Updated May 10, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Window Functions
PostgreSQL window functions are used to compare and contrast data, and it is a key to analytic and various use cases in PostgreSQL. The window function in PostgreSQL is used to compare the values between current rows and related to the current rows from all values of a table. PostgreSQL window function is a part of SQL standard and is used in practical when finding the first time user login action of any performed action. We have used the window function in order by clause to distinguish the data in ascending or descending order.
Window Function available in PostgreSQL
Below is the window function available are as follows:
- Row number()
- Rank()
- Dens rank()
- Percent rank()
- Cume dist()
- Ntile()
- Lag()
- Lead()
- First value()
- Last value()
- Nth value()
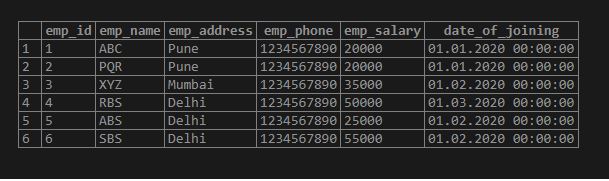
We discuss the above function, one by one, are as follows. We have using the employee table to describe an example of the PostgreSQL window function. Below is the employee table data description are as follows.
Example of employee table to describe an example of an employee table in PostgreSQL
1. lag()
The PostgreSQL lag () function is a function that a row that will come before the current rows as an output or a specified query offset.
Below is the syntax of the lag () function in PostgreSQL are as follows.
Code:
LAG(expression[,[, default_value]]) OVER ([PARTITION BY partition_expression... ]
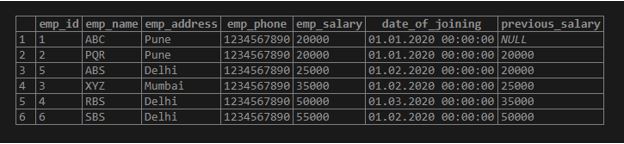
ORDER BYsort_expression [ASC | DESC], ...)Below is an example of a lag () function in PostgreSQL are as follows.
Code:
SELECT *,LAG (emp_salary,1) OVER (ORDER BY emp_salary ASC) AS previous_salary FROM Employee;Output:
2. Lead()
A lead function is used to compare the value if records between the current row and the value of the record which following a current row.
Below is the syntax of the lead () function in PostgreSQL are as follows.
Code:
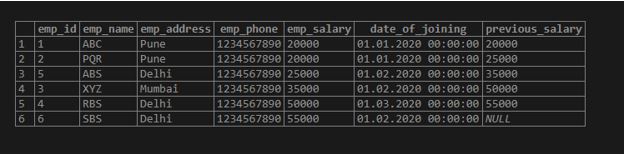
LEAD (expression[,offset [, default_value]]) OVER ( [PARTITION BY partition_expression (Partition column name), ... ] ORDER BY sort_expression [ASC | DESC], ...)Below is an example of a lead () function in PostgreSQL are as follows.
Code:
SELECT *,LEAD (emp_salary,1) OVER (ORDER BY emp_salary ASC) AS previous_salary FROM Employee;Output:
3. Rank()
A rank window function defines the rank of the defined column in PostgreSQL. The rank function is very useful and important in PostgreSQL to define rank.
Below is the syntax of the rank () function in PostgreSQL are as follows.
Code:
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, column_nameN, rank() OVER (PARTITION BY column_name ORDER BY column_name DESC) FROM table_name;Below is an example of a rank () function in PostgreSQL are as follows.
Code:
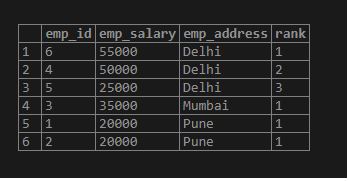
SELECT emp_id, emp_salary, emp_address, rank() OVER (PARTITION BY emp_address ORDER BY emp_salary DESC) FROM employee;Output:
4. Row_number()
The row_number function is very useful and important in PostgreSQL to define the row number of a column.
Below is the syntax of the row number () function in PostgreSQL as follows.
Code:
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, column_nameN, row_number () OVER (PARTITION BY column_name ORDER BY column_name DESC) FROM table_name;Below is an example of the row number () function in PostgreSQL as follows.
Code:
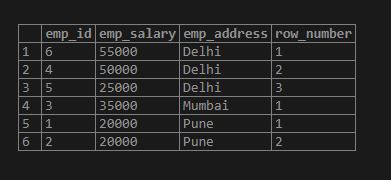
SELECT emp_id, emp_salary, emp_address, row_number() OVER (PARTITION BY emp_address ORDER BY emp_salary DESC) FROM employee;Output:
5. Dense rank()
A dense rank function is very useful and important in PostgreSQL to define the rank of the column.
Below is the syntax of the Dense rank () function in PostgreSQL is as follows.
Code:
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, column_nameN, dense_rank () OVER (PARTITION BY column_name ORDER BY column_name DESC) FROM table_name;Below is an example of the Dense rank () function in PostgreSQL as follows.
Code:
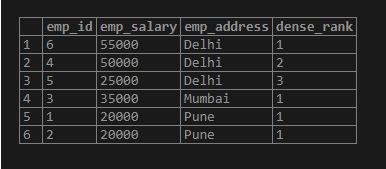
SELECT emp_id, emp_salary, emp_address, Dense_rank () OVER (PARTITION BY emp_address ORDER BY emp_salary DESC) FROM employee;Output:
6. Ntile()
Ntile function is very useful and important in PostgreSQL.
Below is the syntax of ntile() function in PostgreSQL as follows.
Code:
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, column_nameN, ntile (Argument) OVER (PARTITION BY column_name ORDER BY column_name DESC) FROM table_name;Below is an example of ntile() function in PostgreSQL as follows.
Code:
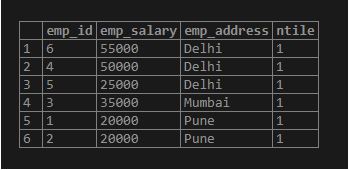
SELECT emp_id, emp_salary, emp_address, ntile(1) OVER (PARTITION BY emp_address ORDER BY emp_salary DESC) FROM employee;Output:
7. Percent rant()
Percent rank function is very useful and important in PostgreSQL.
Below is the syntax of the percent rank() function in PostgreSQL are as follows.
Code:
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, column_nameN, percent_rank () OVER (PARTITION BY column_name ORDER BY column_name ASC) FROM table_name;Code:
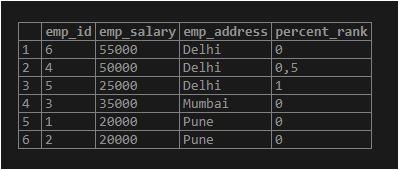
SELECT emp_id, emp_salary, emp_address, percent_rank() OVER (PARTITION BY emp_address ORDER BY emp_salary DESC) FROM employee;Output:
8. Cume dist()
Cume dist function is very useful and important in PostgreSQL.
Code:
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, column_nameN, cume_dist () OVER (PARTITION BY column_name ORDER BY column_name ASC) FROM table_name;Code:
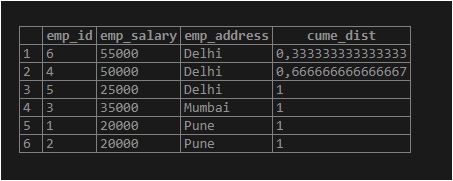
SELECT emp_id, emp_salary, emp_address, cume_dist() OVER (PARTITION BY emp_address ORDER BY emp_salary DESC) FROM employee;Output:
9. First Value()
The first value function is very useful and important in PostgreSQL.
Code:
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, column_nameN, first_value (value) OVER (PARTITION BY column_name ORDER BY column_name ASC) FROM table_name;Code:
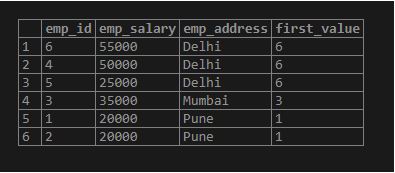
SELECT emp_id, emp_salary, emp_address, first_value(emp_id) OVER (PARTITION BY emp_address ORDER BY emp_salary DESC) FROM employee;Output:
10. Last value()
The last value function is very useful and important in PostgreSQL.
Code:
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, column_nameN, last_value (value) OVER (PARTITION BY column_name ORDER BY column_name ASC) FROM table_name;Code:
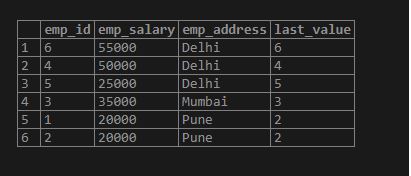
SELECT emp_id, emp_salary, emp_address, last_value(emp_id) OVER (PARTITION BY emp_address ORDER BY emp_salary DESC) FROM employee;Output:
11. Nth value()
The last value function is very useful and important in PostgreSQL.
Code:
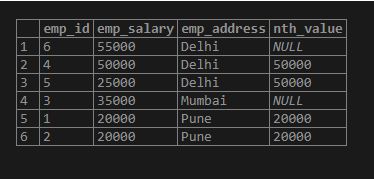
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, column_nameN, nth_value (column_name, value) OVER (PARTITION BY column_name ORDER BY column_name ASC) FROM table_name;Code:
SELECT emp_id, emp_salary, emp_address, nth_value(emp_salary, 2) OVER (PARTITION BY emp_address ORDER BY emp_salary DESC) FROM employee;Output:
Conclusion
PostgreSQL window functions are used to compare and contrast data, and it is a key to analytic and various use cases in PostgreSQL. The window function in PostgreSQL is used to compare the values between current rows and related to the current rows from all values of a table.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Window Functions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.