Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Trigger Functions
The PostgreSQL Trigger Functions is the same as an ordinary function. Still, it gets invoked or performed automatically when we perform a database operation, such as insert, update, or delete, and a defined event occurs. The Trigger function does not take any argument as an input parameter, and it returns a value per the trigger type. We can create a trigger function by using any programming language which needs to be supported by PostgreSQL. We can create a trigger for each row and each statement that executes each row or once for all operations.
Syntax:
Consider the following syntax to understand the Trigger function
CREATE FUNCTION trigger_function()
RETURNS trigger ASHow does the PostgreSQL Trigger function work in PostgreSQL?
To create a new trigger, we need to follow the following steps:
- Create a PostgreSQL trigger function with the help of the CREATE FUNCTION statement.
- Bind the PostgreSQL trigger function with the database table with the help of the CREATE TRIGGER statement.
The PostgreSQL trigger function will be created in two different manners as follows.
- FOR EACH ROW: When we have defined FOR EACH ROW, then the trigger will get invoked once for each row when we operate on a
- FOR EACH STATEMENT: When we have defined FOR EACH STATEMENT, the trigger will get invoked only once despite the number of rows modified or the number of rows on which the operation is performed.
TriggerData is used to define the data received by the PostgreSQL trigger function, which holds the values of local variables such as the keywords OLD and NEW to define the before or after triggering event state of the row in the table.
PostgreSQL uses the prefix TG_ to define the local variables, such as TG_TABLE_NAME and TG_WHEN.
Examples
Consider the following example where we will create a table named ‘Student’ and ‘Student_audit’. Whenever we update the Stud_first_name in the student table, we log the changes in the ‘Student_audit’ table.
Consider the following CREATE TABLE statement, which will create a table named ‘Student’.
CREATE TABLE Student(
Stud_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
Stud_first_name varchar(255) NOT NULL,
Stud_last_name varchar(255) NOT NULL
);Consider the following CREATE TABLE statement, which will create a table named ‘Student_audit’.
CREATE TABLE Student_audit(
Student_audit_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
Stud_id INT NOT NULL,
Stud_first_name varchar(255) NOT NULL,
Stud_first_name_updated_on TIMESTAMP(6) NOT NULL
);Now we will create a function named ‘stud_first_name_update_logs’ as follows:
CREATE FUNCTION public.stud_first_name_update_logs()
RETURNS trigger
LANGUAGE 'plpgsql'
COST 100
VOLATILE NOT LEAKPROOF
AS $BODY$BEGIN
IF NEW.Stud_first_name <> OLD.Stud_first_name THEN
INSERT INTO Student_audit(Stud_id, Stud_first_name, Stud_first_name_updated_on)
VALUES (OLD.Stud_id, OLD.Stud_first_name,now());
END IF;
RETURN NEW;
END;$BODY$;
ALTER FUNCTION public.stud_first_name_update_logs()
OWNER TO postgres;Whenever the student’s first name changes, the above function inserts an old first name of the student in the Student_audit table along with the time of change and its id and first name.
Now we will create and bind the PostgreSQL trigger named ‘stud_first_name_updates’ to the student table. The PostgreSQL trigger function automatically invokes or logs the changes whenever we update a student’s first name.
CREATE TRIGGER stud_first_name_updates
BEFORE UPDATE
ON student
FOR EACH ROW
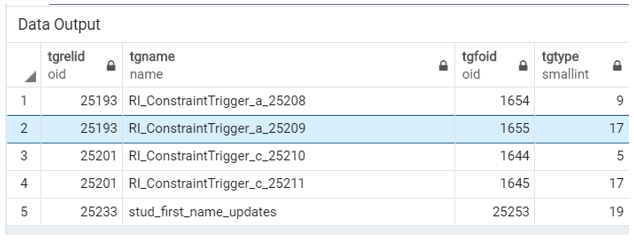
EXECUTE PROCEDURE stud_first_name_update_logs();Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following SQL statement and snapshot.
SELECT * FROM pg_trigger;Now, we will insert a row into the Student table by using the INSERT INTO statement as follows:
INSERT INTO Student(Stud_first_name, Stud_last_name)
VALUES
('Jacob', 'Petter'),
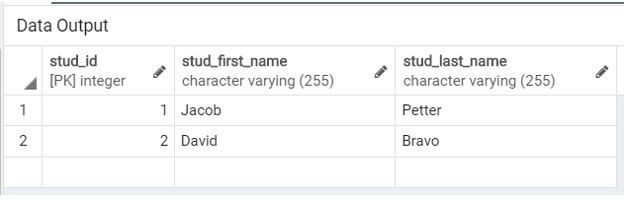
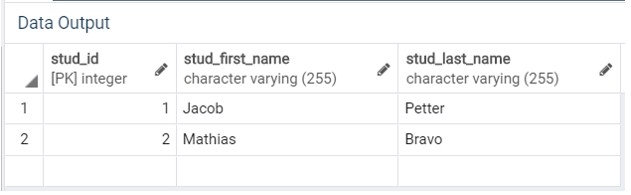
('David', 'Bravo');Illustrate the content of the Student table by using the following SQL statement and a snapshot.
SELECT * FROM Student;Now, we will update the first name of the student whose last name is ‘Bravo’ by using the UPDATE statement as follows:
UPDATE Student
SET Stud_first_name = 'John'
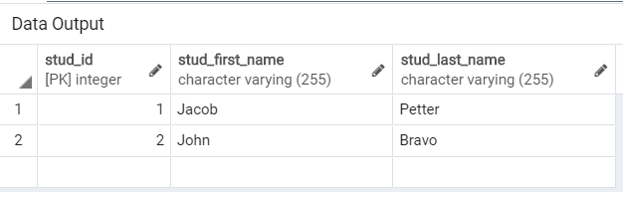
WHERE Stud_last_name = 'Bravo';Illustrate the content of the Student table by using the following SQL statement and a snapshot.
SELECT * FROM Student;Now,
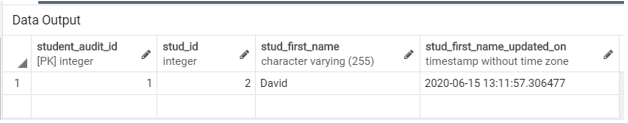
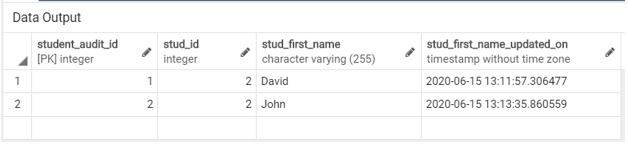
Illustrate the content of the Student_audit table by using the following SQL statement and a snapshot.
SELECT * FROM Student_audit;Now, we will again update the first name of the student whose last name is ‘Bravo’ by using the UPDATE statement as follows:
UPDATE Student
SET Stud_first_name = 'Mathias'
WHERE Stud_last_name = 'Bravo';Illustrate the content of the Student table by using the following SQL statement and a snapshot.
SELECT * FROM Student;Now,
Illustrate the content of the Student_audit table by using the following SQL statement and a snapshot.
SELECT * FROM Student_audit;Conclusion
From the above article, we hope you understand how to use the PostgreSQL Trigger function and how the PostgreSQL Trigger function work. Also, we have added several examples of the PostgreSQL Trigger function to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Trigger Functions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.