Updated May 3, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Views
In these articles, we will learn about PostgreSQL Views. Views are basically a query with a name; therefore, a view is useful for wrapping a commonly used complex query; we can represent data in the database tables using views named query, we can define views using one or more tables known as base tables, the view is a logical table which represents data from one or many tables using the SELECT command.
The query’s complexity can be simplified with the help of view, as users can query a view using a SELECT command. Like a table, we can add permission to the users using a view that stores data for which we need authorized users only.
How to Create PostgreSQL Views?
Let us see how to create the views:
Syntax:
CREATE [OR REPLACE][TEMP OR TEMPORARY] [RECURSIVE]
VIEW view_name [(column_name [, ...])]
[ WITH (view_options_name [= view_options_value] [, ... ])]Explanation: If a view with the same name already exists, it is replaced. The view name must be unique. It should not be the same as any other view, sequence, table, foreign table, or index in the same schema.
- TEMP / TEMPORARY: If the view is created as a temporary view, it is automatically removed at the end of the session.
- RECURSIVE: Creates a recursive view.
- Name: The name of a view to be
- column_name: The user can define a list of column names of the view. Only defined columns will get considered in the query others are
- WITH: ( view_options_name [= view_options_value]…)We can specify optional parameters for a view.
Creating PostgreSQL Views
We can create PostgreSQL views using various ways:
Consider the following tables to understand the PostgreSQL views:
To understand the examples of considering the following ‘student’ and ‘Branch’ table structures
- Student: rollno, firstname, lastname, branch_id, result, joining_date
- Branch: branch_id, branch
1. WHERE clause
Code:
CREATE VIEW student_view
AS SELECT rollno, firstname, lastname, result, joining_date
FROM student
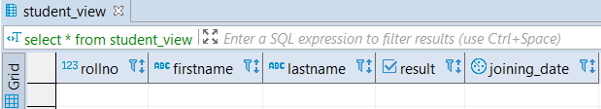
WHERE branch_id = 4;It will create a view’ student _view’ taking records (for rollno, firstname, lastname, result, joining_date columns) of the student table if those records contain the value 4 for the branch_id column.
Code:
select * from student_viewOutput:
2. AND and OR
Code:
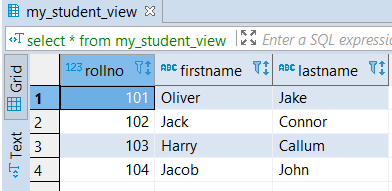
CREATE VIEW my_student_view
AS SELECT *
FROM student
WHERE(branch_id = 1 AND result = false)
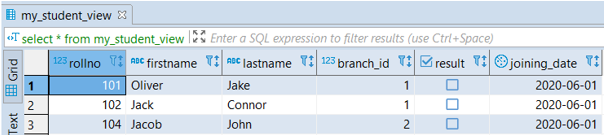
OR(branch_id = 2 AND firstname='Jacob');- It will create a view ‘my_student_view’ taking records for all student table columns
- if branch_id is 1 and the result is false.
- Or branch_id is 2, and the firstname is ‘Jacob’.
Code:
select * from student_viewOutput:
3. GROUP BY
Code:
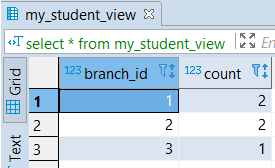
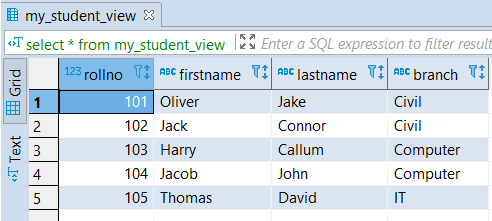
CREATE VIEW my_student_view
AS SELECT branch_id, count (*)
FROM student
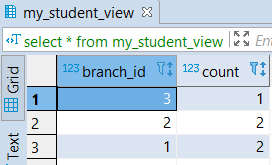
GROUP BY branch_id;It will create a view ‘my_student_view’ taking all records grouped with respect to branch_id and stored branch_id and several students for each Branch (branch_id) from the student table.
Code:
select * from student_viewOutput:
4. ORDER BY
Code:
CREATE VIEW my_student_view
AS SELECT branch_id, count (*)
FROM student
GROUP BY branch_id
order by branch_id;It will create a view of my_student_view, taking all the records grouped with respect to branch_id and sorted against branch_id and the number of student tables for each department (branch_id) from the student table.
Code:
select * from student_viewOutput:
5. BETWEEN and IN
Code:
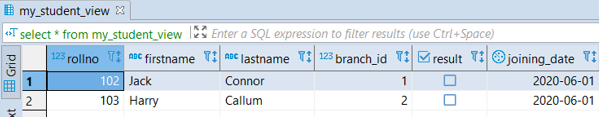
CREATE VIEW my_student_view AS
SELECT * FROM student
WHERE firstname BETWEEN 'G' AND 'K'
AND rollno IN (101,102,103,105);It will create a view ‘my_student_view’ taking all the records of the employee’s table; if the firstname column of the student starts with any of the characters from ‘G’ through ‘K’ and rollno are any of the following 101,102,103,105
Code:
select * from student_viewOutput:
6. LIKE
Code:
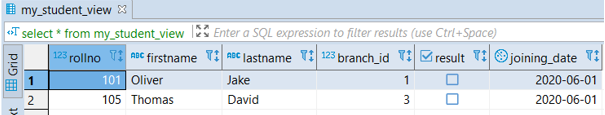
CREATE VIEW my_student_view
AS SELECT *
FROM student
WHERE firstname NOT LIKE 'J%' AND lastname NOT LIKE
'C%';It will create a view my_student_view taking all the records of the student table. If the student’s firstname does not start with ‘J’ and lastname of the student does not start with ‘C’.
Code:
select * from student_viewOutput:
7. Subqueries
Code:
CREATE VIEW my_student_view
AS SELECT rollno,firstname,lastname
FROM student
WHERE branch_id IN(
SELECT branch_id
FROM Branch
WHERE branch_id IN (1,2)
);It will create a view my_student_view taking all the records of rollno, firstname, and lastname of the student table. The subquery retrieves those branch_ids from the Branch table, which branch_id are any of the 1 and 2.
Code:
select * from student_viewOutput:
8. JOIN
Code:
CREATE VIEW my_student_view
AS SELECT s.rollno, s.firstname, s.lastname, b.branch
FROM student s, branch b
WHERE s.branch_id = b.branch_id;It will create a view of my_student_view along with a JOIN statement. The JOIN statement here retrieves rollno, firstname, lastname, from student table and branch_id from the branch table if the branch_id of the student table and that of the Branch are the same.
Code:
select * from student_viewOutput:
How to Modify PostgreSQL Views?
ALTER VIEW statement modifies the definition of an existing view.
1. ALTER with SET DEFAULT
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS] views_name ALTER [ COLUMN ] column_name SET DEFAULT expression2. ALTER with DROP
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS] views_name ALTER [ COLUMN ] column_name DROP DEFAULT3. ALTER with OWNER
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS] views_name OWNER TO new_view_owner4. ALTER with RENAME
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS] views_name RENAME TO new_view_name5. ALTER with SET SCHEMA
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS] views_name SET SCHEMA new_view_schema6. ALTER with SET
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS] views_name SET ( view_options_name [= view_options_value] ... )7. ALTER with RESET
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] views_name RESET ( view_options_name ... )Explanation:
- views_name: The name of the
- IF EXISTS: Do not throw an error if the view does not exist.
- SET/DROP DEFAULT: Set or remove the default value for a column.
- new_view_owner: Defines view’s new owner’s username.
- new_view_name: The new name for the view.
- new_view_schema: The new schema for the view.
- view_options_name : Defines view options to be set/
- view_options_value : Defines the new value for associated view options.
To rename the view ABC to XYZ.
ALTER VIEW test_view RENAME TO testview;How to Drop PostgreSQL Views?
- To remove a view, we must use the DROP VIEW statement.
- Users must have the DROP privilege for each view to drop a view.
Syntax:
DROP VIEW [IF EXISTS]
view_name [, view_name] ...
[ CASCADE | RESTRICT]Explanation:
- IF EXISTS: Do not throw an error if the view does not exist.
- view_name: The name (optionally schema-qualified) of the view to remove.
- CASCADE: It will automatically remove all view-dependent objects.
- RESTRICT: It will not allow you to delete the view if any dependent object exists.
The following command will remove the view called ‘postgresql_view’:
DROP VIEW 'postgresql_view';Conclusion
We hope you have understood the concept of PostgreSQL views. And also learned about how to create, modify, and remove PostgreSQL views.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Views” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

