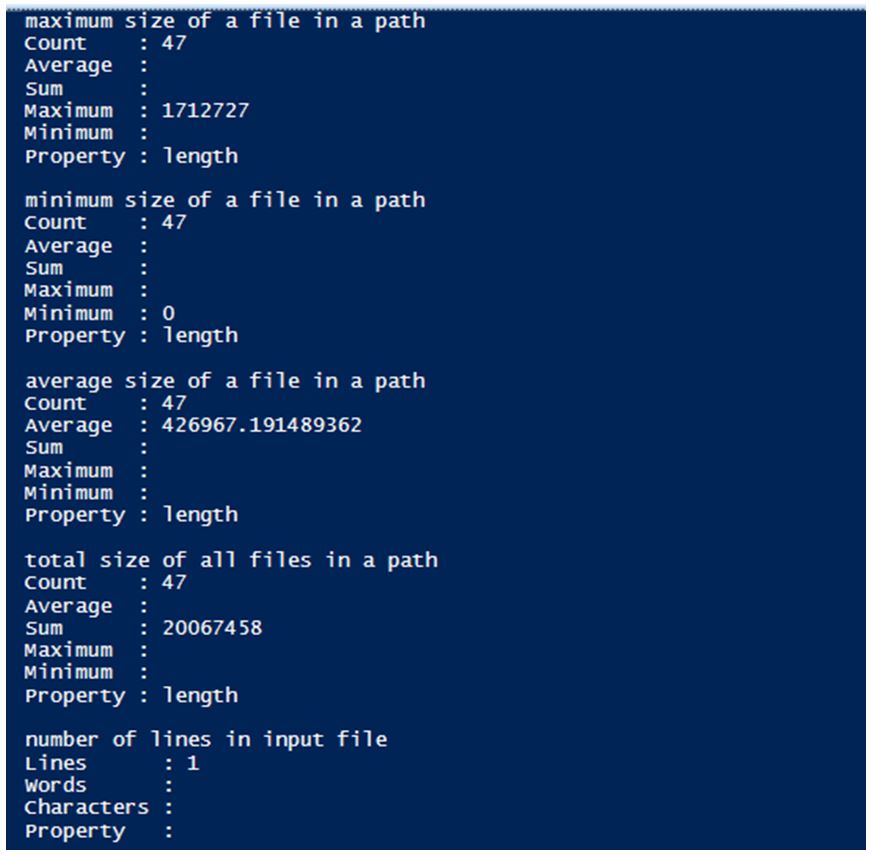
Write-Host "maximum size of a file in a path"
Get-ChildItem -Path c:\vignesh | Measure-Object -Property length -Maximum
Write-Host "minimum size of a file in a path"
Get-ChildItem -Path c:\vignesh | Measure-Object -Property length -Minimum
Write-Host "average size of a file in a path"
Get-ChildItem -Path c:\vignesh | Measure-Object -Property length -Average
Write-Host "total size of all files in a path"
Get-ChildItem -Path c:\vignesh | Measure-Object -Property length -Sum
Write-Host "number of lines in input file"
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Vignesh\KB.txt |Measure-Object -Line
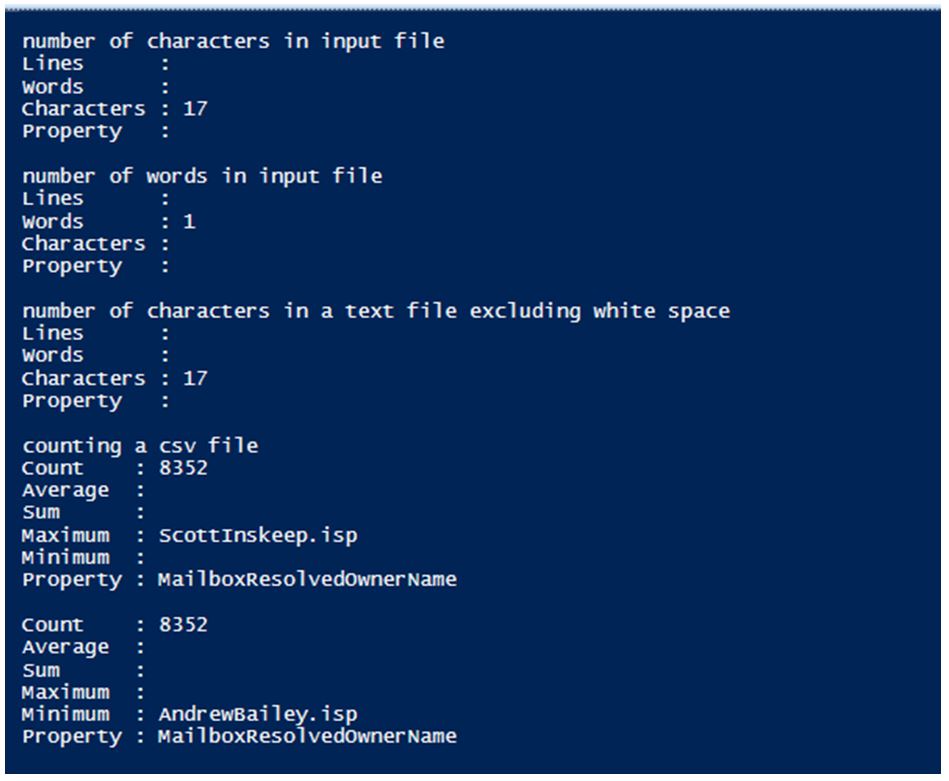
Write-Host "number of characters in input file"
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Vignesh\KB.txt |Measure-Object -Character
Write-Host "number of words in input file"
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Vignesh\KB.txt |Measure-Object -Word
Write-Host "number of characters in a text file excluding white space"
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Vignesh\KB.txt |Measure-Object -IgnoreWhiteSpace -Character
Write-Host "counting a csv file"
Import-Csv C:\vignesh\July3.csv | Measure-Object -Property MailboxResolvedOwnerName -Maximum
Import-Csv C:\vignesh\July3.csv | Measure-Object -Property MailboxResolvedOwnerName -Minimum
Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we explored the usage of the count operation in PowerShell on different objects, including file objects and other types of commands. We discussed the various approaches to utilizing the count object or Measure object cmdlet. The article provided numerous examples showcasing how count can be applied in various scenarios.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Count. Here we discuss the introduction to PowerShell Count along with examples respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –