Updated May 19, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL, where in array
PostgreSQL provides different types of data types. Array is one type of data type which one provided by PostgreSQL (Array is multidimensional with variable length). Array is used where clause to select the specific column from a database table, the array is a user-defined data type or built-in data type. PostgreSQL provides a facility to define columns as an array with any valid data type, the array should be integer [] type, character [] type, or user-defined data type. Sometimes we need to create our own data type. At that time, PostgreSQL created an equivalent array data type in the backend. We can perform different operations using where in the array.
Syntax:
select column name 1, column name 2,…………. columnN from table name where condition;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use to select and where clause, where column name 1 and column name 2 are column names that we want to show, where the table name is the specified table name, and we apply condition using the where clause.
How to use where in array in PostgreSQL?
- We must install PostgreSQL in our system.
- Require basic knowledge of PostgreSQL.
- We must require a database table to perform where in the array.
- Must need basic knowledge about the array, that means how it is used.
- We can perform different operations on users with the help of psql and pgAdmin.
1. Operation of where in array
Before the implementation of the where clause in the array, we need a table to implement where in the array.
So let’s see how we can create tables using array data type.
Syntax:
create table table name(column name 1 data type [], column name 2 data type [],…………………… column name N data type []);Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use create table statement, where the table name is used for specified table name and column name 1, column name 2 is defined with different array data types.
Example:
Code:
create table emp(emp_id serial PRIMARY KEY, emp_name varchar (100),emp_dept varchar [], emp_phones text []);Explanation:
- In the above example, where create table is a statement, emp is a table name, and we created an emp table with four columns such as emp_id, emp_name, emp_dept, and emp_phones with different array data types.
Now we insert records into the database table by using the following insert into statement.
Code:
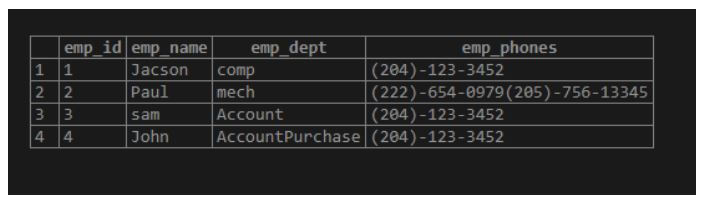
Insert into emp (emp_name, emp_dept, emp_phones) Values
('Jacson', '{"comp"}' , '{"(204)-123-3452"}'),
('Paul', '{"mech"}', '{"(222)-654-0979","(205)-756-13345"}'),
('sam', '{"Account"}','{"(204)-123-3452"}'),
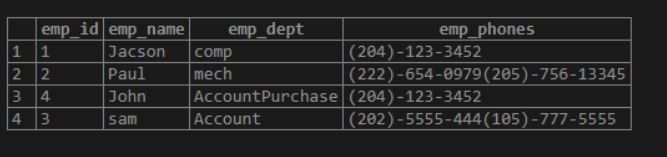
('John', '{"Account", "Purchase"}','{"(204)-123-3452"}');select * from emp;Explanation:
- In the above example, suppose the user needs to insert records into the table. At that time, we use the above statement to insert.
- In the above example, the employee Paul has two contact number, employee John works in two departments such as Account and Purchase.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
2. Display operation using where in array
Suppose the user needs to display a single phone number, and the number must be first from the table at that time, we use the following statement.
Example:
Code:
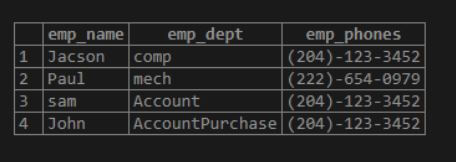
select emp_name, emp_dept,emp_phones [ 1 ] from
emp;Explanation:
- In the above example, we show the employee name, employee department, and employee phones.
- See here we only display the first phone number of the employee.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Suppose users need to display the second number of employees at that time we use the following statement.
Example:
Code:
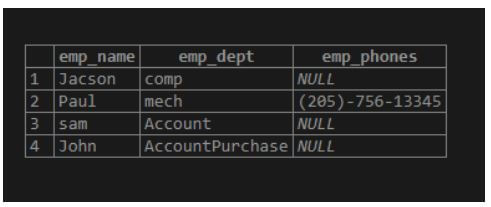
select emp_name,emp_dept, emp_phones [ 2 ] from emp;Explanation:
- The above example shows the employee’s second number using a select statement.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Now let’s see how we can use where clauses in an array. The above examples show how we can implement arrays with different operations.
Suppose the user needs to see a specific phone number from the database table at that time, we use the following syntax.
Syntax:
select column name 1, column name 2,………………… column nameN from table name where condition ;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use to select and where clause, where column name is used to display the specified column name from the table, table name means specified table name, and apply condition using where clause.
Example:
Code:
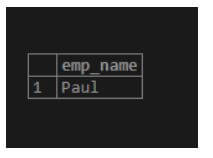
select emp_name from emp where emp_phones [2] = '(205)-756-13345';Explanation:
- In this example, suppose the user needs to show the second number of employees from the database table at that time, we use the above statement.
- The only one employee has a second number.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
In a similar way, we implemented a department column.
Example:
Code:
select emp_name from emp where emp_dept [1] = 'Account';Explanation:
- In the above example, we show those employee works in the Account department using the where clause here, we use condition emp_dept = 1, that indicates the first array value in the emp_dept column.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
3. Update array operation
In this operation, we update array values by using an update statement.
Syntax:
update table name set value where condition;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use an update statement, where table name means specified table name, value means updated values, and apply condition using where clause.
Example:
Code:
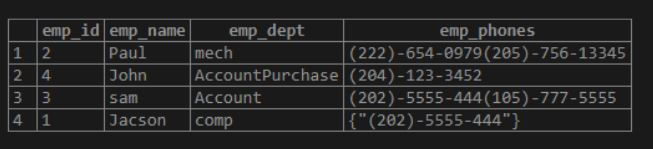
update emp set emp_phones= '{"(202)-5555-444","(105)-777-5555"}'
where emp_name='sam';select * from emp;Explanation:
- In the above example, suppose the user want to update the phone number of a sam employee at that time, we use the above statement see here, we update all phone numbers.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Now let’s see how we can update the first array value.
Example:
Code:
update emp set emp_phones [1]= '{"(202)-5555-444"}'
where emp_name = 'Jacson';select * from emp;Explanation:
- In the above example, we update the first phone number of a Jacson employee.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Similarly, we can update the second value of the array.
Conclusion
The above article shows the basic syntax of where in the array. We also saw how we can implement them in PostgreSQL with different examples of each operation. This article showed us how to handle where in an array in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL where in array” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.