Updated May 6, 2023
Definition of PostgreSQL COMMIT
PostgreSQL commit is used to save the transaction changes to the database which the user made. The default commit value is ON in PostgreSQL, meaning we need not have to execute a commit statement to save the transaction; it will automatically save the transaction into the database. If we set auto-commit off, we need to write commit to save the transaction into the database. To store any modifications made to a transaction in the database, one would use the “commit” function. Commit is very important in PostgreSQL to save any changes the user made.
Syntax:
Below is the syntax of a commit in PostgreSQL, which are as follows.
COMMIT [ WORK (Optional keywords in commit) | TRANSACTION (Optional keywords in commit) ]The transaction commits using begin and end statements.
Begin
Statement1 …., Statement N
End transaction;Parameter:
- Commit: Commit is used in PostgreSQL to save any changes in the database which the user made. Commit is very important in PostgreSQL to save changes.
- Work: Work is an optional keyword in a commit. We can use it as “Commit Work”, which means that we save the work into the database.
- Transaction: Transaction is an optional keyword in a commit. We can use it as a “Commit Transaction”, which means that we save the transaction into the database.
- Begin: Begin is used in PostgreSQL to start the transaction. After starting a transaction, we end the same, and then we commit this transaction into the database.
- Statement 1 to statement N: This statement saves the result into the database. We can use multiple statements at one time.
- End transaction: If you want to halt the ongoing transaction, execute the “end transaction” statement. This will ensure that all modifications made by the user are committed to the database.
How to COMMIT Works in PostgreSQL?
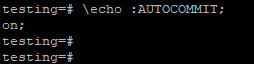
- By default, auto-commit is on in PostgreSQL. The below figure shows the auto-commit transaction is ON in PostgreSQL.
- We must check the default value using the “\echo :autocommit” command.
Output:
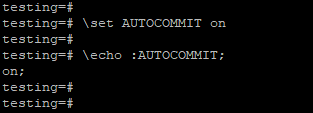
- We have set autocommit on by using the following command at the session-level are as follows.
testing=# \set AUTOCOMMIT on
testing=# \echo :AUTOCOMMIT;Output:
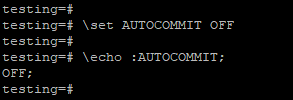
- We have set autocommit OFF by using the following command at the session-level are as follows.
testing=# \set AUTOCOMMIT OFF
testing=# \echo :AUTOCOMMIT;Output:
- We can also commit the transaction using begin and end statements in PostgreSQL. Begin and end statement is also used to commit the transaction.
- The function “commit” performs two purposes: it saves a single transaction and multiple transactions simultaneously.
- Suppose we used to begin and end transaction commands. In that case, a commit will show a warning message that “there is no transaction in progress” because this transaction was already saved into the database. Currently, there was no transaction to commit or save to the database.
- Commit in PostgreSQL is very important to save single or multiple transactions into the database at one time.
- If we set auto commit is ON in PostgreSQL, we need not write commit statements at every statement. It will automatically commit the transaction after every transaction. It will automatically save the transaction into the database.
- Executing the commit statement is necessary to save a transaction into the database, whether executed once or multiple times, as long as the auto commit is off.
Examples
We are giving examples of multiple transaction commit and single transaction commit.
1. Single Transaction COMMIT
- In the below example, we have taken an example of a single transaction commit.
- We have to create an emp_test table, and after creating a table, we have saved the transaction into the database by using commit.
- Below is an example of a single transaction commit as follows.
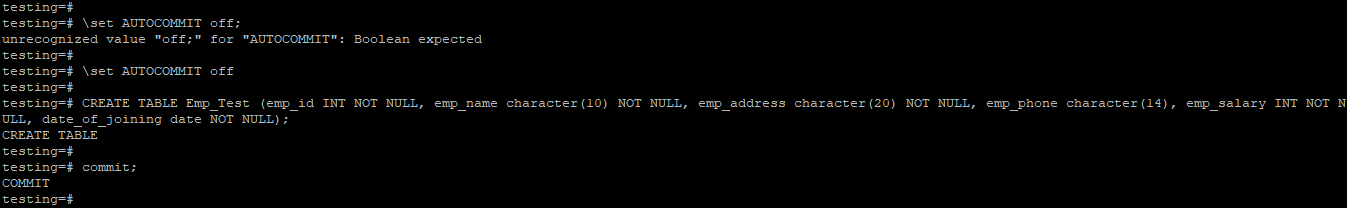
Example
testing=# \set AUTOCOMMIT off
testing=# CREATE TABLE Emp_Test (emp_id INT NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), emp_salary INT NOT NULL, date_of_joining date NOT NULL);
testing=# commit;Output:
- In PostgreSQL, the auto commit is one of every transaction by default, so we need to set it off if we want to save the transaction later.
- In the above example, we have saved the create table transaction into the database.
2. Multiple Transaction COMMIT (Using begin and end statement)
- In the below example, we have taken an example of multiple transaction commit.
- We have to create an emp_test1 table; after creating a table, we insert some value into this table and save the transaction into the database using an end statement.
- Below is an example of multiple transaction commit as follows.
Example
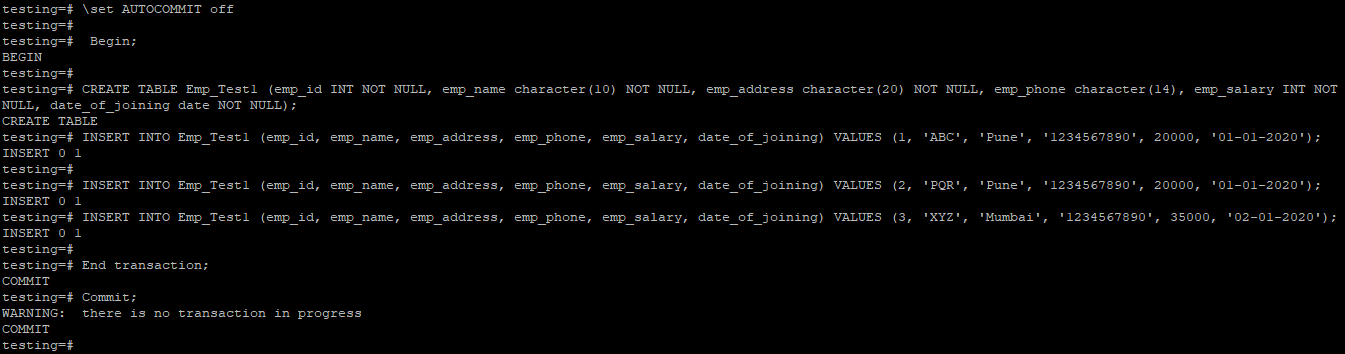
testing=# \set AUTOCOMMIT off
testing=# Begin;
testing=# CREATE TABLE Emp_Test1 (emp_id INT NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), emp_salary INT NOT NULL, date_of_joining date NOT NULL);
testing=# INSERT INTO Emp_Test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (1, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');
testing=# INSERT INTO Emp_Test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (2, 'PQR', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');
testing=# INSERT INTO Emp_Test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (3, 'XYZ', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 35000, '02-01-2020');
testing=# End transaction;
testing=# Commit;Output:
- We can also commit the transaction using begin and end statements in PostgreSQL. Executing the transaction also utilizes the “begin” and “end” statements
- The above example shows that we have committed multiple transactions using PostgreSQL’s beginning and end statements.
- Executing the commit statement after the end transaction statement results in a warning message stating that there is no transaction in progress. The database has already saved the transaction, and no pending transactions need to be saved or committed.
Conclusion
PostgreSQL commit is used to save the transaction into the database. We can also use begin and end statements to save the transaction into the database. By default, auto commit transaction is ON in PostgreSQL. Commit is very important to save the transaction into the database.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL COMMIT” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.