Updated May 6, 2023
Definition of PostgreSQL IN Operator
PostgreSQL IN operator is used in a WHERE clause. We can reduce multiple OR conditions written in where clause with the help of the IN Operator. The PostgreSQL IN operator checks whether a given value is exist or not in the list of values provided. We can use the PostgreSQL IN operator in SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, or DELETE SQL statements.
Syntax:
The syntax of the PostgreSQL IN operator is as follows:
value IN (value1, value2, value3. ...)Explanation:
The expression returns either true or false; it returns true if the value exists in the list of values provided, that is, value1, value2, and value3, etc.
We can provide the list of values of type numbers or strings. We can also use the SELECT statement as follows to retrieve the list of values from the result set of the defined SELECT statement.
value IN (SELECT value FROM table_name);Explanation:
The SQL statement defined in the parentheses is called as a subquery. The subquery is the one that is the query nested in another query.
How IN Operator Works in PostgreSQL?
- The PostgreSQL IN operator returns true if it finds if any value-defined IN condition exists in the defined list of values.
- The PostgreSQL IN operator returns false if it does not find any of the value exists.
- If we are using subquery with IN operator, then it finds value in the result set of sub-query; if it finds then return true, otherwise false.
Examples
Let’s create a table named ‘furniture’ in order to understand the examples:
Example #1 – Inserting Data in the Table
CREATE table furniture
(
furniture_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
furniture_name VARCHAR (256) NOT null,
furniture_type VARCHAR (256) NOT null,
furniture_price int NULL
);Now, insert some data in the furniture table in order to execute SQL statements.
INSERT INTO furniture (furniture_name,furniture_type,furniture_price)
VALUES
('Chair','Wood',2500),
('Chair','Plastic',2000),
('Table','Wood',5000),
('Table','Plastic',4000),
('Sofa','Wood',10000),
('Sofa','Plastic',8000),
('Bed','Wood',15000),
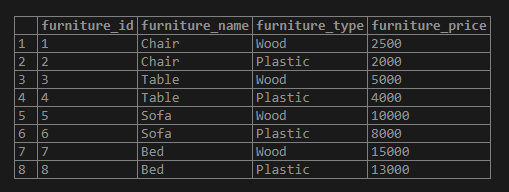
('Bed','Plastic',13000);1Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot and the SELECT statement.
SELECT * FROM furniture;Example #2 – The PostgreSQL IN with Character Values
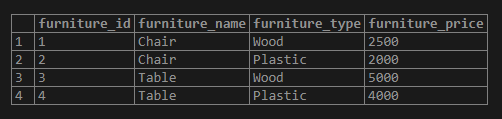
Now we will demonstrate the use of the PostgreSQL IN operator with character or string values. We have defined a list of two furniture names as ‘Chair’ and ‘Table’. Here we find whether any of these furniture names exist in the furniture_name column of the furniture table and returns the matched records of the furniture table as shown below.
SELECT *
FROM furniture
WHERE furniture_name IN ('Chair', 'Table');Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot.
Example #3 – The PostgreSQL IN with Numeric Values
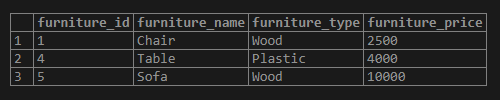
Now we will demonstrate the use of the PostgreSQL IN operator with numeric values. We have defined a list of two furniture prices of 2500, 4000, 10000, etc. Here we find whether any of these furniture prices exist in the furniture_price column of the furniture table and returns the matched records of the furniture table as shown below.
SELECT *
FROM furniture
WHERE furniture_price IN (2500, 4000, 10000);Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot.
Example #4 – PostgreSQL IN with the Subquery
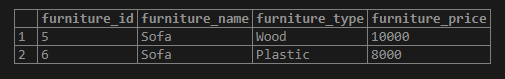
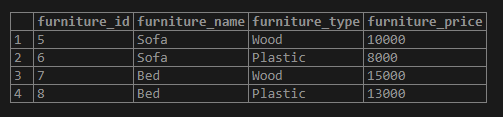
Now we will demonstrate the use of the PostgreSQL IN operator with sub-query written. We have written a sub-query that returns the furniture prices whose furniture_name is ‘Sofa’.
SELECT *
FROM furniture
WHERE furniture_price
IN (
SELECT
furniture_price
FROM
furniture
WHERE
furniture_name = 'Sofa'
);Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot.
Example # 5 – PostgreSQL IN with NOT
Now we will demonstrate the use of PostgreSQL NOT IN operator with character or string values. We have defined a list of two furniture names as ‘Chair’ and ‘Table’. Here we find whether any of these furniture names exist in the furniture_name column of the furniture table, and it skips that row only if it matches and returns the other records of the furniture table as shown below.
SELECT *
FROM furniture
WHERE furniture_name NOT IN ('Chair', 'Table');Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot.
Conclusion
We hope from the above article you have understood how to use the PostgreSQL IN and how the PostgreSQL IN condition works to find the existence from the list of values. Also, we have added some examples of PostgreSQL IN operator to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL IN Operator” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.