Updated May 15, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL JDBC Driver
While creating a database based application and using any of the databases in your java application, you will need to follow certain steps to use the JDBC (Java Database Connectivity), which is an API . i.e., Application Programming Interface that helps us communicate between our java application and database. The database can be any database like MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc. This article will learn how we can connect our java application with our PostgreSQL database with the JDBC driver’s helpr.
Pre-requisites
While creating a database-based java application, it is required to have a few things installed in your system, which are as follows –
- Java JDK toolkit
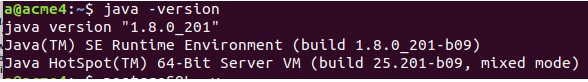
You can check the version of Java available in your system by typing the command ‘java -version’ in your command prompt. The output will display the version of Java available, as shown below.
java -versionIf not present, you should first install Java. Here, we used Java version “1.8.0_201”.
- You should install PostgreSQL and psql on your machine, which you can verify by typing the command’ psql -V’ in your command prompt. The output should display the version information, as shown below.
psql -VIf not available, install it before proceeding with JDBC driver installation. Mine is psql (PostgreSQL) 12.2 (Ubuntu 12.2-2.pgdg18.04+1).
- The last thing is the JDBC driver for the PostgreSQL jar file, which can be downloaded from the link https://jdbc.postgresql.org/download.html. We will use it further while establishing the JDBC connection.
Steps for JDBC initialization
- We first need to import JDBC using the import statement –
import java.sql.*;You should be careful here; you should not import the org. Postgresql package in your application as doing so will confuse the javac for compiling the source file.
- The second step is where you will need to load your JDBC driver. This can be done in two ways. One by using the Class.forName() method and others by passing your driver as a parameter to the JVM while initializing. The second step is preferable because if your application needs to change its database server in the future, it can easily be done without changing the connection-related code.
In the first method, we will use the Class.forName() method in the following way –
Class.forName("org.postgresql.Driver");where org. Postgresql. Driver specifies your PostgreSQL JDBC driver usage. Developers often use this method in JDBC applications to throw a ClassNotFoundException if the driver is not found.
The second method consists of passing your JDBC driver as a parameter to the initialization string using the -D option as follows –
java -Djdbc.drivers=org.postgresql.Driver example.ImageViewer- Now is the time to connect to the database. In JDBC applications, we represent the database using a URL (Uniform Resource Locator), which can take any of the three forms when using the PostgreSQL database.
jdbc:postgresql:databaseNamejdbc:postgresql://hostName/databaseNamejdbc:postgresql://hostName:portNumber/databaseNamewhere
the hostName is localhost by default, and if remote is the Ipv6 address of the machine.
portNumber is the socket/port address which is by default 5432 for PostgreSQL.
DatabaseName is the name of the database you want to connect to for your JDBC application.
Finally, you can now connect using the statement.
Connection dbConnectionObject= DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);- To complete your database manipulations, you should close your JDBC connection by calling the close() method on your Connection object, as shown below.
dbConnectionObject.close();Example of PostgreSQL JDBC Driver
Let us consider one example of a JDBC application with PostgreSQL. We will first need to create a database in our PostgreSQL database server for this. We will create a database named educba and connect to it using our JDBC program in Java.
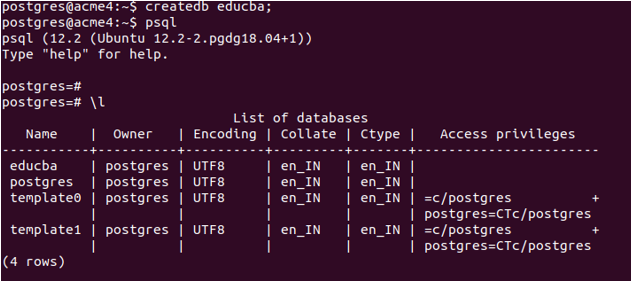
createdb educba;
psql
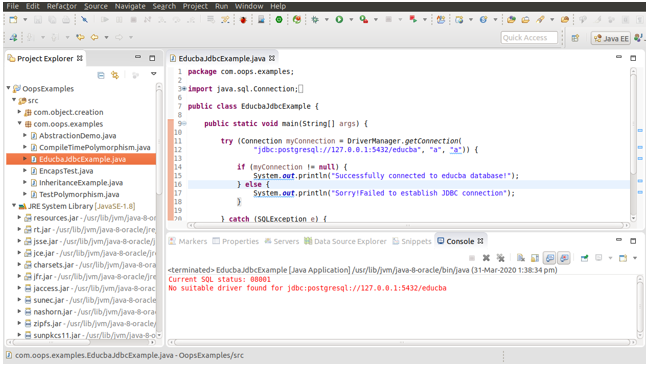
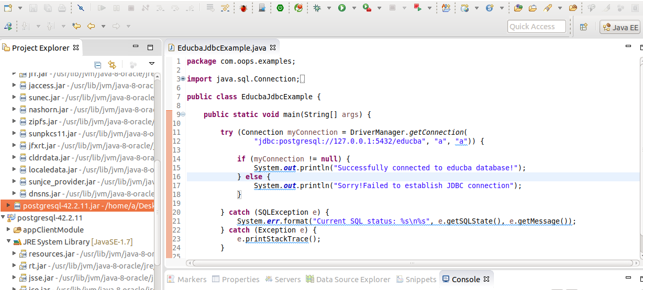
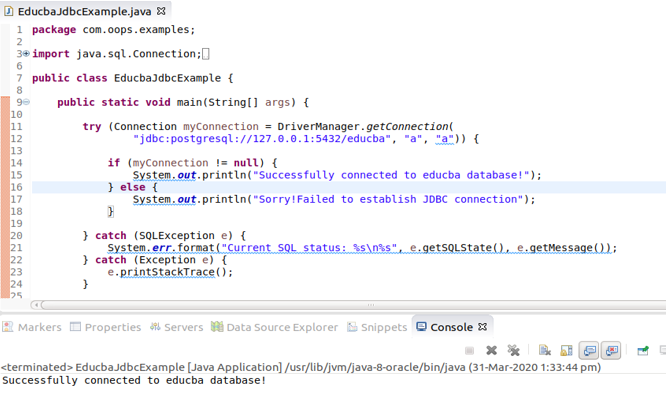
\lCreate a new file named EducbaJdbcExample.java which will contain a program like this -Our program’s first three statementsm are for importing the packages required for using the JDBC related methods. The next thing is that we are trying to establish the connection with our PostgreSQL using the following statement –
Connection myConnection = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/educba", "postgres", "a")where 127.0.0.1 stands for localhost, i.e., same machine address, and 5432 is the PostgreSQL port, and we want to connect to the educba database name, and our username and password are ‘a’ and ‘a’, respectively. Here, we have inserted this statement in try because if any exception arises while establishing the connection, it will give an immediate exception and display the message related to the exception. If the connection is established, then the message saying “Successfully connected to the educba database!” will be displayed; else, “Sorry! The system will display a message that reads ‘Failed to establish the JDBC connection’ if it cannot be established.
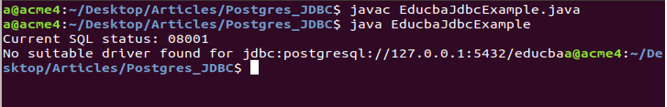
After saving, compiling, and running the application, if it gives the exception like the following –
If you are using Eclipse IDE, creating a Java class file for your program, and right-clicking your file ->Run As -> Java application option, you can run your program. In that case, it will give the following output. Our current project does not have the JDBC driver file for PostgreSQL downloaded, which is why it is not present.
This is because the JDBC driver is not loaded. In such applications, we must manually load our JDBC driver using cp. If you are running the program through the command line, you need to store your EducbaJdbcExample.java program file and the downloaded PostgreSQL JDBC driver JAR file in the same directory. Alternatively, if you are using Eclipse IDE, you can import the JAR file into your project.
Then you can run your application as a Java application if you are using eclipse –
As you can see, the console displays the message ‘Successfully connected to educba database!’, indicating that we have successfully connected to our database.
Conclusion
We can connect with our PostgreSQL database from our java application by following all the above steps properly.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL JDBC Driver” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.