Updated May 17, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL Partition
PostgreSQL partition is used on large table sizes, also, we have used partition on large table rows. Creating partitioning on the table can increase the performance of the query, thereby speeding up its execution. We divide it into list partition, range partition, hash partition, and multilevel partition, and each type of partition has multiple forms. We can increase the performance of select operations on a large table, partition wise aggregate, and join increases the performance of our query.
Syntax:
Below is the syntax mentioned:
1. List partition
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column1 data_type, name_of_column2 data_type, name_of_column3 data_type, …, name_of_columnN data_type) Partition BY List (name_of_column);
Create table name_of_table PARTITION of partition_table_name for values in (‘partition value’);2. Range partition
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column1 data_type, name_of_column2 data_type, name_of_column3 data_type, …, name_of_columnN data_type) Partition BY Range (name_of_column);
Create table name_of_table PARTITION of partition_table_name for values from value1 to value2;3. Hash partition
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column1 data_type, name_of_column2 data_type, name_of_column3 data_type, …, name_of_columnN data_type) Partition BY Hash (name_of_column);
Create table name_of_table PARTITION of partition_table_name for values with(Modulus, remainder);Parameter:
- Create table: Creating a partition table using a list, range, and hash partition defines the process of table creation. We are creating a table partition at the time of table creation.
- Name of table: This is defined as creating a table using a partition. We can define a partition to the table at the time of table creation.
- Name of column 1 to the name of column N: Creating a column on a table and defining a partition on the same is referred to as naming column 1 to column N.
- Data type: The data type is assigned to the table column at the time of table creation. We can define data type as per partitioning, which we have configured on the table.
- Partition by hash: This is defined as creating a hash partition on the table. We can use modulus and remainder while creating a partition.
- Partition by list: Creating a list partition on the table defines the process of partitioning by list. We can use the column name of the table while creating a partition.
- Partition by range: Creating a range partition on the table defines the process of partitioning by range. We can use the column name of the table while creating a partition.
- Modulus and remainder: During the creation of a hash partition, we employ modulus and remainder as the hash partition arguments.
How to Perform Partition in PostgreSQL?
We can perform partition, which are as follows:
It is basically divided into three types as follows.
- List partition
- Range partition
- Hash partition
PostgreSQL 10 supports the range and list type partition, and from PostgreSQL version 11, the hash partition is available.
1. List Partition
In PostgreSQL, you create a list partition to store the data of the partitioned table for predefined values. List partition holds the values which was not part of any other partition in PostgreSQL.
2. Range Partition
Range partition holds the values within the range provided in the partitioning in PostgreSQL. We need to specify the minimum and maximum range values at the time of range partition creation. The minimum value in the range partition is inclusive, and the maximum value in the range partition is exclusive.
3. Hash Partition
We can create a hash partition using the modulus and remainder of each partition in PostgreSQL. In hash, partition rows will insert by generating hash value using the remainder and modulus.
- Using partition in PostgreSQL, we can increase the speed of query, we can increase the speed of select query in PostgreSQL.
- Using partition bulk load data and data deletion from the table is faster as compared to the normal table. The operation executes within each partition to achieve faster performance compared to a regular table.
- Each partition in PostgreSQL will contain the data based on a frequency we defined at the time of partition creation.
- Declarative partition is very flexible in PostgreSQL to provide good control on the user, which we have used to access the data in PostgreSQL.
- We can create a partition on a table column, as per column data, we have decided the type of partitioning.
- Basically, we are using list and range partition in PostgreSQL.
Examples of PostgreSQL Partition
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
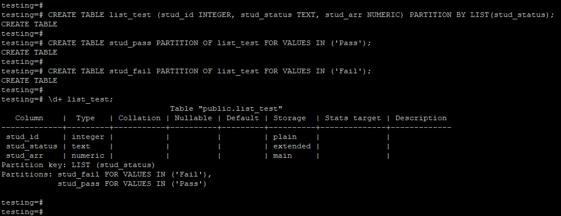
Create List Partition on Table.
The below example shows that create a list partition on the table. We have created a list partition on the stud_status column.
Code:
CREATE TABLE list_test (stud_id INTEGER, stud_status TEXT, stud_arr NUMERIC) PARTITION BY LIST(stud_status);
CREATE TABLE stud_pass PARTITION OF list_test FOR VALUES IN ('Pass');
CREATE TABLE stud_fail PARTITION OF list_test FOR VALUES IN ('Fail');
\d+ list_test;Output:
Example #2
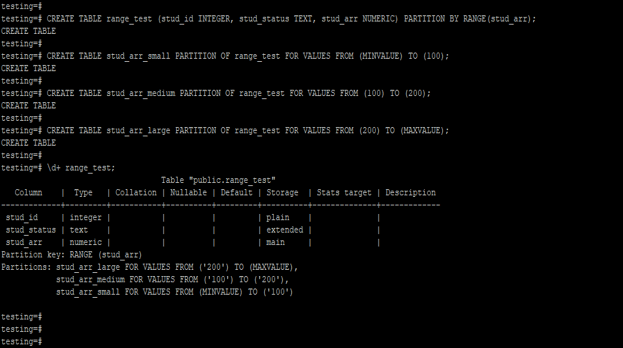
Create Range Partition on Table.
Below example shows that create a range partition on the table. We have created a range partition on the stud_arr column.
Code:
CREATE TABLE range_test (stud_id INTEGER, stud_status TEXT, stud_arr NUMERIC) PARTITION BY RANGE(stud_arr);
CREATE TABLE stud_arr_small PARTITION OF range_test FOR VALUES FROM (MINVALUE) TO (100);
CREATE TABLE stud_arr_medium PARTITION OF range_test FOR VALUES FROM (100) TO (200);
CREATE TABLE stud_arr_large PARTITION OF range_test FOR VALUES FROM (200) TO (MAXVALUE);
\d+ range_test;Output:
Example #3
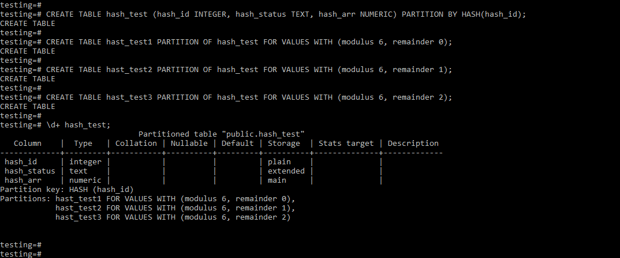
Create hash Partition on Table.
The below example shows that create a hash partition on the table. We have created a hash partition on the hash_id column.
Code:
CREATE TABLE hash_test (hash_id INTEGER, hash_status TEXT, hash_arr NUMERIC) PARTITION BY HASH(hash_id);
CREATE TABLE hast_test1 PARTITION OF hash_test FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 6, remainder 0);
CREATE TABLE hast_test2 PARTITION OF hash_test FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 6, remainder 1);
CREATE TABLE hast_test3 PARTITION OF hash_test FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 6, remainder 2);
\d+ hash_test;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Partition” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

