Updated May 26, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE
The regular expression is a sequence of characters, the short name for the list of strings. If any string matches with any of the strings, which is part of a list of the strings defined by the regular expression. PostgreSQL supports the regular expression, and the function provided by PostgreSQL is used to replace substrings with a new substring that matches a POSIX regular expression. The PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE() function uses a POSIX regular expression pattern.
Syntax:
Consider the following syntax.
REGEXP_REPLACE(input_string, regex_pattern, replace_string,[, flags])Explanation:
- input_string: This defines the input string in which replacement should be taken place for a specified pattern, a POSIX regular expression.
- regex_pattern: This defines the POSIX regular expression to match the string.
- flags: This flag is used to control the behavior of the REGEXP_REPLACE() function, This can have the value of one or more characters.
- Replace_string: This string defines a string that replaces the substring, which matches the POSIX regular expression pattern.
Examples of PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE
Here are the following examples of implementing the PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE function
Example #1 – Example to arrange the name
Consider the following name format like the first name and then last name:
‘Jacob David’
Suppose we want to re-arrange the last name and the first name for purposes like the last name and then the first name. So, we can use the PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE() function to do this as follows:
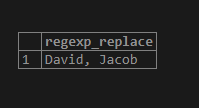
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE('Jacob David',
'(.*) (.*)',
'\2, \1');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
Example #2
Example, to remove the string, consider we have a string in the following as follows:
"xyz54321ABC"Now, we will remove all alphabets characters from the above string by using the following statement:
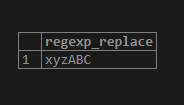
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE('xyz54321ABC',
'[[:alpha:]]',
'',
'g');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
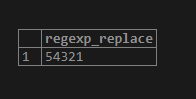
Now, we will remove all digits from the above string by using the following statement:
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE('xyz54321ABC',
'[[:digit:]]',
'',
'g');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
In the above examples, we have used the following regular expressions.
'[[:alpha:]]'and
'[[:digit:]]'Also, we have used the replacement string as ‘’ and the flag ‘g’ we have used to instruct the PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE function to replace all of the occurrences of the matched string and not just the first occurrence.
Example #3
Remove multiple occurrences of the spaces. Consider the following example, which removes more than one space that occurred in a string. Consider the following statement to do the same.
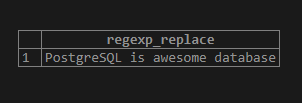
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE('PostgreSQL is awesome database',
'( ){2,}',
' ',
'g');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
Example #4
We will create a table named ‘student’ by using the CREATE TABLE statement as follows:
create table student
(
stud_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
stud_fname VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL,
stud_lname VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL
);Now, we will insert some data into the student table by using the INSERT INTO statement as follows
INSERT INTO student(stud_fname,stud_lname)
VALUES
('Smith','Johnson'),
('Williams','Jones'),
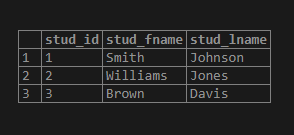
('Brown','Davis');Illustrate the above INSERT statement’s result using the following SQL statement and snapshot.
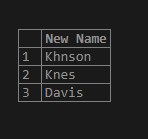
select * from student;Consider the following SQL statement where we are checking whether the stud_lname is having ‘Jo’ substring, and if it exists, then we replace it with ‘K.’
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE(stud_lname , 'Jo', 'K') AS "New Name"
FROM student;Illustrate the result of the above SQL statement by using the following snapshot.
Also, consider the other example,
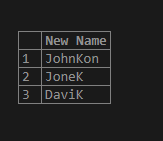
Consider the following SQL statement where we are checking whether the stud_lname is having ‘s’ substring, and if it exists, then we replace it with ‘K’
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE(stud_lname , 's', 'K') AS "New Name"
FROM student;Illustrate the result of the above SQL statement by using the following snapshot.
Advantages of using PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE () function
1. The PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE () function supports various flags,
Consider examples like:
- flag ‘i’ : match case-insensitively
- flag ‘g’: search globally for each occurrence.
2. The PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE() replaces all occurrences of the substring with the new string.
3. We can use The PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE() function, the substring in variable length or dynamic strings.
Conclusion
From the above article, we hope you understand how to use the PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE() function and how the PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE() function works. Also, we have added several examples of the PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE() function to understand it in detail.
Recommended articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL REGEXP_REPLACE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.