Updated May 12, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Restore Database
The Database Restore process in PostgreSQL is used to copy the data from the backup. This means we use the database backup file and convert it into the database. Using Data Restore, we create a copy of the data for regenerating corrupted or missed data; we make sure that the loss data is completely recovered and consistent at a particular time, generally, the time before the data corrupted or damaged occurred. There are several cases where we need to perform the Data Restore; first human error, like a user has deleted the data by mistake. Second, the data has been hacked, stolen, or exposed to the outside world or corrupted due to power cuts, natural calamities, theft, or hardware or software failure.
How to Restore the Database in PostgreSQL?
To perform the database restore in PostgreSQL, we have to terminate all active connections for the database to be restoring. There are two ways to perform data restore in PostgreSQL as follows:
Method #1
1. Restore SQL script created by ‘pg_dump’ and ‘pg_dumpall’ using the psql utility.
Consider the following examples to understand the psql utility commands.
To perform a full backup, we have to use the following command and ignore all of the errors that occurred during the restore by skipping the option –set ON_ERROR_STOP as defined below.
Code:
psql
-U username
-f backupSqlFile.sqlWe can use the following command with the option –set ON_ERROR_STOP=on, If while performing database restores in the PostgreSQL and some error occurs, we want to stop the process immediately.
Code:
psql
-U username
--set ON_ERROR_STOP=on
-f backupSqlFileWe can use the following command to restore the particular database in PostgreSQL as defined below.
Code:
psql
-U username
-d databaseName
-f objectDB.sqlMethod #2
2. Restore the tar file and directory format
- The PostgreSQL pg_restore programme allows us to recover the backup files created by the pg_dump or pg_dumpall tools.
- We can use multiple threads for restoring the database by using the pg_restore program, to do the same, we have specified option -j, which defines the number of threads getting used for the restoration process.
- Using the pg_restore programme, we can transition between multiple database versions, allowing us to transfer a database backup from an older version to a more recent one.
- We can restore a specific database using the pg_restore programme if we have a complete database backup file.
Consider the following examples to understand the pg_restore program in PostgreSQL.
We will create a database named eduCBADB by using the following CREATE DATABASE statement. Consider we have a backup eduCBADB.tar file created at path c:\PostgreSQLEduCBA\eduCBADB.tar
Code:
CREATE DATABASE eduCBADB;We can restore the eduCBADB database in the tar file format by using the following command:
Code:
pg_restore
--dbname=eduCBADB
--verbose c:\PostgreSQLEduCBA\eduCBADB.tarIf we want to restore the database in PostgreSQL, which is similar to the backed up database, then we can use the following command:
Code:
pg_restore
--dbname=eduCBADB
--create
--verbose c:\PostgreSQLEduCBA\eduCBADB.tarPostgreSQL Restore Databases using the pgAdmin tool
We can use the pgAdmin restore tool for performing restore databases in PostgreSQL.
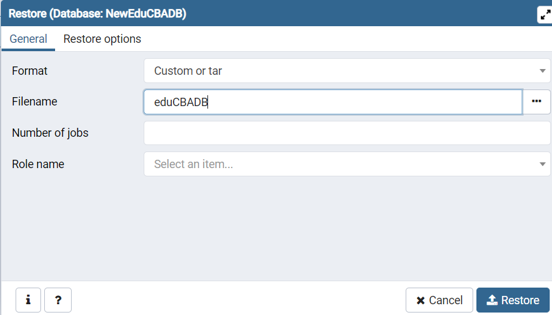
Consider the following examples, which show how we can restore the NewEduCBADB database from the eduCBADB.tar file
- DROP the existing NewEduCBADBdatabase: DROP DATABASE NewEduCBADB;
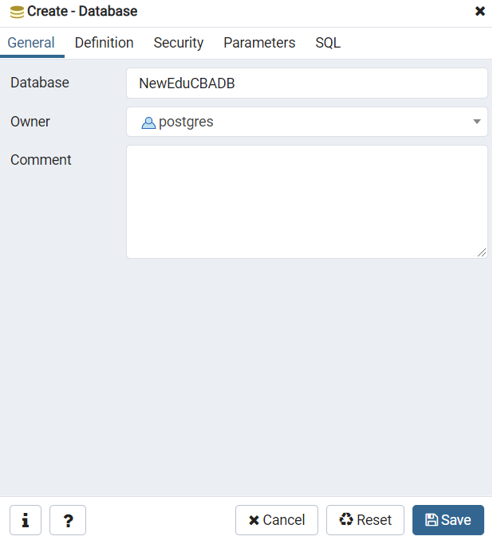
- Create a new empty eduCBADB database: CREATE DATABASE NewEduCBADB;
Consider the following screenshot, which is used to create a database in PostgreSQL by using pgAdmin 4:
Consider the following screenshot, which shows the list of the database in PostgreSQL by using pgAdmin 4:
3. Now, we can perform the following actions on the UI
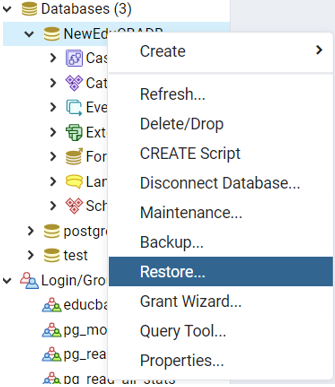
- Select the eduCBADB database
- Right mouse click
- Select the Restore…
And then
- Select required options like as user, backed up file, and restore options
- Click on the Restore button to start restoring the database.
We will have to go through the following dialogs step by step:
Step1: Consider the following screenshot, which shows the context menu items available on the database in pgAdmin 4:
Step 2: Consider the following screenshot, which shows the Restore dialog when we click on the “Restore…” context menu item available on the database in pgAdmin 4:
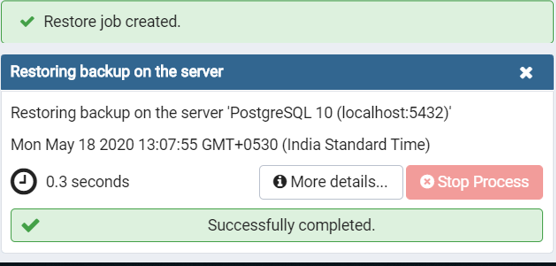
Step 3: Consider the following screenshot, which shows on successful creation of the job to restore the database in pgAdmin 4:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Restore Database” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.