Updated May 6, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL Subquery
PostgreSQL Subquery is also known as the nested query or inner query; It is an embedded where clause query within another query. A subquery in PostgreSQL can retrieve data that narrows down the data retrieved in the main query by using it as a condition. It is used to select, insert, update, and delete statements with operators like >, =, <, >=, <=, IN, etc. There are many rules available to use a subquery in PostgreSQL.
Syntax
Below is the syntax as follows.
1. With a select statement
Select column_name1, .., column_nameN
From table_name1 [, table_name2]
Where column_name operator
Select column_name from table_name1 [, table_name2]
[Where] condition)2. With Insert statement
INSERT INTO table_name [ (column_name1 [, column_name2 ]) ]
SELECT [ *|column_name1 [, column_name2 ] ]
FROM table_name1 [, table_name2]
[WHERE VALUE OPERATOR]3. With update statement
UPDATE table_name
SET column_name = new_value
[WHERE OPERATOR [VALUE]
(SELECT COLUMN_NAME
FROM TABLE_NAME)
[WHERE) ]4. With delete statement
DELETE FROM TABLE_NAME
[ WHERE OPERATOR [ VALUE ]
(SELECT COLUMN_NAME
FROM TABLE_NAME)
[ WHERE) ]Below is the parameter description of the above syntax as follows.
- Select – Used to select the statement.
- Column_name1 to column_nameN – It specifies the Column name.
- From – You use the “From” clause to retrieve data from the chosen table.
- TABLE_NAME – Used to specify the Table name.
- Where condition – Where condition specified to fetch data per the query described to fetch the data.
- Operator – Operator is used to specifying the condition. Operators like >, =, <, >=, <=, IN, etc., are used in PostgreSQL.
- Insert – Used to Insert statement.
- Delete – Used to Delete statement.
- Update – Used to Update statement.
Working of PostgreSQL Subquery
Below is the working as follows.
- A nested subquery, also known as an inner query, is what this refers to.
- We have used the PostgreSQL subquery to select, insert, update, and delete statements.
- We have selected Subquery in operators like >, =, <, >=, <=, and IN. These operators are used along with the where condition.
- It’s important to note that when working with PostgreSQL, you cannot use a subquery between operators with another subquery. However, you can use it within the Subquery itself.
- Enclose it with parentheses.
- We have used only one column in the select clause and multiple columns in the main query to compare it with the selected columns. Subqueries in PostgreSQL do not support the use of the “Order by” clause, but they can still be utilized in the main query.
- Instead of the order by, we have used group by to perform the same operation as order by.
- It will return more than one row.
- You can use a subquery to return data that serves as a condition to restrict further the data retrieved by the main query.
Types of PostgreSQL Subquery
Below is the type as follows. We have used Employee_test1 and Employee_test2 tables to describe types.
1. Table1 – Employee_test1
CREATE TABLE Employee_Test1 ( emp_id INT NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), emp_salary INT NOT NULL, date_of_joining date NOT NULL);
INSERT INTO Employee_Test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (1, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (2, 'PQR', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (3, 'XYZ', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 35000, '02-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (4, 'BBS', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 45000, '02-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (5, 'RBS', 'Delhi', '1234567890', 50000, '03-01-2020');
select * from Employee_Test1;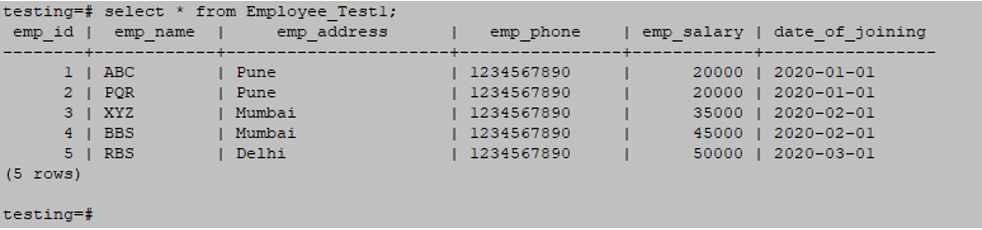
2. Table2 – Employee_test2
CREATE TABLE Employee_Test2 ( emp_id INT NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), emp_salary INT NOT NULL, date_of_joining date NOT NULL);
INSERT INTO Employee_Test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (1, 'PQR', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (2, 'XYZ', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 35000, '02-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (3, 'BBS', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 45000, '02-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (4, 'RBS', 'Delhi', '1234567890', 50000, '03-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (6, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');
select * from Employee_test2;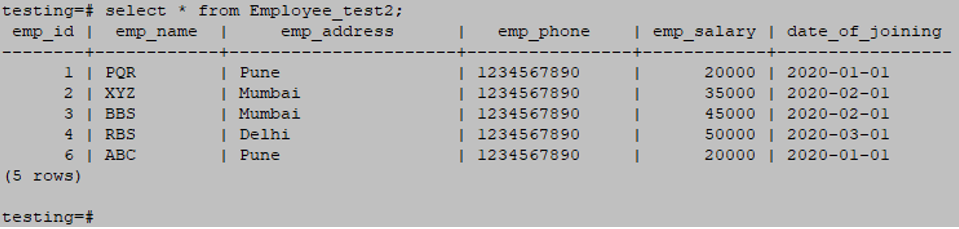
- Subqueries with the SELECT Statement
Below is the example of the Subqueries with the SELECT Statement as follows.
select * from Employee_Test1 where emp_id IN (select emp_id from Employee_Test2 where emp_salary > 35000);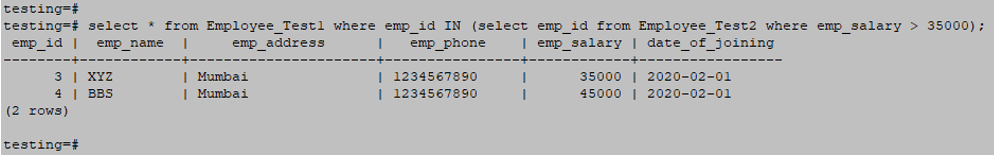
- Subqueries with the INSERT Statement
Below is the example of the Subqueries with the INSERT Statement as follows.
INSERT INTO Employee_Test1 SELECT * FROM Employee_Test2 WHERE EMP_ID IN (SELECT EMP_ID FROM Employee_Test2) ;
select * from Employee_test1;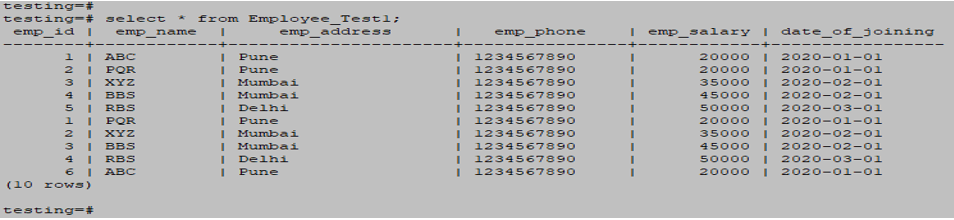
- Subqueries with the UPDATE Statement
Below is the example of the Subqueries with the UPDATE Statement as follows.
UPDATE Employee_Test1 SET EMP_SALARY = EMP_SALARY * 5 WHERE EMP_ID IN (SELECT EMP_ID FROM Employee_Test2 WHERE EMP_ID > 2 );
select * from Employee_test1;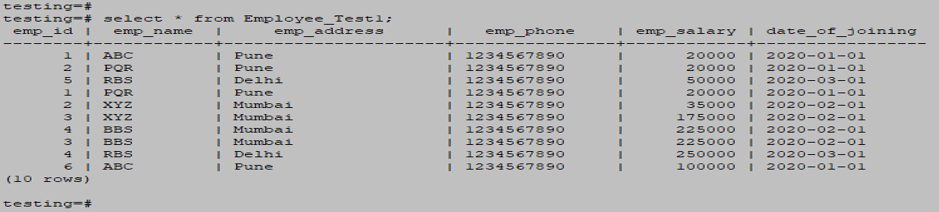
- Subqueries with the DELETE Statement
Below is the example of the Subqueries with the DELETE Statement as follows.
DELETE FROM Employee_Test1 WHERE EMP_ID IN (SELECT EMP_ID FROM Employee_Test2 WHERE EMP_ID > 2);
select * from Employee_test1;
Conclusion
A subquery in PostgreSQL is also called a nested or inner subquery. It does not use the ORDER BY clause, but the main query can use it to order the results. We used to group by clause instead of the order by clause in the PostgreSQL subquery.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Subquery” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

