Updated May 12, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Like
When dealing with string manipulation in PostgreSQL, it often needs to match the strings with a particular pattern and then perform some action and operation on the string if match successes are performed. This is one of the most common use-cases when it comes to string comparisons and manipulation. The traditional method for performing pattern matching in SQL uses the LIKE expression. PostgreSQL introduced several other methods for pattern matching, including POSIX regular expression matching and SIMILAR TO expressions, which can also be used to match patterns. This article will learn about the syntax of the LIKE expression and how we can use it in PostgreSQL to perform pattern matching in strings.
Syntax of PostgreSQL Like
demoString LIKE anyPattern [ESCAPE characterThatNeedsToBeEscaped]
demoString NOT LIKE anyPattern [ESCAPE characterThatNeedsToBeEscaped]DemoString: It can be any string value or the column of the particular table that stores string and that you want to check whether it matches a pattern or contains some characters or substring.
AnyPattern: The pattern is a particular string that you want to match with the demoString. It may contain the %(percentage) sign and _(underscore) sign that help in defining the pattern. The underscore sign indicates that any character can occupy that particular position in the pattern string, while the percent sign specifies the presence of one or more characters before, after, or in between the pattern string, wherever it appears in the pattern string. In the upcoming session, we will discuss it in detail and have examples to clarify the concept.
CharacterThatNeedsToBeEscaped: Whenever you go for pattern matching, there are certain characters in the demoString that is the original string that you wish to skip while matching. These characters are called escape characters. The backslash is considered an escape character by default and will be ignored during pattern matching. If you want to consider backslash in pattern matching, specify double backslash as the escape character. You can specify any other character you want to skip in the CharacterThatNeedsToBeEscaped parameter. This field is optional and has backslash as the default value.
Functions of PostgreSQL Like
When you use the LIKE expression to match a certain string with the pattern, if the pattern matches, then true is returned; else, false is returned by the like expression. NOT LIKE expression behaves oppositely. It returns true when the string does match the pattern and false when the match is successful. demoString NOT LIKE anyPattern [ESCAPE characterThatNeedsToBeEscaped] is equivalent to NOT (LIKE anyPattern [ESCAPE characterThatNeedsToBeEscaped] ).
The pattern can be any string you want to compare, containing underscore and percent signs to match multiple cases. When no such signs are mentioned in the pattern and are a plain string, then the Like behaves the same as that of an equal operator. If an underscore is present, any character in the original string can occupy that position for a match to occur. The percent sign allows for the presence of zero or more characters wherever it appears. Let us study all these cases one by one.
Examples to Implement of PostgreSQL Like
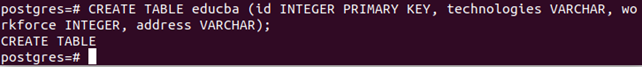
Let us create one example and insert a few records in the table to learn how to use a LIKE expression for pattern matching. Open your PostgreSQL command-line prompt and enter the following command to create a table named educba:
Example #1
Query:
CREATE TABLE educba
(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
technologies VARCHAR,
workforce INTEGER,
address VARCHAR);Output:
Example #2
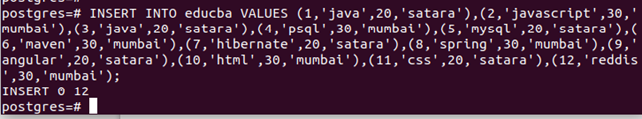
Let us insert some values in the educba table using the following statement:
Query:
INSERT INTO educba VALUES (1,'java',20,'satara'),(2,'javascript',30,'mumbai'),(3,'java',20,'satara'),(4,'psql',30,'mumbai'),(5,'mysql',20,'satara'),(6,'maven',30,'mumbai'),(7,'hibernate',20,'satara'),(8,'spring',30,'mumbai'),(9,'angular',20,'satara'),(10,'html',30,'mumbai'),(11,'css',20,'satara'),(12,'reddis',30,'mumbai');Output:
Example #3
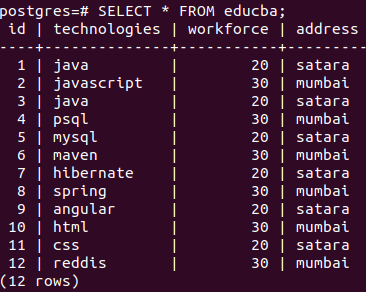
Let us create a simple select query statement to retrieve all the records from the educba table. Our query statement will be as follows.
Query:
SELECT * FROM educba;Here, * represents all the columns to be retrieved, and firing the above query results in the following output:
Output:
Example #4 – String Matching a String
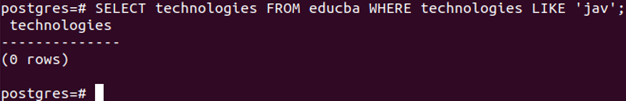
Let us match a pattern without any underscore or percent sign in it with a LIKE expression.
Query:
SELECT technologies FROM educba WHERE technologies LIKE 'jav';Output:
There is no record with a technologies column with a jav value, so it returns zero rows.
Example #5
Let us now fire the following query.
Query:
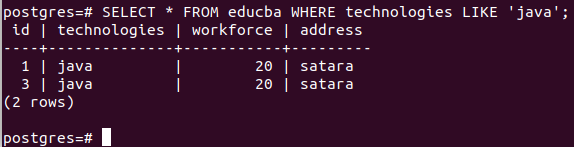
SELECT * FROM educba WHERE technologies LIKE 'java';Output:
There are two records with technology names that include “Java,” so two records are returned.
Example #6 – String Matching with _ in a Pattern
Now, we will retrieve all the records that will have underscore for the first position and then the string SQL for the technologies column value. For this, we will fire the following query statement –
Query:
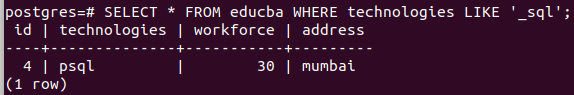
SELECT * FROM educba WHERE technologies LIKE '_sql';that gives the following output: just one record with technologies value psql matches the pattern.
Output:
Example #7
Now, we will retrieve the records with __ two underscores in the first and second positions and then the string SQL using the following query statement.
Query:
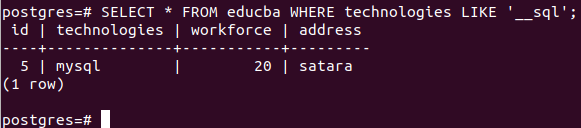
SELECT * FROM educba WHERE technologies LIKE '__sql';Output:
Only one record with MySQL technologies value is there that matches the pattern specified by us.
Example #8
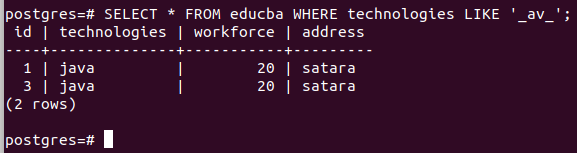
Similarly, we can place underscore any number of times at any position we wish to build up our pattern. When we want to find records having technologies field value such that it contains one character previous and one character after the av substring, we will fire the query statement as follows –
Query:
SELECT * FROM educba WHERE technologies LIKE '_av_';Output:
Example #9
Inserting one more _ in the above pattern gives the following query:
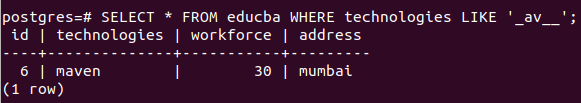
Query:
SELECT * FROM educba WHERE technologies LIKE '_av__';Output:
Example #10 – String Matching with % in a Pattern
Suppose we want to retrieve all the records with string SQL in the ending and any number of characters before it in the technologies field. Then we can make use of the % sign that checks for zero or more character presence, and my query statement will be as follows:
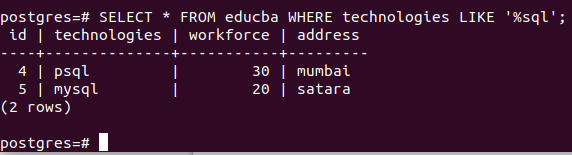
Query:
SELECT * FROM educba WHERE technologies LIKE '%sql';That results in the output containing psql and MySQL, as there can be any number of characters before the SQL string in the technologies field value.
Example #11
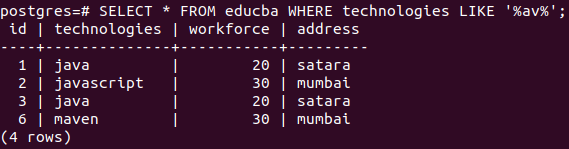
Now, for retrieving records containing av between the string and present anywhere in a technologies field value, we will have to mention % before and after av to search for substring av presence in an original string of technologies field value. Y query statement will be as follows.
Query:
SELECT * FROM educba WHERE technologies LIKE '%av%';Output:
Conclusion
We can perform pattern matching using the LIKE expression in PostgreSQL to retrieve the records that match the particular pattern. Further, we can perform operations based on whether they match the pattern, such as splitting or replacing the original string’s substring.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Like” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.